NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 – Areas Related to Circles is developed for students to solve problems in a carefree manner and without any frustration. This article covers all the problems related to this chapter in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths.
Chapter 12 – Areas Related to Circles covers The topic of calculating the area and circumference of a circle using common formulas. Additionally, there are inquiries about calculating the areas of composite figures, a sector, and a segment.
Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 12 Exercises |
|---|
|
- NCERT Maths Solutions Class 10 Exercise 12.2 Set 1, Set 2 – 14 Questions (9 Short Answers, 5 Long Answers)
|
- NCERT Maths Solutions Class 10 Exercise 12.3 Set 1, Set 2 – 16 Questions (9 Short Answers, 7 Long Answers)
|
Areas Related to Circles: Exercise 12.1
Question 1. The radii of the two circles are 19 cm and 9 cm respectively. Find the radius of the circle which has a circumference equal to the sum of the circumferences of the two circles.
Solution:
Since we have to find the radius of the final circle we will use the formula of the circumference of circle C = 2πr.
Radius (r1) = 19 cm
Radius (r2) = 9 cm
Circumference of a circle with a radius of 19 cm is 2π * 19 = 38π cm.
Circumference of a circle with a radius of 9 cm is 2π * 9 = 18π cm.
Total Circumference is = 38π + 18π = 56π cm
Now using C = 2πr3 we will find r3 which is:
56π = 2π * (r3)
Therefore, the radius of the circle which has a circumference equal to the sum of the circumference of the given two circles is 28 cm.
Question 2. The radii of the two circles are 8 cm and 6 cm respectively. Find the radius of the circle having an area equal to the sum of the areas of the two circles.
Solution:
Area of circle is = πr2 cm2
Area of circle1 = 64π cm2
Area of circle2 = 36π cm2
Total Area = 100π cm2
Now in order to find the radius of the required circle:
100π = πr2
r = 10 cm.
Therefore, the radius of the circle having an area equal to the sum of the areas of the two circles is 10cm.
Question 3. The Figure depicts an archery target marked with its five scoring regions from the centre outwards as Gold, Red, Blue, Black, and White. The diameter of the region representing the Gold score is 21 cm and each of the other bands is 10.5 cm wide. Find the area of each of the five scoring regions.

Solution:
Radius (r1) of gold region (i.e., 1st circle) = 21/2 = 10.5 cm
Also, as per the question, it is Given that each circle is 10.5 cm wider than the previous circle.
Therefore, radius (r2) of 2nd circle = 10.5 + 10.5 = 21 cm
Radius (r3) of 3rd circle = 21 + 10.5 = 31.5 cm
Radius (r4) of 4th circle = 31.5 + 10.5 = 42 cm
Radius (r5) of 5th circle = 42 + 10.5 = 52.5 cm
Area of gold region = Area of 1st circle = π*(10.5)*(10.5) cm2 = 346.5 cm2
Area of red region = Area of 2nd circle − Area of 1st circle = π*(21)*(21) – π*(10.5)*(10.5) = 1039.5 cm2
Area of blue region = Area of 3rd circle − Area of 2nd circle =π*(31.5)*(31.5) -π*(21)*(21) = 1732.5 cm2
Area of black region = Area of 4th circle − Area of 3rd circle = π*(42)*(42)-π*(31.5)*(31.5)= 2425.5 cm2
Area of white region = Area of 5th circle − Area of 4th circle=π*(52.5)*(52.5)- π*(42)*(42)= 3118.5 cm2
Hence, areas of gold, red, blue, black, and white regions are 346.5 cm2, 1039.5 cm2, 1732.5 cm2, 2425.5 cm2, and 3118.5 cm2 respectively.
Question 4. The wheels of a car are of diameter 80 cm each. How many complete revolutions does each wheel make in 10 minutes when the car is traveling at a speed of 66 km per hour?
Solution:
The diameter of the wheel of the car = 80 cm
So the Radius (r) of the wheel of the car = 40 cm
Now Calculating the Circumference of wheel = 2πr = 2π (40) = 80π cm
Speed of car = 66 km/hour
Speed(cm/min)= 110000 cm/min
Distance travelled by the car in 10 minutes = 110000 × 10 = 1100000 cm
Let the number of revolutions of the wheel of the car be p.
So, equating it now
We get, p × Distance traveled in 1 revolution = Distance traveled in 10 minutes
80π * p = 1100000
p = 4375
Hence, each wheel of the car will make 4375 revolutions.
Question 5. Tick the correct answer in the following and justify your choice:
If the perimeter and the area of a circle are numerically equal, then the radius of the circle is
(A) 2 units (B) π units (C) 4 units (D) 7 units
Solution:
Let the radius of the circle be r.
Circumference of circle = 2πr
Area of circle = πr2
Also in the question, it is given that, the circumference of the circle and the area of the circle are equal.
Hence, 2πr = πr2
r = 2 units
Hence, the radius of the circle is 2 units.
Option A is the correct answer.
Areas Related to Circles: Exercise 12.2
Question 1. Find the area of a sector of a circle with radius 6 cm if angle of the sector is 60°.
Solution:
Given: r=66cm and ∅=60°
Area of sector=∅/(360°) *πr2
=60/360*22/7*6*6
=132/7

