Implementation of Contiguous Memory Management Techniques
Last Updated :
06 Dec, 2023
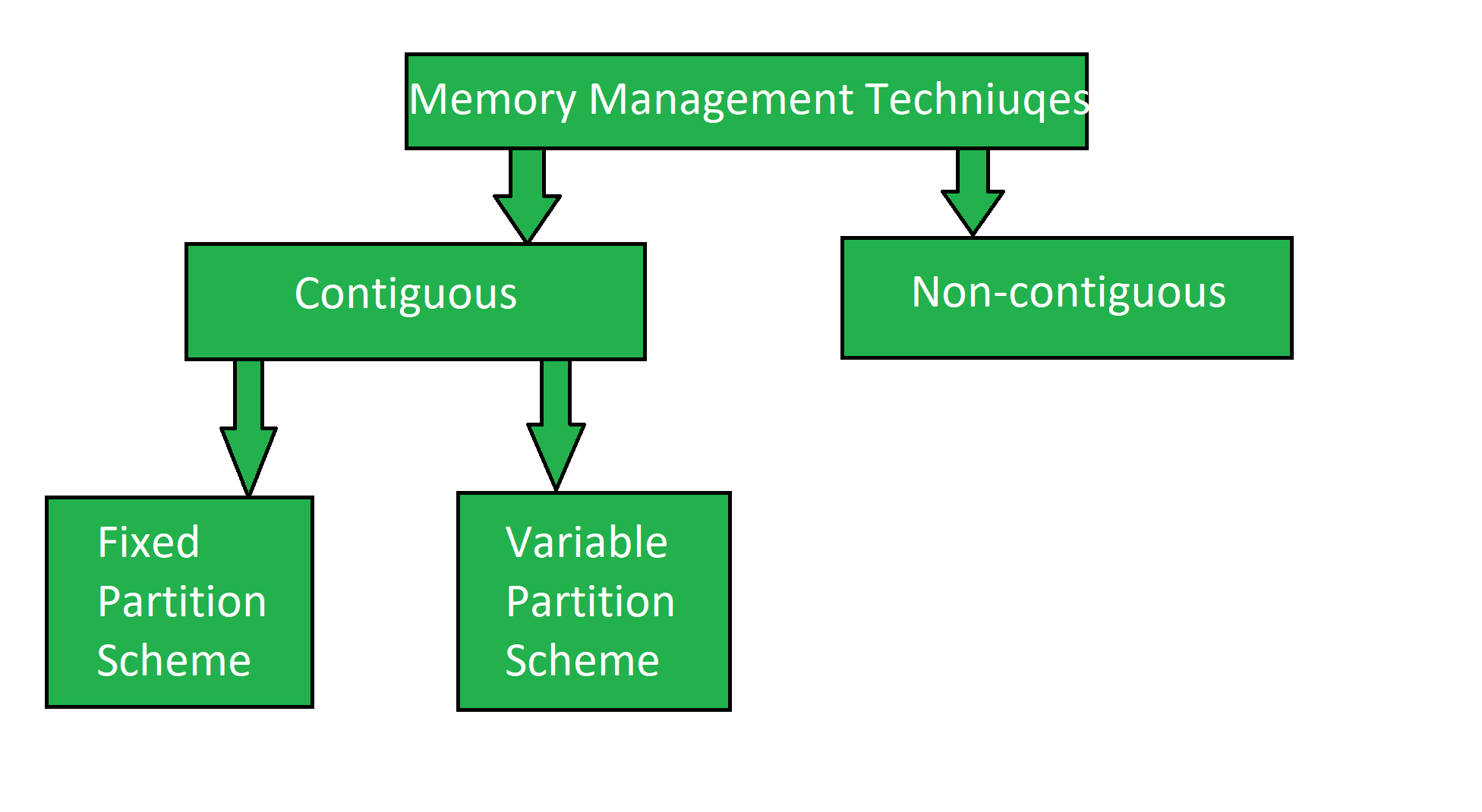
Memory Management Techniques are basic techniques that are used in managing the memory in the operating system. In this article, we will deal with the implementation of Continuous Memory Management Techniques. Memory Management Techniques are classified broadly into two categories:
- Contiguous
- Non-contiguous
What is Contiguous Memory Management?
Contiguous memory allocation is a memory allocation strategy. As the name implies, we utilize this technique to assign contiguous blocks of memory to each task. Thus, whenever a process asks to access the main memory, we allocate a continuous segment from the empty region to the process based on its size. In this technique, memory is allotted in a continuous way to the processes. Contiguous Memory Management has two types:
- Fixed(or Static) Partition
- Variable(or Dynamic) Partitioning
Contiguous Memory Management Techniques
Below are two Contiguous Memory Management Techniques. Lets understand these in detail.
1. Fixed Partition Scheme
In the fixed partition scheme, memory is divided into fixed number of partitions. Fixed means number of partitions are fixed in the memory. In the fixed partition, in every partition only one process will be accommodated. Degree of multi-programming is restricted by number of partitions in the memory. Maximum size of the process is restricted by maximum size of the partition. Every partition is associated with the limit registers.
