Aperiodic Signals
Last Updated :
27 Feb, 2024
Aperiodic Signals are an important tool in the electronic industry. They are unavoidable in modern electronics and are almost used in every daily appliance for generating signals that are random and show no pattern in their behaviour. In this article, we will study what is an Aperiodic signal, how does it looks like. We will also represent the Aperiodic signal mathematically. Later we will discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and some applications of Aperiodic Electronic Signal. We will conclude the article by summing up what we have learned. The electronics industry especially the communication system uses these signals in various circuits and readers can read about these other signals as well.
What is an Aperiodic Signal?
Aperiodic signals are a type of electrical signals which show randomness in their behaviour and show no repetition in behaviour after any interval of time. It is also known as a non-periodic signal since it does not have any continuous periods. For example, the given signal might appear to be a period but we observe that the waveform doesn’t repeat but rather keeps changing. This means that the wave is an aperiodic signal.

Aperiodic Signal
Aperiodic Signal Graph
If we plot the graph representing the magnitude of periodic signal with time ,the graph of periodic signal looks like this

Aperiodic Signals
Examples of non-periodic signals include white noise, impulses, and arbitrary waveforms.
Types of Aperiodic Signals
Periodic signals can be divided into two parts:
Continuous Time Aperiodic Signal
A signal which is continuous and doesn’t repeat after regular intervals of time is a Continuous Time Aperiodic Signal i.e there is no value of time that satisfies the condition of periodicity. Some examples have been shown below.
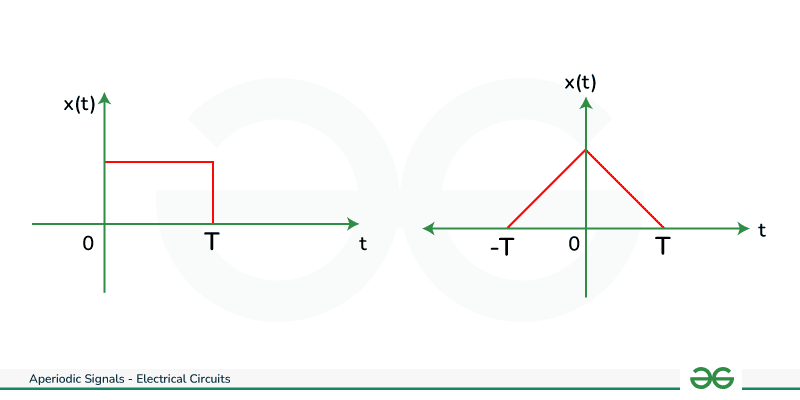
Continuous Time Aperiodic Signal
Discrete Time Aperiodic Signal
If we have a discrete signal which doesn’t satisfy the condition of periodicity for any value of n for signal x(n) , then it is Discrete Time Aperiodic Signal. Some examples have been given below

Discrete Time Aperiodic Signal
Difference Between Periodic Signal and Non Periodic Signal
The difference between period and aperiodic signals:
|
Periodic Signal
|
Non-Periodic Signal
|
|
They have a definite pattern
|
They have a indefinite pattern
|
|
They repeat after a certain interval of time
|
They don’t repeat after a certain interval of time
|
|
They have discrete and harmonically related frequency
|
They can have a continuous and non-harmonic frequency
|
|
They can be mathematically represented using Fourier Series
|
It is not possible to represent them through Fourier series due to lack of periodicity
|
|
This include sine waves or regular rectangular pulses
|
This include random signals arising from unpredictable disturbances of all kinds.
|
Properties of Aperiodic Signal
Here are some properties of Aperiodic signal:
- One important property of periodic signals is their non-repetitiveness. Periodic signals have this property since they show a unique pattern that does not repeat after any interval.
- Another important property if Periodic Signals is that it can be continuous or discrete. Continuous signals are defined for all values of time but discrete signals are defined for certain values only.
- We can define energy of aperiodic signals and divide them on the basis of whether it is finite or infinite. Energy signal have a finite area under their squared magnitude curve, while power signals have finite average power.
- Aperiodic signals can be random or deterministic. Deterministic signals have a predictable values at different points in time. Random signals display some of unpredictability and are determined using mathematical tools.
Advantages of Aperiodic Signals
The advantages of Aperiodic signals are stated below:
- Aperiodic Signals are practical signals. In real-world ,signals are not periodic and contains complex variations thereby making aperiodic signals more real.
- Aperiodic signals are flexible and can be used to represent various patterns and shapes. This is because they have no restrictions of repeating after an interval.
- These signals have wide-applications due to their ability to represent wide signals. They are widely used in communication systems, audio processing, image processing, and control systems.
- These signals are adaptable to dynamic changes, they are well-suited with systems showing time-variations. This adaptive effectiveness is not shown by periodic signals.
Disadvantages of Aperiodic Signals
The limitations of periodic signal are stated below:
- These signals have complex analysis as compared to periodic signals. This is because aperiodic signals have no repetitiveness or pattern thereby making it difficult to apply techniques like Fourier Series.
- The lack of a pattern makes these signals unpredictable. We can’t determine how signals will behave with accuracy after certain time.
- Sometimes signal-to-noise ratio of a aperiodic signals can be really low. This makes it difficult to get important information from these signals.
- These signals might involve some rigorous calculations done using tools like Fourier Series and La Place to analyse the signals.
Applications of Aperiodic Signals
Aperiodic signal is used in various applications like:
- Aperiodic signals are abundantly used in communication system. Those with broadband characteristics are used for high rate data transmission. Generally they involve aperiodic pulses.
- Aperiodic signals are widely used in speech and audio processing. This is because techniques used for analysis of aperiodic signals are used in speech recognition, audio compression, and digital audio processing.
- Aperiodic signals are used in control systems. The impulse response of a system provides insights into the system’s behaviour when subjected to abrupt changes.
- Periodic signals are essentially used in signal compression. Whenever there is limited bandwidth or storage space, compression techniques of aperiodic signals are applied.
Solved Examples of Aperiodic Signals
Q. Which of the following is not periodic?
- sin(10πt)
- sin(31t)
- sin(10πt)+ sin(31t)
- sin(10πt+31t)
In the 3rd example the two frequencies are
f1=2π/w1
f2=2π/w2
f1=2π/10π=1/5 (rational)
f2=2π/31 (irrational)
Hence, sin(10πt)+ sin(31t) is non-periodic
Conclusion
As we have seen that aperiodic signals play an important role in modern electronics. We have already discussed the non-periodic nature of these signals along with other properties. As we discuss the uses of this signal we realize it is used in control systems and as an input signal to various circuits in communication system for various purposes. These applications signify the need to find appropriate methods to generate aperiodic signals. There are different methods to generate these signals and they have been stated to the readers. There are various examples of aperiodic signals each used for a different use.
FAQs on Aperiodic Signals
1. What are Periodic waveforms?
Periodic signals are a kind of signals that repeat themselves after a certain period of time.
2. What are Aperiodic waveforms?
Aperiodic signals are the kind of signals that do not repeat after a specific period of time. This means they do not have a definite pattern.
3. What is the difference between Periodic pulse and Aperiodic pulse?
A periodic pulse has a definite pattern that repeats after a certain interval of time whereas a aperiodic pulse doesn’t have a definite pattern and doesn’t repeat.
4. What are some examples of Aperiodic signals?
Some other basic Aperiodic signals are signals by microphone or telephone.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...