Base Stations
Last Updated :
09 May, 2024
The present-day tele-space is incomplete without the base stations as these constitute an important part of the modern-day scheme of wireless communications. They are referred to as cell towers or cellular antennas. These types of objects are an inevitability since they serve the purpose of providing signal transfer for data and voice between mobile mobiles.
The idea of base stations is anchored in their function to provide coverage, capacity, and connectivity, hence allowing for extending the working capabilities of mobile phones and other radio gear.
What is Base Station?
A base station represents an access point for a wireless device to communicate within its coverage area. It usually connects the device to other networks or devices through a dedicated high bandwidth wire of fiber optic connection. Base stations typically have a transceiver, capable of sending and receiving wireless signals;
Otherwise if they only send the trailer it will be considered a transmitter or broadcast point only. The base station will have one or more RF antennas installed to transmit and receive RF signals from other devices.

Base Station System
Components of Base Stations
- Baseband Processor
- Duplexer
- Antenna System
- Transceiver
- Power Amplifier
- Control Unit
- Backhaul Connection
- Power Supply
- Baseband Processor
- Tower or Mast
- Antennas
- Controller and Processor
Working and Construction of Base Stations
The block diagram of a base station typically includes the following key components:
- Baseband Processor: The baseband processor too deals with different communication protocols and interfaces with mobile network infrastructure.
- Duplexer: The duplexer enables the employment of a single antenna for both transmission and reception.
- Antenna System: The antenna transmits and receives radio frequency (RF) signals. That the response of this string when run again is the transcript. The antenna system can comprise several antennas to support different frequency bands and technologies.
- Transceiver: The transceiver, a term for transmitter-receiver, is the the essential part that manages various modulation and demodulation activities. In transmission and reception it converts electrical signals to radio waves and vice versa. The transceiver too deals with the power control, frequency tuning, and other necessary operations.
- Power Amplifier: The RF signals are power amplified before transmission to their destinations for increased signal strength. Therefore, this is very important for enabling the signals to cover long distances and even penetrate barriers in the communication environment.
- Control Unit: The controller is in charge of the operation of the whole base station. It controls the transmission power, frequency allocation, handovers between different cells and other network management functions. The control unit also connects with the core network central infrastructure.
- Backhaul Connection: The backhaul connection links the base station to the core network in the mobile communication system. It provides for the interchange of data between the base station and other network components, hence communication with extrinsic systems and processes.
- Power Supply: The power source provides the electrical energy to base station elements. It often features auxiliary power supply mechanisms that guarantee operation in case of lost or interrupted electricity, during blackouts.
- Baseband Processor: The baseband processor is responsible for the processing of the digital signals. It converts the analog signals obtained from mobile devices to digital for processing and back again. It also handles different control functions.
- Tower or Mast: The tower or mast serves as the physical support for antenna system and other components. It guarantees that the antennas are raised for adequate coverage and communication radius.
- Antennas: Signals are received and transmitted through antennas mounted on a mast or tower. They come in various types such as omnidirectional or sector antennas responding to diverse coverage needs.
- Controller and processor: These components manage the functioning of an entire base station. They handle such activities as signal routing, allocation of resources and network coordination.
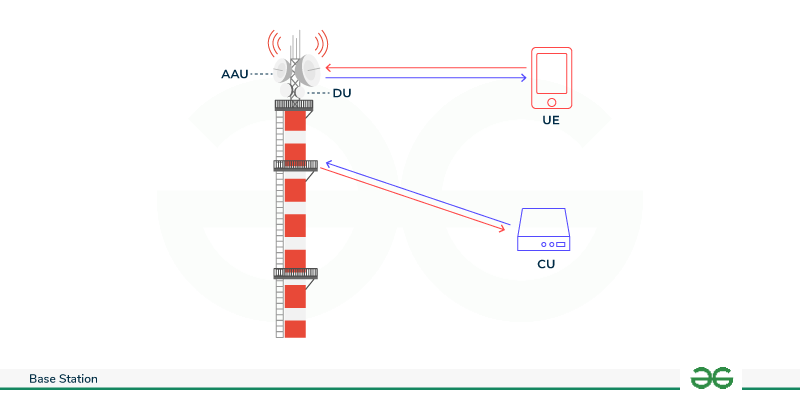
Construction of Base Station
Why are Base Stations so Important?
