Cloud Radio Access Network (C-RAN)
Last Updated :
17 May, 2023
Traditional architectures of cellular networks come up with tremendous challenges due to rapid increase in mobile data traffic. Limited spectrum availability make data traffic to consume high power. Due to such demerits industries as well as research communities are in constant search in developing novel network architectures for supporting the exploding user demand, with reduction in capital as well as operational expenditures for network operators. So, network operators are meet such demand by adopting Cloud/Centralized Access Networks(C-RAN) This C-RAN approach to network have two main advantages:-
- Reduced Capital Expenditures (CAPEX) or Operating Expenses (OPEX)
- Improved user experience through less interference
C-RAN Solution : Area where Network Users Concentration is high, such as transportation stations or large commercial complexes put high stress on the Base transceiver station (BTS) that serve them. With addition of more base stations increases cost and increases signal inferences if E-UTRAN Node B (eNB) is not properly coordinated. If network is separated into two parts as following –
1. Baseband Unit (BBU)
2. Remote Radio Head (RRH)
Then Network Operators can increase the number of Network Access Points while centralizing the baseband processing functions into a “master base station”. C-RAN System Structure : C-RAN System Structure is divided into 3 parts:-
- Fully Centralized – A fully centralized structure would move all physical, MAC and network layers into Baseband Unit. This Baseband Unit is capable of handling all the functions of managing and processing resources and hence such structure can benefit from easy operation and maintenance significantly.
- Partially Centralized – In this partially Centralized structure, the physical layer functioning is accomplished at BBU Baseband Unit while MAC layer is performed at RRU Remote Radio Unit. This will simply reduce the overhead of RRUs-BBUs communication due to reason being the physical layer take a major computation burden of C-RANs.
- Hybrid Centralized – In this centralized system physical layer functioning is done at RRU while others are done at BBU layer. Remote Radio Unit (RRU) take major responsibility of users which is mainly concerned with signal processing.
Virtualization Concept : In C-RAN Network Visualization is done at Baseband Unit (BBU) pool level. BBU will act as a virtual node and the link between them is Virtual Link. The pool will operate at one physical Virtual machine sharing CPU. Remote Radio Unit (RRU) will be connected to BBU, which will distribute them over virtual machine. This technology will offer many advantages such as cost reduction and minimization of time requirement and most important is scalability. Addition and removal is easier as BBU’s are virtual machines, which are much easier to turn off and up than physical machines. Below figure shows the virtualization of BBU in C-RAN – 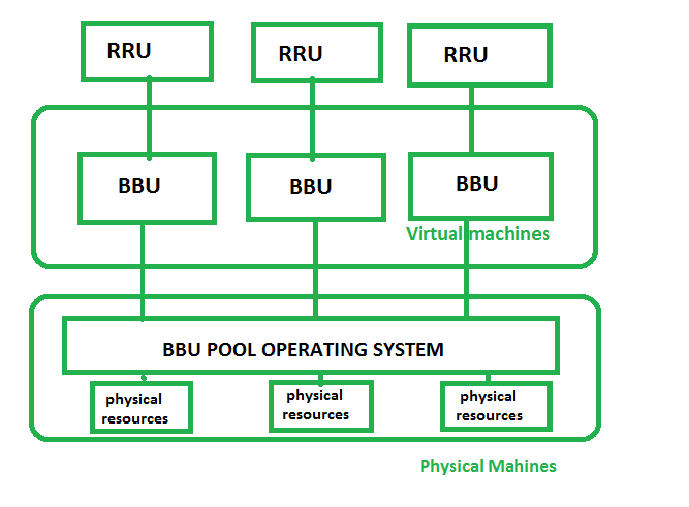
Advantages of C-RAN :
- Possibility of implementing advanced technologies.
- Resource virtualization
- Service deployment at the edge facilitation
- Resource sharing can become feasible and hence allocation can be more flexible and on demand unlike traditional networks.
- Improves resource utilization and reduce backbone server pressure.
- More user satisfaction due to the larger pool of resources.
- Enhanced scalability: C-RAN provides a scalable architecture that can accommodate a large number of radio access points without requiring additional hardware resources. This makes it easier to expand the network as the number of connected devices increases.
- Improved energy efficiency: C-RAN enables the centralization of processing resources, which can result in reduced power consumption and energy costs. This is because the remote radio heads (RRHs) can be designed with lower power consumption, and the centralized processing unit (CPU) can be optimized for energy efficiency.
- Lower latency: C-RAN enables the implementation of advanced network optimization techniques that can reduce latency and improve the quality of service (QoS). This is particularly important for real-time applications that require low latency, such as video streaming and online gaming.
- Simplified network management: C-RAN provides a centralized management interface that simplifies the deployment, configuration, and management of the network. This can reduce operational costs and improve network efficiency.
Disadvantages of C-RAN :
- High bandwidth requirements: C-RAN requires high bandwidth to transfer real-time data between the central processing unit (CPU) and remote radio heads (RRHs). This high bandwidth requirement can result in increased latency and lower system performance.
- High hardware and maintenance costs: The centralized baseband processing unit (BBU) in C-RAN requires high-capacity processors, storage devices, and other equipment, which can be expensive to acquire and maintain.
- Single point of failure: C-RAN has a single point of failure at the central processing unit (CPU). If the CPU fails, the entire network will be disrupted.
- Security concerns: C-RAN has a centralized architecture that increases the vulnerability of the network to cyber attacks. Any security breach in the central processing unit (CPU) can lead to the compromise of the entire network.
- Limited coverage area: C-RAN is typically used for dense urban areas and high traffic areas. It may not be suitable for low traffic or rural areas due to the limited coverage area of the radio heads.
- Interference issues: C-RAN may experience interference issues due to the deployment of multiple remote radio heads in the same location. This can result in signal degradation and lower system performance.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...