Question 2. Find the area of a quadrant of a circle whose circumference is 22 cm. Quadrant of circle is sector making 90°.
Solution:
Given: circumference of circle=22cm and ∅=90°
To find r=?
2πr=22
Radius =r=22/2πr cm=7/2cm
Area of quadrant =∅/(360°) *πr2
=90/360*22/7*7/2*7/2
=77/8cm2

Question 3. The length of the minute hand of a clock is 14 cm. Find the area swept by the minute hand in 5 minutes.
Solution:
Let assume, Minute hand of clock acts as radius of the circle.
Angle rotated by min (hand in 5minutes)=∅=360/60*5=30°
Radius=r=14cm
Area of swept middle hand=
=∅/(360°) *πr2
=30/360*22/7*14*14
=154/3cm2
Area swept by the minute hand in 5min=154/3cm2

Question 4. A chord of a circle of radius 10 cm subtends a right angle at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding: (i) minor segment (ii) major sector. (Use π = 3.14)
Solution:
Radius =r=10cm
Major segment is =360°-90°=270°
(i) Area of minor segment =Area of sector-Area of triangle
=∅/(360°) *πr2-1/2*h*b
=90/306*3.14*10*10-1/2*10*10
=314/4-50
=78.5-50
Area of minor segment =28.5cm2
(ii) Area of major sector=∅/(360°) *πr2
=270/360*3.14*10*10
=3*314/4=235.5cm2
Area of major segment=235.5cm2

Question 5. In a circle of radius 21 cm, an arc subtends an angle of 60° at the centre. Find:
(i) the length of the arc
(ii) area of the sector formed by the arc
(iii) area of the segment formed by the corresponding chord
Solution:
(i) Radius=r=21cm
Length of arc=∅/(360°) *2πr
60/360*2*22/7*21
=22cm
(ii) Area of sector=∅/(360°) *πr2
60/360*22/7*21*21
11*21=231cm2
(iii) Area of segment =Area of sector -Area of triangle
=231-√3/4(side)2
=231-1.73/4*21*21
=231-762.93/4
=231-190.73
=40.27cm2

Question 6. A chord of a circle of radius 15 cm subtends an angle of 60° at the centre. Find the areas of the corresponding minor and major segments of the circle. (Use π = 3.14 and √3 = 1.73)
Solution:
Radius of circle=15cm
∆AOB is isosceles
∴∠A = ∠B
=∠A+∠B+C=180°
=2∠A=180°-60°
=∠A=120°/2
=∠A=60°
Area of minor segment =Area of sector-Area of triangle
=∅/(360°) *πr2-√3/4(side)2
=(60°)/360*3.14*15*15-1.73/4
=706.5/6-389.25/4
=117.75-97.31
=20.44cm2
Area of major segment-Area of circle-Area of minor segment
=πr2-20.44
=3.14*15*15-20.44
=686.06cm2

Question 7. A chord of a circle of radius 12 cm subtends an angle of 120° at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding segment of the circle. (Use π = 3.14 and √3 = 1.73)
Solution:
Radius=r=12cm
Area of triangle=1/2*base*height
Area of segment=Area of sector -area of triangle
=∅/(360°)*π*r2-1/2(side)2*sin∅
=120°/360°*3.14-1/2(side)2*sin120°∅
=150.72-6*12*sin60°
=150.72-6*12*√3/2
=150.72-36*1.73
=150.72-62.28
=88.44cm2

Question 8. A horse is tied to a peg at one corner of a square-shaped grass field of side 15 m by means of a 5 m long rope (see Fig.). Find
(i) the area of that part of the field in which the horse can graze.
(ii) the increase in the grazing area if the rope were 10 m long instead of 5 m. (Use π = 3.14)
Solution:
(i) Horse with graze=∅/(360°) × π × r2
= 90°/360° × 3.14 × 5 × 5
= 78.5/4
=19.625cm2
Area of circle the length of rope is increased to 10m
=∅/(360°) × π × r2
=90°/360° × 3.14 × 10 × 10
=314/4
=78.5cm2
(ii) Increasing in grazing area=78.5m2-19.635m2=58.875m2