Base stations are important in the cellular communication as it facilitate seamless communication between mobile devices and the network communication. The demand for efficient data transmission are increased as we are advancing towards new technologies such as 5G and other data intensive applications. As the mobile traffic continues to increase due to actors like video streaming and online gaming the need for base station is becoming important. These Station uses advanced signal processing techniques to mange the increasing data throughput.
Base Stations in Wireless Data Networks
Cell towers in cellular telephone networks are known as base stations. When a person makes or receives a call using their cell phone, each of these devices connects to a specific cell tower which in turn connects the handset to a wired type public switched telephone network (PSTN), among other potential participants. Also “connects” to the Internet potion. Equally, both the area covered and the customers supported determine the local geography.
Difference between Macrocells, Smallcells and Femtocells
Given below is the difference between Macrocells, Smallcells and Femtocells :
|
Feature
|
Macrocells
|
Smallcells
|
Femtocells
|
|
Coverage Area
|
Large
|
Small
|
Very Small
|
|
Capacity
|
High
|
Moderate to High
|
Low to Moderate
|
|
User Density
|
Low to moderate
|
High
|
Low
|
|
Deployment
|
Outdoor
|
Indoor and Outdoor
|
Indoor
|
|
Usage
|
Urban and Suburban areas
|
Urban areas, Venues, enterprises
|
Residential and small office areas
|
Types of Base Stations
Some basic types of base stations are as follows:
Macro Cell Base Stations
Macro-base stations are tall towers ranging from 50 to 200 feet in height, placed at strategic locations to provide maximum coverage in a given area. Those are equipped with large towers and antennas that transmit and receive radio signals from wireless devices.
Pico Cell Base Station
A Pico cell base station is a small wireless tower that provides improved phone and Internet services to local areas such as homes or small offices; More specifically for specific rooms. It is a very small, low-power station that works like a personal signal booster that improves call and Internet quality in limited space.
Femto-Cell Base Stations
Femto-base station (commonly known as access point base station, femtocell or HHP), is an in-home base transceiver system. Like a normal base station, it connects the phone’s voice and data to the cell network but covers a smaller scale (home).The advantage of using a femto-base station is that it frees up cell tower traffic for the service provider.
Remote Radio Heads (RRH)
The base station’s RF circuitry is housed in a small outdoor module known as a remote radio head (RRH) or remote radio unit (RRU). RRH performs all RF functions such as transmit and receive functionality, filtering and amplification. It also has analog-to-digital or digital to analog and digital upconverters.
Cloud Radio Access Network
The state of cellular networks is reconsidered from one’s mind, as almost all complex functions located in base stations are transferred to the clouds. Unlike traditional base stations, where all processing is performed by separate sites, C-RAN centrally involves the cloud data center in executing the baseband process.
Mobile Switching Centers
The Mobile Switching Centers (MSCs) are one of the most important base station network , as they act as the central point for call routing and management. Unlike base stations, which deal with direct communications between mobile devices and towers, Mobile Switching Centers (MSCs) oversee the routing of calls and data over various cellular networks to ensure that your call reaches its intended receiver.
Properties of Base Station
The main properties of a base station determine the performance and functionality of a mobile communication network. Here are some essential properties:
- Capacity: Capacity of a base station is its capability to handle a given number of simultaneous connections or users.
- Coverage Area: The coverage area is a base station is that geographical area within which mobile devices can maintain a stable connection with the base station.
- Data Rate: The Data rate supported by a base station determines how fast data can be sent and received.
- Reliability: The base stations should be constructed to be resilient against environmental challenges, equipment failures, and others so to guarantee a constant connection with mobile phones.
- Interference Management: Base stations require means to handle interference from neighbor base stations or external sources.
- Scalability: The scalability is about of the base stations capability to accommodate more number of users and data traffic as the network grows. .
