Type Conversion in C
Last Updated :
10 Apr, 2023
Type conversion in C is the process of converting one data type to another. The type conversion is only performed to those data types where conversion is possible. Type conversion is performed by a compiler. In type conversion, the destination data type can’t be smaller than the source data type. Type conversion is done at compile time and it is also called widening conversion because the destination data type can’t be smaller than the source data type. There are two types of Conversion:
1. Implicit Type Conversion
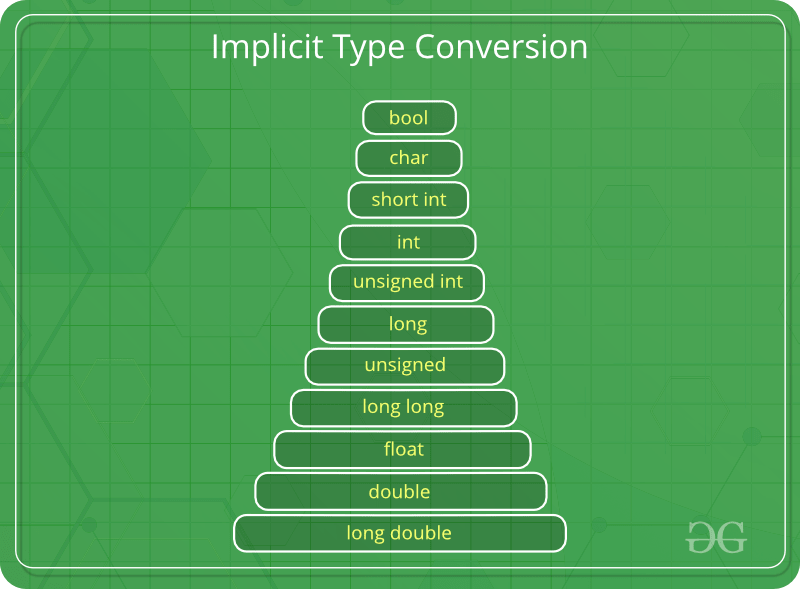
Also known as ‘automatic type conversion’.
A. Done by the compiler on its own, without any external trigger from the user.
B. Generally takes place when in an expression more than one data type is present. In such conditions type conversion (type promotion) takes place to avoid loss of data.
C. All the data types of the variables are upgraded to the data type of the variable with the largest data type.
bool -> char -> short int -> int ->
unsigned int -> long -> unsigned ->
long long -> float -> double -> long double
D. It is possible for implicit conversions to lose information, signs can be lost (when signed is implicitly converted to unsigned), and overflow can occur (when long is implicitly converted to float).
Occurrences of Implicit Type Conversion in C
Implicit type conversion is also called automatic type conversion. Some of its few occurrences are mentioned below:
- Conversion Rank
- Conversions in Assignment Expressions
- Conversion in other Binary Expressions
- Promotion
- Demotion
Example of Type Implicit Conversion
Example no 1
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 10;
char y = 'a';
x = x + y;
float z = x + 1.0;
printf("x = %d, z = %f", x, z);
return 0;
}
|
Output
x = 107, z = 108.000000
2. Explicit Type Conversion
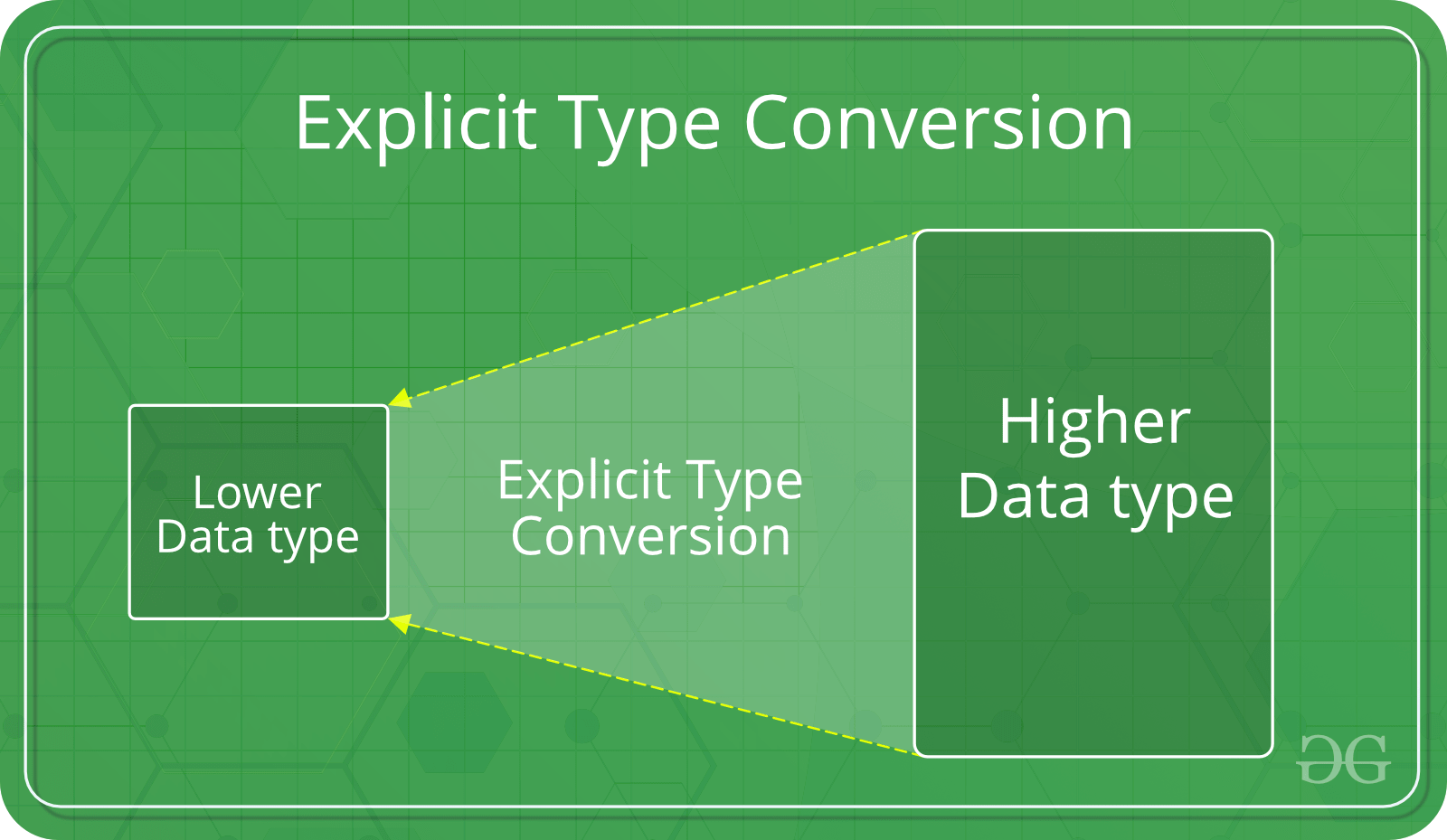
This process is also called type casting and it is user-defined. Here the user can typecast the result to make it of a particular data type. The syntax in C Programming:
(type) expression
Type indicated the data type to which the final result is converted.
Example no 2
C
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
double x = 1.2;
int sum = (int)x + 1;
printf("sum = %d", sum);
return 0;
}
|
Example no 3
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float a = 1.5;
int b = (int)a;
printf("a = %f\n", a);