Question 9. A brooch is made with silver wire in the form of a circle with a diameter of 35 mm. The wire is also used in making 5 diameters which divide the circle into 10 equal sectors as shown in Fig. Find:
(i) the total length of the silver wire required.
(ii) the area of each sector of the brooch.
Solution:
(i) Total length of silver wire required=circumference of broach+5diameter
=5 × 35 mm × πd
=175+22/7 × 35
=175+110
=285mm
(ii) Area of each sector=1/10×Area of circle
=1/10×π×r2
=1/10×22/7×35/2×35×2
=11×35/4
=385/4mm2

Question 10. An umbrella has 8 ribs that are equally spaced (see Fig.). Assuming the umbrella to be a flat circle of radius 45 cm, find the area between the two consecutive ribs of the umbrella.
Solution:
Total ribs in umbrella=8
Radius of umbrella is =45cm
Area between the two consecutive ribs=1/8π×r2
=1/8×22/7×45×45cm2
=22275/28

Question 11. A car has two wipers which do not overlap. Each wiper has a blade of length 25 cm sweeping through an angle of 115°. Find the total area cleaned at each sweep of the blades.
Solution:
Angle made by sector=∅=115°
r=25cm
Total area clean at each sweep of the blades=2×Area of sector
=2×∅/(360°)×π×r2
=2×(115°)/(360°)×22/7×25×25cm2
=23×11×25×25cm2
=158125/126cm2
=1254.96cm2
The total area clean at each sweep of blades=1254.96cm2

Question 12. To warn ships for underwater rocks, a lighthouse spreads a red colored light over a sector of angle 80° to a distance of 16.5 km. Find the area of the sea over which the ships are warned.
Solution:
(Use π = 3.14)
Distance over which light fall =r=16.5km
Angle made by the sector=∅=80°
Area of the sea over which the ships are warned=Area of sector
=∅/(360°)×π×r2
=(80°)/(360°)×3.14×16.5×16.5
=1709.73
=189.97km2
The area of ships is +warned =189.97km2

Question 13. A round table cover has six equal designs as shown in Figure. If the radius of the cover is 28 cm, find the cost of making the designs at the rate of ₹ 0.35 per cm2. (Use √3 = 1.7)
Solution:
Total equal designs==6
Radius =28cm
Cost for making design=RS.035 per cm2
∠O=360°/6=60°
Area of 1 design =Area of sector-Area of triangle
=∅/(360°)×π×r2×–

Question 14. Tick the correct answer in the following:
Area of a sector of angle p (in degrees) of a circle with radius R is
(A) p/180 × 2πR (B) p/180 × π R2 (C) p/360 × 2πR (D) p/720 × 2πR2
Solution:
Area of sector angle p=p/360×2πr2
Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Areas Related to Circles: Exercise 12.3
Question 1. Find the area of the shaded region in Fig., if PQ = 24 cm, PR = 7 cm and O is the center of the circle.
Solution:
In fig. By Pythagoras theorem
RQ2=RP2+PQ2
RQ2=(7)2+(24)2
RQ2=625
RQ=√625
RQ=√5*5*5*5
RQ=5*5
=25
Radius of circle =25/2cm
Areas of shaded region=Area of semi circle -Area of ∆RPQ
=1/2πR2-1/2*b*h
=(1/2*22/7*25/2)-(1/2*7*24)
=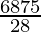 -84
-84
=161.53cm2

Question 2. Find the area of the shaded region in Fig., if radii of the two concentric circles with center O are 7 cm and 14 cm respectively and ∠AOC = 40°.
Solution:
Area of shaded Region=Area of sector AOC – Area of sector BOD
∠AOC = θ
Radius of inner circle = r
Radius of outer circle = R
=θ/360 πR2 – θ/360 πr2
= θ/360 π(R2-r2)
=40/(360)*22/7(14*14-7*7)
=40/360*22/7(196-49)
=(22/63) * 147
=154/3
=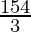 cm2
cm2

Question 3. Find the area of the shaded region in Fig., if ABCD is a square of side 14 cm and APD and BPC are semicircles.
Solution:
Radius =14/2=7
Area of shaded region=Area of square-Area of 2 semi-circles
=side*side-2*1/2πr2
=14*14 – 22/7*7*7
=196-154
=42 cm2

