Blockchain Structure
Last Updated :
16 Nov, 2022
Blockchain is a Distributed Ledger Technology. It is a distributed and decentralized database and it is secured ever as compared to other technologies.
What is Blockchain Architecture?
Blockchain is a technology where multiple parties involved in communication can perform different transactions without third-party intervention. Verification and validation of these transactions are carried out by special kinds of nodes.
Benefits of Blockchain:
- It is safer than any other technology.
- To avoid possible legal issues, a trusted third party has to supervise the transactions and validate the transactions.
- There’s no one central point of attack.
- Data cannot be changed or manipulated, it’s immutable.
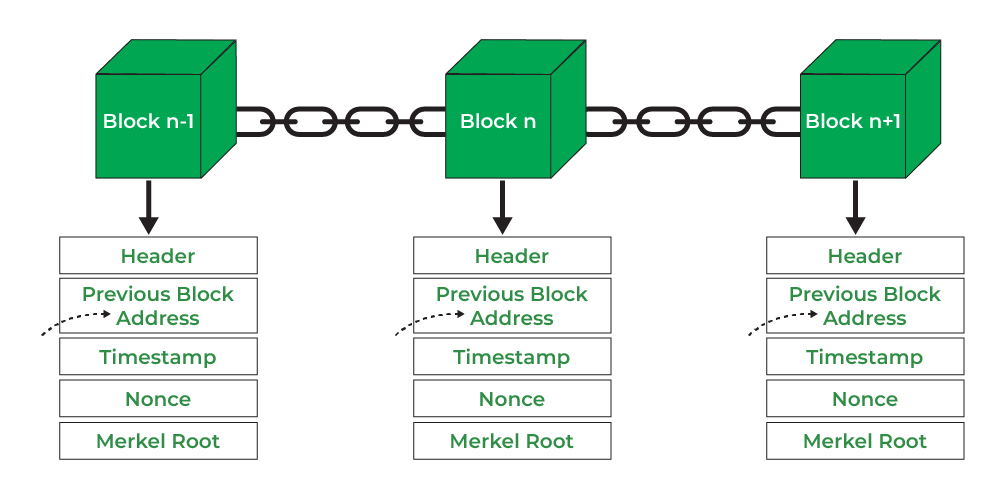
- Header: It is used to identify the particular block in the entire blockchain. It handles all blocks in the blockchain. A block header is hashed periodically by miners by changing the nonce value as part of normal mining activity, also Three sets of block metadata are contained in the block header.
- Previous Block Address/ Hash: It is used to connect the i+1th block to the ith block using the hash. In short, it is a reference to the hash of the previous (parent) block in the chain.
- Timestamp: It is a system verify the data into the block and assigns a time or date of creation for digital documents. The timestamp is a string of characters that uniquely identifies the document or event and indicates when it was created.
- Nonce: A nonce number which uses only once. It is a central part of the proof of work in the block. It is compared to the live target if it is smaller or equal to the current target. People who mine, test, and eliminate many Nonce per second until they find that Valuable Nonce is valid.
- Merkel Root: It is a type of data structure frame of different blocks of data. A Merkle Tree stores all the transactions in a block by producing a digital fingerprint of the entire transaction. It allows the users to verify whether a transaction can be included in a block or not.
Key Characteristics of Blockchain Architecture
- Decentralization: In centralized transaction systems, each transaction needs to be validated in the central trusted agency (e.g., the central bank), naturally resulting in cost and the performance jam at the central servers. In contrast to the centralized mode, a third party is not needed in the blockchain. Consensus algorithms in blockchain are used to maintain data stability in a decentralized network.
- Persistency: Transactions can be validated quickly and invalid transactions would not be admitted by persons or miners who mining the crypto. It is not possible to delete or roll back transactions once they are included in the blockchain network. Invalid transactions do not carry forward further.
- Anonymity: Each user can interact with the blockchain with a generated address, which does not disclose the real identity
of the miner. Note that blockchain cannot guarantee perfect privacy preservation due to the permanent thing.
- Auditability: Blockchain stores data of users based on the Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) model.
Every transaction has to refer to some previous unspent transactions. Once the current transaction is recorded into the
blockchain, the position of those referred unspent transactions switches from unspent to spent. Due to this process, the transactions can be easily tracked and not harmed between transactions.
- Transparency: The transparency of blockchain is like cryptocurrency, in bitcoin for tracking every transaction is done by the address. And for security, it hides the person’s identity between and after the transaction. All the transactions are made by the owner of the block associated with the address, this process is transparent and there is no loss for anyone who is involved in this transaction.
- Cryptography: The blockchain concept is fully based on security and for that, all the blocks on the blockchain network want to be secure. And for security, it implements cryptography and secures the data using the cipher text and ciphers.
Types of Blockchain Architecture
1. Public Blockchain:
A public blockchain is a concept where anyone is free to join and take part in the core activities of the blockchain network. Anyone can read, write, and audit the ongoing activities on a public blockchain network, which helps to achieve the self-determining, decentralized nature often authorized when blockchain is discussed. Data on a public blockchain is secure as it is not possible to modify once they are validated.
