PostgreSQL – TIME Data Type
Last Updated :
22 Feb, 2021
PostgreSQL provides user with TIME data type that is used to handle time values. It requires 8 bytes of storage and can have precision up to 6 digits. It can range from 00:00:00 to 24:00:00.
Syntax: column_name TIME(precision);
The common TIME formats are illustrated below:
HH:MM
HH:MM:SS
HHMMSS
If precision is required the following format needs to be followed:
MM:SS.pppppp
HH:MM:SS.pppppp
HHMMSS.pppppp
For instance below are sample TIME value formats:
Without precision:
01:02
01:02:03
010203
With precision:
04:59.999999
04:05:06.777777
040506.777777
Now let’s look into some examples for better understanding.
Example:
In this example we will create a table that holds team schedules details of a company. First, create a new table named team_schedule by using the following commands:
CREATE TABLE team_schedule (
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
team_name VARCHAR NOT NULL,
clock_in_time TIME NOT NULL,
clock_out_time TIME NOT NULL
);
Now, insert some rows into the team_schedule table:
INSERT INTO team_schedule(team_name, clock_in_time, clock_out_time)
VALUES('Marketing', '09:00:00', '18:00:00'),
('Sales', '10:00:00', '19:00:00'),
('Mentors', '09:00:00', '18:00:00'),
('Software', '11:00:00', '20:00:00'),
('Content', '10:00:00', '19:00:00');
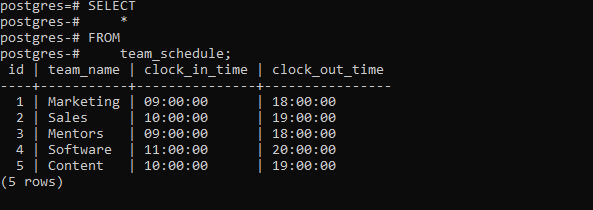
Finally, we query from the shifts table using the below command:
SELECT
*
FROM
team_schedule;
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...