AC Servo Motor
Last Updated :
27 Feb, 2024
In this article, we will be going through what are AC servo motors, We will start our article with the definitions of AC servo motors. We will see different types, then we will move to our Topic construction of AC servo motors, We will go through their working principle and transfer function. At last, we will conclude our Article with its Applications and Some FAQs.
What is an AC Servo Motor?
AC servo motors act as the powerhouses that generate accurate motion control in lots of applications, ensuring accurate movement. Compared to conventional AC motors, they are far more responsive. These motors work in closed-loop systems by continuously receiving and adapting to real-time feedback. They are ideal for highly accurate tasks like controlling a 3D printer nozzle or manipulating the arm of a surgical robot. Modern robotics and automation depend on AC servo motors due to their small size, high torque-to-inertia ratio, and precision. These motors are transforming a range of industries, including manufacturing and healthcare. They are crucial to boosting productivity while encouraging innovation in everything.
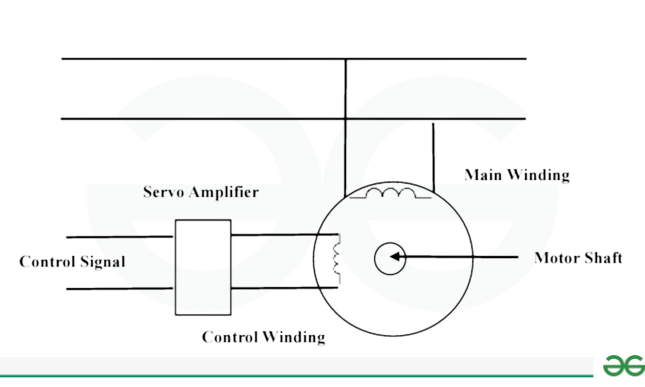
AC Servo motor
- An AC servo motor is a type of electric motor designed to precisely regulate linear or angular motion.
- It uses feedback signals to change its torque, speed, or position as it functions as a closed-loop system.
- Automation systems, robotics, CNC machines, and other applications that require a a lot of accuracy commonly use these motors.
- Robots are a component of automation due to their accuracy. They excel at tasks like making precise movements and placing objects precisely where they should be.
Construction of AC Servo Motor ?
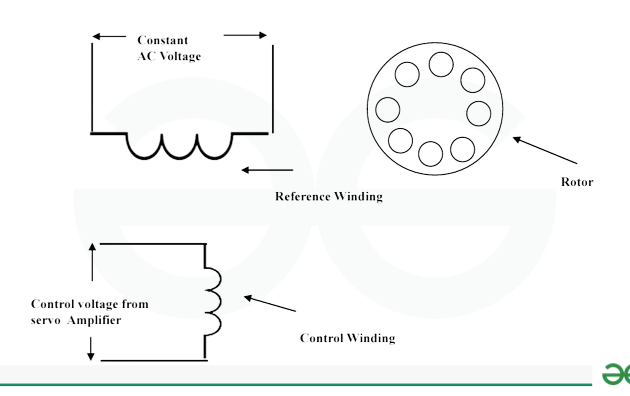
Construction of Ac Servo Motor
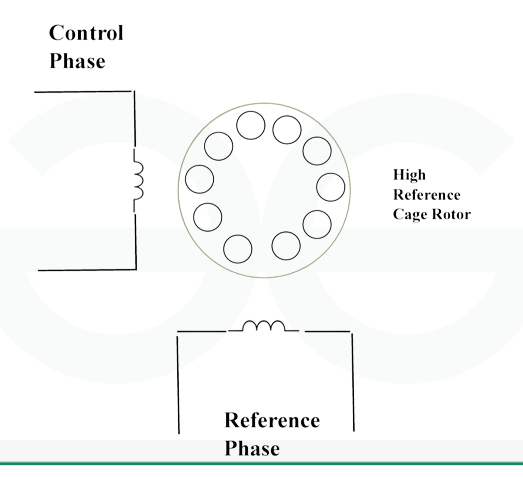
An AC servo motor is a two-phase induction motor. This motor has a stator and rotor, like a usual induction motor. The stator of this servo motor consists of laminate. This stator has two windings that are 90 degrees apart. This phase change results in a rotating magnetic field.
