SQL Date and Time Functions
Last Updated :
22 Mar, 2024
In SQL, dates are complicated for newbies, since while working with a database, the format of the data in the table must be matched with the input data to insert. In various scenarios instead of date, datetime (time is also involved with date) is used.
For storing a date or a date and time value in a database,MySQL offers the following data types:
| DATE |
format YYYY-MM-DD |
| DATETIME |
format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI: SS |
| TIMESTAMP |
format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI: SS |
| YEAR |
format YYYY or YY |
Now, come to some popular functions in SQL date functions.
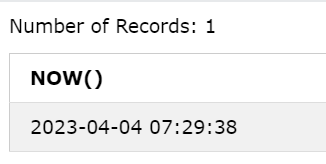
NOW()
Returns the current date and time.
Query:
SELECT NOW();
Output:
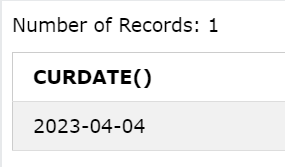
CURDATE()
Returns the current date.
Query:
SELECT CURDATE();
Output:
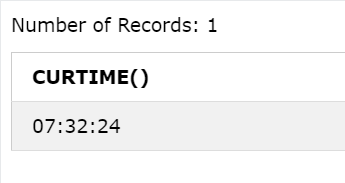
CURTIME()
Returns the current time.
Query:
SELECT CURTIME();
Output:
DATE()
Extracts the date part of a date or date/time expression. Example: For the below table named ‘Test’
| Id |
Name |
BirthTime |
| 4120 |
Pratik |
1996-09-26 16:44:15.581 |
Query:
SELECT Name, DATE(BirthTime)
AS BirthDate FROM Test;
Output:
| Name |
BirthDate |
| Pratik |
1996-09-26 |
EXTRACT()
Returns a single part of a date/time.
Syntax
EXTRACT(unit FROM date);
Several units can be considered but only some are used such as MICROSECOND, SECOND, MINUTE, HOUR, DAY, WEEK, MONTH, QUARTER, YEAR, etc. And ‘date’ is a valid date expression. Example: For the below table named ‘Test’
| Id |
Name |
BirthTime |
| 4120 |
Pratik |
1996-09-26 16:44:15.581 |
Query:
SELECT Name, Extract(DAY FROM
BirthTime) AS BirthDay FROM Test;
Output:
Query:
SELECT Name, Extract(YEAR FROM BirthTime)
AS BirthYear FROM Test;
Output:
| Name |
BirthYear |
| Pratik |
1996 |
Query:
SELECT Name, Extract(SECOND FROM
BirthTime) AS BirthSecond FROM Test;
Output:
| Name |
BirthSecond |
| Pratik |
581 |
DATE_ADD()
Adds a specified time interval to a date.
Syntax:
DATE_ADD(date, INTERVAL expr type);
Where, date – valid date expression, and expr is the number of intervals we want to add. and type can be one of the following: MICROSECOND, SECOND, MINUTE, HOUR, DAY, WEEK, MONTH, QUARTER, YEAR, etc. Example: For the below table named ‘Test’
| Id |
Name |
BirthTime |
| 4120 |
Pratik |
1996-09-26 16:44:15.581 |
Query:
SELECT Name, DATE_ADD(BirthTime, INTERVAL
1 YEAR) AS BirthTimeModified FROM Test;
Output:
| Name |
BirthTimeModified |
| Pratik |
1997-09-26 16:44:15.581 |
Query:
SELECT Name, DATE_ADD(BirthTime,
INTERVAL 30 DAY) AS BirthDayModified FROM Test;
Output:
| Name |
BirthDayModified |
| Pratik |
1996-10-26 16:44:15.581 |
Query:
SELECT Name, DATE_ADD(BirthTime, INTERVAL
4 HOUR) AS BirthHourModified FROM Test;
Output:
| Name |
BirthSecond |
| Pratik |
1996-10-26 20:44:15.581 |
DATE_SUB()
Subtracts a specified time interval from a date. The syntax for DATE_SUB is the same as DATE_ADD just the difference is that DATE_SUB is used to subtract a given interval of date.
DATEDIFF()
Returns the number of days between two dates.
Syntax:
DATEDIFF(date1, date2);
date1 & date2- date/time expression
Query:
SELECT DATEDIFF('2017-01-13','2017-01-03') AS DateDiff;
Output:
DATE_FORMAT()
Displays date/time data in different formats.
Syntax:
DATE_FORMAT(date,format);
the date is a valid date and the format specifies the output format for the date/time. The formats that can be used are:
- %a-Abbreviated weekday name (Sun-Sat)
- %b-Abbreviated month name (Jan-Dec)
- %c-Month, numeric (0-12)
- %D-Day of month with English suffix (0th, 1st, 2nd, 3rd)
- %d-Day of the month, numeric (00-31)
- %e-Day of the month, numeric (0-31)
- %f-Microseconds (000000-999999)
- %H-Hour (00-23)
- %h-Hour (01-12)
- %I-Hour (01-12)
- %i-Minutes, numeric (00-59)
- %j-Day of the year (001-366)
- %k-Hour (0-23)
- %l-Hour (1-12)
- %M-Month name (January-December)
- %m-Month, numeric (00-12)
- %p-AM or PM
- %r-Time, 12-hour (hh:mm: ss followed by AM or PM)
- %S-Seconds (00-59)
- %s-Seconds (00-59)
- %T-Time, 24-hour (hh:mm: ss)
- %U-Week (00-53) where Sunday is the first day of the week
- %u-Week (00-53) where Monday is the first day of the week
- %V-Week (01-53) where Sunday is the first day of the week, used with %X
- %v-Week (01-53) where Monday is the first day of the week, used with %x
- %W-Weekday name (Sunday-Saturday)
- %w-Day of the week (0=Sunday, 6=Saturday)
- %X-Year for the week where Sunday is the first day of the week, four digits, used with %V
- %x-Year for the week where Monday is the first day of the week, four digits, used with %v
- %Y-Year, numeric, four digits
- %y-Year, numeric, two digits
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...