Area of hexagon with given diagonal length
Last Updated :
27 Aug, 2022
You are given the length of the diagonal of a hexagon, d. Your task is to find the area of that hexagon.
Examples:
Input : 5
Output : Area of Hexagon: 16.238
Input : 10
Output : Area of Hexagon: 64.9519
Hexagon
Hexagon is a regular polygon having six equal sides and all equal angles. The interior angles of Hexagon are of 120 degrees each and the sum of all angles of a Hexagon is 720 degrees.

Let d be the diagonal of Hexagon, then the formula to find the area of Hexagon given by
Area =
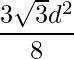
How does above formula work? We know that
area of hexagon with side length a = (3 √3(a)
2 ) / 2. Since all sides are of same size and angle is 120 degree, d = 2a or a = d/2. After putting this value, we get area as (3 √3(d)
2 ) / 8.
Below is the implementation .
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
float hexagonArea(float d)
{
return (3 * sqrt(3) * pow(d, 2)) / 8;
}
int main()
{
float d = 10;
cout << "Area of hexagon: " << hexagonArea(d);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.lang.Math;
public class GfG {
public static float hexagonArea(float d)
{
return (float)((3 * Math.sqrt(3) * d * d) / 8);
}
public static void main(String []args) {
float d = 10;
System.out.println("Area of hexagon: " + hexagonArea(d));
}
}
|
Python3
from math import sqrt
def hexagonArea(d) :
return (3 * sqrt(3) * pow(d, 2)) / 8
if __name__ == "__main__" :
d = 10
print("Area of hexagon:",
round(hexagonArea(d), 3))
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG{
public static float hexagonArea(float d)
{
return (float)((3 * Math.Sqrt(3) * d * d) / 8);
}
static public void Main (){
float d = 10;
Console.WriteLine("Area of hexagon: " + hexagonArea(d));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function hexagonArea($d)
{
return (3 * sqrt(3) * pow($d, 2)) / 8;
}
$d = 10;
echo "Area of hexagon: ",
hexagonArea($d);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function hexagonArea( d)
{
return (3 * Math.sqrt(3) * Math.pow(d, 2)) / 8;
}
let d = 10;
document.write("Area of hexagon: " + hexagonArea(d).toFixed(3));
</script>
|
Output:
Area of Hexagon: 64.952
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1), since no extra space has been taken.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...