The primary winding is the first winding. It is also known as the fixed phase or reference winding. Here, the variable control voltage activates the other winding, also referred to as the control winding or control phase, while the constant voltage supply source powers the main winding. The control voltage is supplied entirely by a servo amplifier.
The aluminum bars in the rotor of this motor are fixed in slots and short-circuited through end rings, making it a cage-type rotor. Minimizing the air gap ensures optimal flux connection. Generally, a drag cup is used where the inertia of the rotating system decreases. As a result, this helps to lower power consumption.
Working Principle of AC Servo Motor
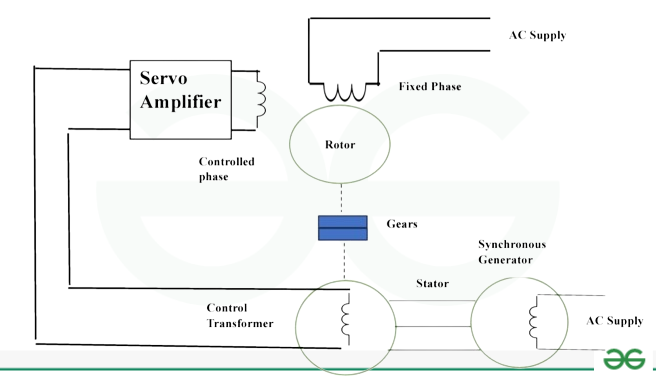
Working principle of AC servo motor
When an AC servo motor works, a number of parts and procedures come together to provide precise motion control :
- Stator and Rotor: The two most important parts of the AC servo motor are the rotor which is the revolving part and other is the stator which is the stationary part. The AC passing through the wire coils inside the stator creates a rotating magnetic field.
- Feedback System: Servo motors, as compared to AC motors, have a feedback mechanism that makes use of encoders or resolvers. These devices give data regarding the position, speed, and torque of the motor.
- Control System: A control system compares the parameters associated with motion , like position, speed, etc., with the feedback signals it gets from the motor. In response to this comparison, the control system generates a corrective signal, which changes how the motor operates.
- Power Amplifier: By amplifying the signal from the control system, a power amplifier increases the signal strength required to drive the motor.
- Motion: The motor windings produce a magnetic field that interacts with the stator’s magnetic field after receiving the amplified signal. The rotor rotates as a result of this interaction, producing a motion.
- Closed-loop Operation: In this process, the motor’s performance is evaluated and that information is sent back to the control system. Because of its closed-loop operation, the motor can precisely and accurately alter its operation in real-time to achieve the desired motion.
Transfer Function of AC Servo motor
The relationship between the input command signal and the output motion response is displayed by the transfer function of an AC servo motor. Usually, it takes into account factors such as motor dynamics, control system properties, and load dynamics. Briefly, the transfer function describes how the motor responds to changes in the input signal, which aids engineers in analyzing and designing control systems for optimal performance and stability.
AC Servo Motor Speed Control Methods
AC servo motors offer three different speed control techniques: torque control, position control, and speed control.
- Position Control: This method allows the motor to follow a predetermined angular or linear path. This technique makes it possible to precisely control the motor’s rotation to achieve the result. The feedback devices that are used to gather data are resolvers and encoders.
- Torque Control: It’s aim is to regulate the motor’s output torque, or the rotational force it applies. This technique guarantees accurate control over the motor’s power output for tasks requiring constant torque levels.
- Speed Control: Maintaining a constant speed for the motor shaft is known as speed control. It is essential for applications requiring precise speed requirements, like conveyor belt systems in machining operations, because it allows the motor to be adjusted precisely in terms of velocity. AC servo motors use a variety of feedback systems and control algorithms to provide accurate speed control.
Characteristics of AC Servo Motor
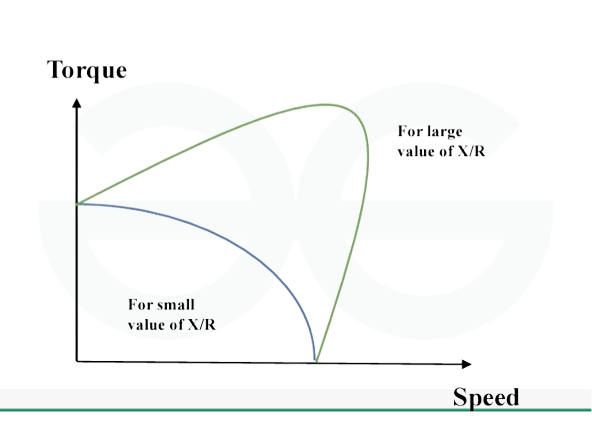
characteristic curve
- The graph indicates AC servo motor torque and speed characteristics. As torque is mostly constant at low speeds, large loads can be started and handled with ease.