Question 4. Find the area of the shaded region in Fig., where a circular arc of radius 6 cm has been drawn with vertex O of an equilateral triangle OAB of side 12 cm as center.
Solution:
Area of shaded region=Area of big sector+ Area of equilateral
=θ/360 πr2+√3/4(side)2
=(300/360)*22/7*6*6+(√3/4)*12*12
=5/6*22/7*6*6+36*1.73
=660/7+62.28
=94.28+62.28
=156.56 cm2

Question 5. From each corner of a square of side 4 cm a quadrant of a circle of radius 1 cm is cut and also a circle of diameter 2 cm is cut as shown in Figure. Find the area of the remaining portion of the square.
Solution:
radius, r = 1cm
Area of remaining poison=Area of square – Area of 4 quadrants – Area of circle in the middle
=side*side – 4(90/360 πr2) – πr2
=4*4 – 2 πr2
=16-2*22/7*1*1
=16-44/7
=9.72cm2

Question 6. In a circular table cover of radius 32 cm, a design is formed leaving an equilateral triangle ABC in the middle as shown in Figure. Find the area of the design.
Solution:
Area of circle= πr2=22/7*32*32=22528/7=3218.28cm2 —–1
Area of ∆ABC=3*Area of ∆BOC
=3*1/2*side*side*sin120°
=3/2*32*32*sin60°
=1536*√3/2
=768*1.73
=1328.64cm2 ———2
Area of design =Area of circle – Area of ∆ABC
=321.28-1328.64
=1889.64 cm2

Question 7. In Fig., ABCD is a square of side 14 cm. With centers A, B, C and D, four circles are drawn such that each circle touch externally two of the remaining three circles. Find the area of the shaded region.
Solution:
Area of shaded region=Area of square – Area of 4 quarters
=side*side – 4(90/360 πr2)
=14*14-22/7*7*7
=196-154
=42cm2

Question 8. Fig. here depicts a racing track whose left and right ends are semi-circular. The distance between the two inner parallel line segments is 60 m and they are each 106 m long. If the track is 10 m wide, find:
i) the distance around the track along its inner edge
ii) the area of the track
Solution:
i) A distance along inner edge=length of 2 parallel lines+ circumference of 2 circles
=106+106+2πr
=212+2*22/7*30
=212+188.57
=400.57m
ii) Area of track=Area of 2 rectangles+ semi rings
=106*10*2+π (R-r)2
=2120+22/7((40)2-(30)2)
=210+22/7(1600-900)
=210+2200
=4320 m2

Question 9. In Fig., AB and CD are two diameters of a circle (with center O) perpendicular to each other and OD is the diameter of the smaller circle. If OA = 7 cm, find the area of the shaded region.
Solution:
Area of smaller circle=πr2
=22/7*7/2*7/2
=78/2 =38.5m2
Area of segment=Area of quadrant-Area of ∆BOC
=1/4πR2-1/2*BO*OC
=1/4*22/7*7*7-1/2*7*7
=77/2-49/2
=77-49/2
=28/2
=14 cm2
Area of shaded region=Area of smaller circle+2*Area of segment
=38.5 + 2*14
=38.5+28
=66.5 cm2

Question 10. The area of an equilateral triangle ABC is 17320.5 cm2. With each vertex of the triangle as center, a circle is drawn with radius equal to half the length of the side of the triangle (see Fig.). Find the area of the shaded region. (Use π = 3.14 and √3 = 1.73205)
Solution:
Area of equilateral ∆ =1.73205
π=3.14
√3=1.73205
√3/4 (side)2=173205
1.73205/4*(side)2=1.73205
(side)2=173205*4/1.73205
(side)2=173205*100000/10*173205
=√1000*4
=√(100 *100*2*2)
=100*2
=200cm
∴Radius of each circle=200/2=100
Area of shaded region=Area of∆ ABC-3*Area of sector
=1.73205*60/360*3.14*100*100
=1.73205-31400/2
=17320.5-15700
=1620.5cm2

Question 11. On a square handkerchief, nine circular designs each of radius 7 cm are made (see Fig.). Find the area of the remaining portion of the handkerchief.
Solution:
Side of square=6*Radius
=6*7
=42 cm
Area of shaded region=Area of square – Area of 9 circles
=side*side – 9πr2
=42*42 – 9*22/7*7*7
=1764-1386
=378 cm2
The area of the remaining portion of the handkerchief =378 cm2