The public blockchain is fully decentralized, it has access and control over the ledger, and its data is not restricted to persons, is always available and the central authority manages all the blocks in the chain. There is publicly running all operations. Due to no one handling it singly then there is no need to get permission to access the public blockchain. Anyone can set his/her own node or block in the network/ chain.
After a node or a block settled in the chain of the blocks, all the blocks are connected like peer-to-peer connections. If someone tries to attack the block then it forms a copy of that data and it is accessible only by the original author of the block.
Advantages:
- A public network operates on an actuate scheme that encourages new persons to join and keep the network better.
- There is no agreement in the public blockchain.
- This means that a public blockchain network is immutable.
- It has Rapid transactions.
Disadvantages:
- Public blockchain can be costly in some manner.
- The person need not give identity, that’s why there is a possibility of corruption of the block if it is in under attack.
- Processing speed is sometimes slow.
- It has Integration issues.
2. Private Blockchain
Miners need permission to access a private blockchain. It works based on permissions and controls, which give limit participation in the network. Only the entities participating in a transaction will have knowledge about it and the other stakeholders not able to access it.
By it works on the basis of permissions due to this it is also called a permission-based blockchain. Private blockchains are not like public blockchains it is managed by the entity that owns the network. A trusted person is in charge of the running of the blockchain it will control who can access the private blockchain and also controls the access rights of the private chain network. There may be a possibility of some restrictions while accessing the network of the private blockchain.
Advantages:
- In a private blockchain, users join the network using the invitations and all are verified.
- Only permitted users/ persons can join the network.
- Private Blockchain is partially immutable.
Disadvantages:
- A private blockchain has trust issues, due to exclusive information being difficult to access it.
- As the number of participants increases, there is a possibility of an attack on the registered users.
3. Consortium Blockchain
A consortium blockchain is a concept where it is permissioned by the government and a group of organizations, not by one person like a private blockchain. Consortium blockchains are more decentralized than private blockchains, due to being more decentralized it increases the privacy and security of the blocks. Those like private blockchains connected with government organizations’ blocks network.
Consortium blockchains is lies between public and private blockchains. They are designed by organizations and no one person outside of the organizations can gain access. In Consortium blockchains all companies in between organizations collaborate equally. They do not give access from outside of the organizations/ consortium network.
Advantages:
- Consortium blockchain providers will always try to give the fastest output as compared to public blockchains.
- It is scalable.
- A consortium blockchain is low transaction costs.
Disadvantages:
- A consortium blockchain is unstable in relationships.
- Consortium blockchain lacks an economic model.
- It has flexibility issues.
Core Components of Blockchain Architecture
- Node: Nodes are network participants and their devices permit them to keep track of the distributed ledger and serve as communication hubs in various network tasks. A block broadcasts all the network nodes when a miner looks to add a new block in transactions to the blockchain.
- Transactions: A transaction refers to a contract or agreement and transfers of assets between parties. The asset is typically cash or property. The network of computers in blockchain stores the transactional data as copy with the storage typically referred to as a digital ledger.
- Block: A block in a blockchain network is similar to a link in a chain. In the field of cryptocurrency, blocks are like records that store transactions like a record book, and those are encrypted into a hash tree. There are a huge number of transactions occurring every day in the world. It is important for the users to keep track of those transactions, and they do it with the help of a block structure. The block structure of the blockchain is mentioned in the very first diagram in this article.
- Chain: Chain is the concept where all the blocks are connected with the help of a chain in the whole blockchain structure in the world. And those blocks are connected with the help of the previous block hash and it indicates a chaining structure.
- Miners: Blockchain mining is a process that validates every step in the transactions while operating all cryptocurrencies. People involved in this mining they called miners. Blockchain mining is a process to validate each step in the transactions while operating cryptocurrencies.
- Consensus: A consensus is a fault-tolerant mechanism that is used in computer and blockchain systems to achieve the necessary agreement on a single state of the network among distributed processes or multi-agent systems, such as with cryptocurrencies. It is useful in record keeping and other things.
There are different kinds of consensus mechanism algorithms, each of which works on different principles:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Proof of Work required a stakeholder node to prove that the work is done and submitted by them certifying them to receive the right to add new transactions in the blockchain.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): The proof of Stake is also a common consensus algorithm that evolved as a low-cost low-energy-consuming, low-energy-consuming alternative for the PoW algorithm. For providing the responsibilities the public ledger provides by the virtual currency token like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Proof of Capacity (PoC): Proof of Capacity (PoC) allow sharing of memory space of the nodes in the blockchain network.
- Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET): It encrypts the passage of time cryptographically to reach an agreement without expending many resources.
Blockchain Architecture Vs Database
Below are some of the differences between blockchain architecture and database:
| Parameters |
Blockchain Architecture |
Database |
| Control |
Blockchain is decentralized because there is no single point of failure and there is no central authority to control the blockchain. |
The database is Centralized. |
| Operations |
Blockchain has only an Insert operation. |
The database has Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations. |
| Strength |
It is robust technology. |
The database is not fully robust technology. |
| Mutability |
Blockchain is immutable technology and we cannot change it back or we cannot go back. |
The database is a fully mutable technology, The data can be edited in the database. |
| Rights |
Anyone with the right proof of work can write on the blockchain. |
In the database reading and writing can do so. |
| Speed |
It is slow in speed. |
It is faster as compared to blockchain. |
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...