- Due to factors like the back electromotive force (EMF) and winding resistance, torque steadily decreases as speed increases. We refer to this area as the continuous torque region.
- The maximum speed region occurs when the torque suddenly drops below a given speed, at which point the motor is unable to drive heavy loads.
- The torque and speed have an inverse relationship, as seen by the graph, with torque decreasing as speed increases.
Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications of AC Servo Motor
There are some list of Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications of AC Servo Motor given below :
Advantages
- AC servo motors offer exceptional accuracy and repeatability in motion control.
- These motors can guarantee accurate and rapid motion because of their quick adaptation to changes in input commands.
- They can run at a range of speeds, from low to high, with seamless speed changes .
- Because of their high torque output relative to their inertia, they have an efficient operation and can easily handle heavy loads.
- Closed-loop control systems, which monitor performance continuously and adapt to input to ensure steady operation under changing circumstances, are used to operate AC servo motors.
Disadvantages
- For precise motion control, AC servo motors require additional control systems and have a more complex design.
- The use of more complex control systems, like amplifiers and feedback mechanisms, is required when using AC servo motors.
- The feedback components of AC servo motors are subject to wear and tear namely resolvers and encoders.
- Noise is produced while operating if proper wiring guidelines aren’t followed.
- AC servo motors may use more power than regular AC motors when they are working faster or with larger loads.
Applications
- AC servo motor are used in robots due to their precision and motion .
- AC servo motors are used in axes of CNC machines used for cutting, milling, and machining operations.
- Several automation systems, including pick-and-place operations, packaging machinery, and conveyor belts, depend on AC servo motors as vital parts.
- To achieve exact control over paper feed, print head movement, and registration, printing equipment uses AC servo motors.
- Radar antennas, aerial vehicles, and missile guidance systems are a few of the defines and aerospace systems that use AC servo motors.
Two Phase and Three Phase Servo Motor
Given below are Two phase and Three Phase Servo motor
Two Phase AC Servo Motor
- An electric motor that runs on two alternating current phases is known as a two-phase AC servo motor. Two-phase motors are easier to construct and wire than three-phase motors, which are more common.
- They are commonly used in places where there is a shortage of space or where efficiency is crucial.
- Even though three-phase motors are more efficient and effective, two-phase AC servo motors can still manage torque and speed well enough for a variety of industrial and commercial uses.
- They are commonly found in automation systems, small appliances, and machinery that needs precise motion control.
Two phase AC servo motor
Three phase AC Servo Motor
- An electric motor that runs on three phases of AC power is known as a three-phase AC servo motor.
- It has a stator and a rotor. The stator’s three sets of windings produce a magnetic field that rotates.
- On comparing this design to single-phase motors, smoother operation and increased efficiency are possible.
- Three-phase AC servo motors have many applications, including conveyor belts, automation systems, robotics, etc. requiring precise motion control.
- Their high torque-to-inertia ratio, rapid acceleration, and precise speed control make them suitable for demanding tasks.
Conclusions
In conclusion, AC servo motors are a crucial part of accurate control systems and provide a number of advantages to a variety of sectors. Strong construction, comprising parts like feedback systems, stators, and rotors, ensures reliable and precise operation. Their ability to precisely control motion can be revealed by knowing their operating principle, which includes dynamic feedback mechanisms and closed-loop control systems. Two- or three-phase AC servo motors are more common than single-phase models because of their simpler and more effective operation. Their characteristics, which include torque-speed profiles and transfer functions, demonstrate how ideal they are for jobs requiring precise control over torque, speed, and position.
FAQs of AC Servo Motor
Can harsh environments be managed by AC servo motors?
AC servo motors are designed to withstand excessive heat, humidity, and vibration by using special coverings.
Which components affect the response time in AC servo motor?
Many factors can affect the response time in AC servo motor such as the inertia of the load, the tuning of the control system, the speed at which the controller and motor communicate.
How do overload situations affect AC servo motors?
Safety features like thermal protection and current limiting are frequently included with AC servo motors to prevent overload damage.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...