Question 12. In Fig., OACB is a quadrant of a circle with Centre O and radius 3.5 cm. If OD = 2 cm, find the area of the
(i) quadrant OACB, (ii) shaded region.
Solution:
(i) Area of shaded region=Area of quadrant
=1/4πr2
=1/4*22/7*3.5*3.5
=38.5/4
=9.625 cm2
(ii) Area of shaded region=Area of quadrant -Area of ∆BOD
=9.625-1/2*BO*OD
=9.625-1/2*3.5*2
=9.625-3.5
=6.125 cm2

Question 13. In Fig., a square OABC is inscribed in a quadrant OPBQ. If OA = 20 cm, find the area of the shaded region. (Use π = 3.14)
Solution:
By Pythagoras theorem,
OB2=DA2+AB2
BO2=(20)2+(20)2
OB2=400+400
OB2=800
OB=√800
OB=√(2*2*2*2*5*5)
OB=2*2*5√2
OB=20√2
Area of shaded region=Area of quadrant -Area of square
=1/4πr2 – side*side
=1/4*3.14*20√2*20√2-20*20
=1/4*3.14*800-400
=1*3.14
=22cm2
=1/4*3.14
The area of shaded region is =1/4*3.14

Question 14. AB and CD are respectively arcs of two concentric circles of radii 21 cm and 7 cm and centre O (see Fig.). If ∠AOB = 30°, find the area of the shaded region.
Solution:
Area of shaded region=Area of sector AOB-Area of sector COD
=θ/(360°) πR2-θ/(360°) πr2
=θ/(360°) π[R2-r2]
=30°/360*22/7[(21)2-(7)2]
=1/12*22/7*28*14
=308/3cm2
=102.66cm2
The area of shaded region 102.66cm2

Question 15. In Fig., ABC is a quadrant of a circle of radius 14 cm and a semicircle is drawn with BC as diameter. Find the area of the shaded region.
Solution:
Area of segment=Area of quadrant -Area of ∆BAC
=1/4πr2-1/2*AC*AB
=1/4*22/7*14*14-1/2*14*14
=11*14-98
=154-98
=56 cm2
Semicircle R=?
In rt. ∆BAC, By Pythagoras theorem,
BC2=AB2+BC2
BC2= (14)2+(14)2
BC=√((14)2+(14)2)
BC=√((14)2[1+1] )
BC=14√2
∴Diameter of semicircle=14√2cm
then radius R of semicircle=14√2/2=7√2cm
Area of semicircle =1/2πR2
=1/2*22/7*7√2*7√2
=22*7
=154 cm2
Area of shaded region=Area of semicircle-Area of segment
=154-56 cm2
=98 cm2
The area of shaded region is =98cm2

Question 16. Calculate the area of the designed region in Fig. common between the two quadrants of circles of radius 8 cm each.
Solution:
Area of design=Area of 2 quadrant -Area of square
=2*1/4πr2-side*side
=1/2*22/7*8*8-8*8
=704/7-64
=100.57-64
=36.57cm2
Area designed region in figure is 36.57cm2

Important Points to Remember:
- These NCERT solutions are developed by the GfG team, focusing on students’ benefit.
- These solutions are entirely accurate and can be used by students to prepare for their board exams.
- Each solution is presented in a step-by-step format with comprehensive explanations of the intermediate steps.
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles
Q1: Why is it important to learn about Areas related to Circles?
Answer:
Learning about areas related to circles is important for students because circles are prevalent in real-life scenarios. Understanding how to calculate the area of a circle enables students to solve practical problems involving circular objects, such as finding the area of a circular field or the surface area of a cylindrical container. Additionally, learning about areas helps students develop a deeper understanding of geometric concepts and their applications.
Q2: What topics are covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 – Areas Related to Circles?
Answer:
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 – Areas Related to Circles covers topics such as the area of a circle, the circumference of a circle, and their interconnection. They also explore the concept of circumference, which is the distance around the circle, and learn the formula 2πr for its calculation. Additionally, students may learn about the application of these concepts in real-life situations, such as finding the area of circular objects or calculating the length of circular paths
Q3: How can NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles help me?
Answer:
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 – Areas Related to Circles can help you solve the NCERT exercise without any limitations. If you are stuck on a problem you can find its solution in these solutions and free yourself from the frustration of being stuck on some question.
Q4: How many exercises are there in Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 – Areas Related to Circles?
Answer:
There are 3 exercises in the Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 – Areas Related to Circles which covers all the important topics and sub-topics.
Q5: Where can I find NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 – Areas Related to Circles?
Answer:
You can find these NCERT Solutions in this article created by our team of experts at GeeksforGeeks.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...