printf("b = %d\n", b);
return 0;
}
|
Output
a = 1.500000
b = 1
Advantages of Type Conversion
- Type safety: Type conversions can be used to ensure that data is being stored and processed in the correct data type, avoiding potential type mismatches and type errors.
- Improved code readability: By explicitly converting data between different types, you can make the intent of your code clearer and easier to understand.
- Improved performance: In some cases, type conversions can be used to optimize the performance of your code by converting data to a more efficient data type for processing.
- Improved compatibility: Type conversions can be used to convert data between different types that are not compatible, allowing you to write code that is compatible with a wider range of APIs and libraries.
- Improved data manipulation: Type conversions can be used to manipulate data in various ways, such as converting an integer to a string, converting a string to an integer, or converting a floating-point number to an integer.
- Improved data storage: Type conversions can be used to store data in a more compact form, such as converting a large integer value to a smaller integer type, or converting a large floating-point value to a smaller floating-point type.
Disadvantages of type conversions in C programming:
- Loss of precision: Converting data from a larger data type to a smaller data type can result in loss of precision, as some of the data may be truncated.
- Overflow or underflow: Converting data from a smaller data type to a larger data type can result in overflow or underflow if the value being converted is too large or too small for the new data type.
- Unexpected behavior: Type conversions can lead to unexpected behavior, such as when converting between signed and unsigned integer types, or when converting between floating-point and integer types.
- Confusing syntax: Type conversions can have confusing syntax, particularly when using typecast operators or type conversion functions, making the code more difficult to read and understand.
- Increased complexity: Type conversions can increase the complexity of your code, making it harder to debug and maintain.
- Slower performance: Type conversions can sometimes result in slower performance, particularly when converting data between complex data types, such as between structures and arrays.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...