- Power Efficiency: The energy-efficient base stations are contributing to minimize the operational expenditure and the environmental impact.
Applications of Base Station
- Internet of Things (IoT): In light of the popularity, base stations assist in connecting several sensors from different types to smart devices and machines that are connected to a network.
- Emergency Services: In case of emergencies, base stations play a critical role in facilitating communication for emergency services and to allow people place an emergency call.
- Capacity and Load Balancing: Base stations thus play a substantial role in load balancing for the network by distributing user traffic across various cells.
- Frequency Allocation: The base stations are responsible for assigning frequencies to various users within an area of which they have control. This prevents conflicts between various users and ensures the best use of radio spectrum.
- Wireless Communication: Base stations play a fundamental role in establishing and supporting wireless connectivity with mobile devices within their range.
- Network Coverage: Base stations cover a given part of the earth. Various base stations are set up in such a way that forms a network to encompass all areas of the city, region or even an entire country.
Advantages of Base Station
- Connectivity: They provide persistent wireless connectivity to allow voice calls, text messages, and data transfers between mobile devices within their coverage area.
- Network coverage: Extended network coverage is achieved through base stations that reach users with communication services even in remote or previously underserved geographic areas.
- Capacity and Scalability: Therefore, they serve multiple users at a time, so the network can handle multiple devices and people with better results.
- Seamless handover: With base stations, handover is smooth as calling or data sessions will not be interrupted when users move between areas of coverage.
- Better Signal Quality: They enhance signal strength and quality, reduce dropped calls, increase data transfer speed for better user experience.
- Technological advancements: The New technologies result in evolved base stations that support upgrades and enhancements such as 4G, 5G and beyond, its providing faster speeds with better bandwidth.
- Emergency services: They provide access to emergency services, so that in case of emergency, people can call through their mobile phones.
Disadvantages of Base Station
- Health Concerns: Concerns about potential health risks resulting from long-term exposure to electromagnetic radiation emitted by base stations continues as science has thus far failed prove that the emission causes any harm.
- Cost and infrastructure: Base station construction, as well as retrofitting base stations for deeper penetration requiring additional investment in infrastructure like land purchase costs and equipment purchases , is costly. Launching networks in isolated or sparsely populated areas can be a costly process.
- Limited coverage in remote areas: Also, base stations are used to expand network services; But because of the costs and operational challenges that come with installing base stations in remote or logistically difficult locations, these areas may still not receive enough coverage amounts due to lack of necessary networks.
- Interference and congestion: Network congestion and interplay between many base stations in high-density areas may lead to poor performance, dropped calls or slow data speeds.
- Power consumption: Thus, permanent power supply is needed for the operation of base stations; energy consumption required to operate these facilities contributes significantly to carbon emissions and environmental impact.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: Base stations need constant maintenance and updates to follow the technological changes. This process can be time consuming, costly and disruptive to network operations.
Conclusion
Base stations form a key part of modern wireless communication networks because they offer some crucial advantages, such as wide coverage, continuous communications and an array of services. They increase the extent of mobile networks so that users can remain connected to access data and use innovative applications, but along with such advantages base stations bring many issues. There are concerns in regard to health effects, environmental impacts, infrastructure costs and maintenance requirements. To achieve maximum benefits while minimizing drawbacks of communication network deployment, it is essential to find a balance between advantages and disadvantages.
Base Stations – FAQs
What are the potential health risks associated with long-term exposure to base station radiation?
Scientific evidence is inconclusive, regulatory bodies say current exposure levels are generally considered safe but further studies continue.
In what ways do users derive benefits from the incorporation of edge computing into base stations?
Edge computing mitigates latency, allowing applications like augmented reality and real-time data processing to react much faster thus improving the user experience.
Is it possible to run base stations in off-grid or remote areas?
There are lots of challenges associated with deploying base stations in off-grid or remote areas due to the infrastructure and power supply issues. In some cases it may not be economically viable.
What role do base stations play in the rollout of 5G networks?
5G deployment is also highly reliant upon base stations that will serve as the necessary physical infrastructure to achieve higher speeds, increased capacity and new integration technologies such as massive MIMO and small cells.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...