Assessment Criteria for RCM
Last Updated :
06 May, 2023
Introduction :
RCM (Reliability Centered Maintenance) is a method used to develop maintenance strategies for equipment and systems. It involves analyzing the potential failure modes of equipment and developing maintenance plans to address those failures.
Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) is one of most effective approaches for establishing and development as well as improving Preventive Maintenance Program. It simply makes system more reliable and safer. It focuses on preserving and protecting functions of system i.e. To maintain functions of system in its existing or original state rather than protecting and conserving equipment’s. Assessment i.e. Evaluation criteria of RCM is not very difficult one. It simply asks seven questions about particular asset or system or equipment that is under review. These questions are given below : 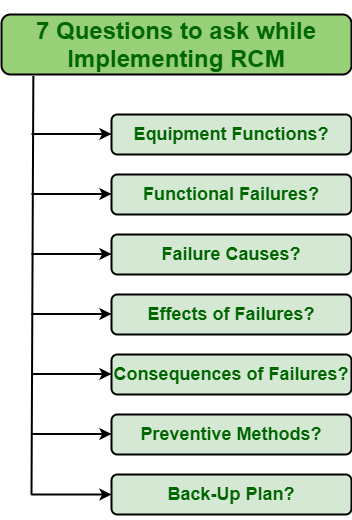 These are explained as following below.
These are explained as following below.
- Identify System or equipment Functions :
Which pieces of equipment you will measure and evaluate and how well they should perform? One need initially determines equipment or asset that is needed to be analyzed and then determines what and how does particular equipment work. One should know that how does particular equipment meet desired goals of company as well as how it increases customer satisfaction and fulfill customer needs.
- Identify Failure Modes : What are different ways in which your selected piece of equipment might fail? After determining functions of equipment, one needs to analyze and determines different ways in which particular equipment can breakdown or fail. In simple words, one needs to determine all possible sources of failure of particular equipment. Different failures modes can be :
- Human error
- Manufacturing flaws
- Design Failure
- Engine Malfunction, etc.
- Identify Failure Causes : What are different causes of each failure that is identified? After determining different failure modes, one needs to determine various causes that can lead to particular failure of equipment. In simple words, one needs to determine main root cause of particular failure. One should know that why particular failure occurred, what are its main causes that lead to occurrence of failure.
- Identify Effects of Failures : What will be possible effect of failure on system if it occurs? After identifying all possible root causes of failure, one needs to determine overall impact of particular failure on system if somehow failure occurs. One needs to determine how particular failure affects system, productivity, overall cost, quality of end product, etc. In simple words, one needs to determine how severe or critical failure can be if it happens.
- Identify Consequences of Failure : How does each failure that is identified affects company’s bottom line? After identifying effect of failures, one needs to determine how particular failure affects health and environment of system. One should know how do particular failure can affect safety of individual and working environment of system as well as physical condition of system or equipment. One should also determine cost associated with particular failures.
- Determine Preventive Tasks : What are different ways in which one can prevent each failure from its occurrence? After determining consequences of failures, one should determine what possible tasks or methods can be implemented simply to prevent failure from its occurrence. One should choose most suitable method to prevent particular failure after analyzing severity, criticality of failure, and needs of the facility. Its one of major tasks to do so and is not an easy one. Identifying most effective maintenance task or method that is cost-effective also requires one to be more careful and selective. Particular task chosen should prevent failure from its future occurrence.
- Identify Alternatives : What else can be done to ensure that failures are addressed quickly if suitable preventive method is not identified? If somehow selected maintenance method gets failed or does not prevent failure from its occurrence, then one should know what other methods are available and can be applied to prevent failure. RCM Team should have a replacement of particular method if it gets failed somehow or does not work properly. This replacement decision is very critical and essential.
There are several criteria that can be used to evaluate its effectiveness:
- Equipment criticality: The criticality of equipment should be assessed to determine which equipment requires the most attention and resources. This helps to prioritize maintenance activities and allocate resources effectively.
- Failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA): FMEA is a structured method of identifying potential failure modes and their effects on equipment. The effectiveness of RCM can be assessed by evaluating the accuracy and completeness of the FMEA conducted.
- Maintenance tasks: RCM involves developing maintenance tasks to address potential failure modes. The effectiveness of RCM can be assessed by evaluating the appropriateness and effectiveness of these maintenance tasks.
- Maintenance intervals: RCM involves determining the appropriate maintenance intervals for equipment based on the criticality and potential failure modes. The effectiveness of RCM can be assessed by evaluating the appropriateness of the maintenance intervals and whether they result in effective equipment performance.
- Cost-effectiveness: The effectiveness of RCM can also be evaluated based on its cost-effectiveness. This involves comparing the costs of implementing RCM with the benefits it provides, such as reduced downtime and improved equipment performance.
- Continuous improvement: RCM is an iterative process that involves continuous improvement. The effectiveness of RCM can be assessed by evaluating whether the maintenance strategies and tasks are regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in equipment performance and operating conditions.
Advantages :
There are several advantages of using RCM (Reliability Centered Maintenance)
- Increased equipment reliability: RCM helps identify and address potential equipment failure modes before they occur. This helps to increase equipment reliability and reduce unexpected downtime.
- Improved safety: RCM includes evaluating potential safety risks associated with equipment failure modes and developing maintenance strategies to address those risks. This helps to improve safety for workers and the surrounding environment.
- Cost-effectiveness: RCM helps to optimize maintenance activities by focusing on the critical equipment and addressing potential failure modes. This helps to reduce unnecessary maintenance activities and minimize costs while still maintaining equipment reliability.
- Increased asset lifespan: RCM helps to extend the lifespan of assets by identifying potential failure modes and developing maintenance strategies to prevent those failures. This helps to reduce the need for premature replacements or costly repairs.
- Compliance with regulations: RCM helps to ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards by developing maintenance strategies that meet those requirements.
- Improved maintenance planning: RCM helps to improve maintenance planning by providing a structured approach to identify potential failure modes and develop maintenance strategies. This helps to optimize maintenance activities and resources.
Dis-advantages :
- Resource-intensive: RCM requires significant time, resources, and expertise to conduct the necessary analysis and develop effective maintenance strategies. This can be a disadvantage for organizations with limited resources.
- Complexity: RCM can be a complex process, and it may require significant training and experience to conduct effectively. This can be a disadvantage for organizations with limited expertise or experience with RCM.
- Potential for analysis paralysis: RCM involves analyzing potential failure modes and developing maintenance strategies to address those failures. However, there is a risk of spending too much time on analysis and not enough time on implementation, leading to analysis paralysis.
- Difficulty in implementation: RCM can be difficult to implement effectively, particularly in complex or large-scale systems. This can be a disadvantage for organizations with limited experience or resources to implement RCM effectively.
- Limited applicability: RCM may not be applicable for all types of equipment or systems. Some equipment may be too simple or too complex for RCM to be effective.
- Resistance to change: Implementing RCM may require changes to existing maintenance practices and procedures. This can be met with resistance from workers or stakeholders who are resistant to change.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...