- Limit Registers: It has two limit:
- Lower Limit: Starting address of the partition.
- Upper Limit: Ending address of the partition.
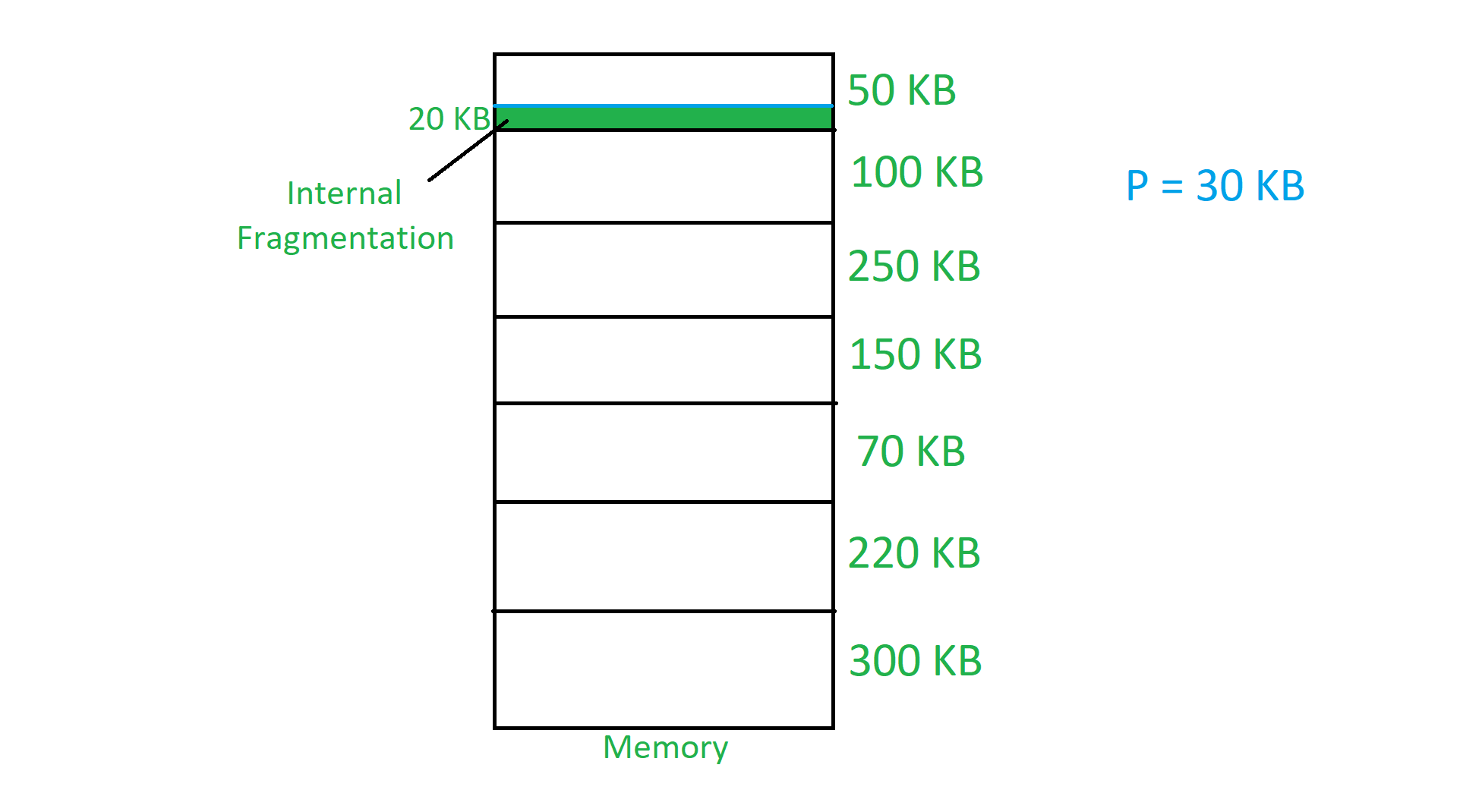
Internal Fragmentation is found in fixed partition scheme. To overcome the problem of internal fragmentation, instead of fixed partition scheme, variable partition scheme is used.
Disadvantages Fix partition scheme
- Maximum process size <= Maximum partition size.
- The degree of multiprogramming is directly proportional to the number of partitions.
- Internal fragmentation which is discussed above is present.
- If a process of 19kb wants to allocate and we have free space which is not continuous we are not able to allocate the space.
2. Variable Partition Scheme
In the variable partition scheme, initially memory will be single continuous free block. Whenever the request by the process arrives, accordingly partition will be made in the memory. If the smaller processes keep on coming then the larger partitions will be made into smaller partitions.
- In variable partition schema initially, the memory will be full contiguous free block
- Memory divided into partitions according to the process size where process size will vary.
- One partition is allocated to each active partition.
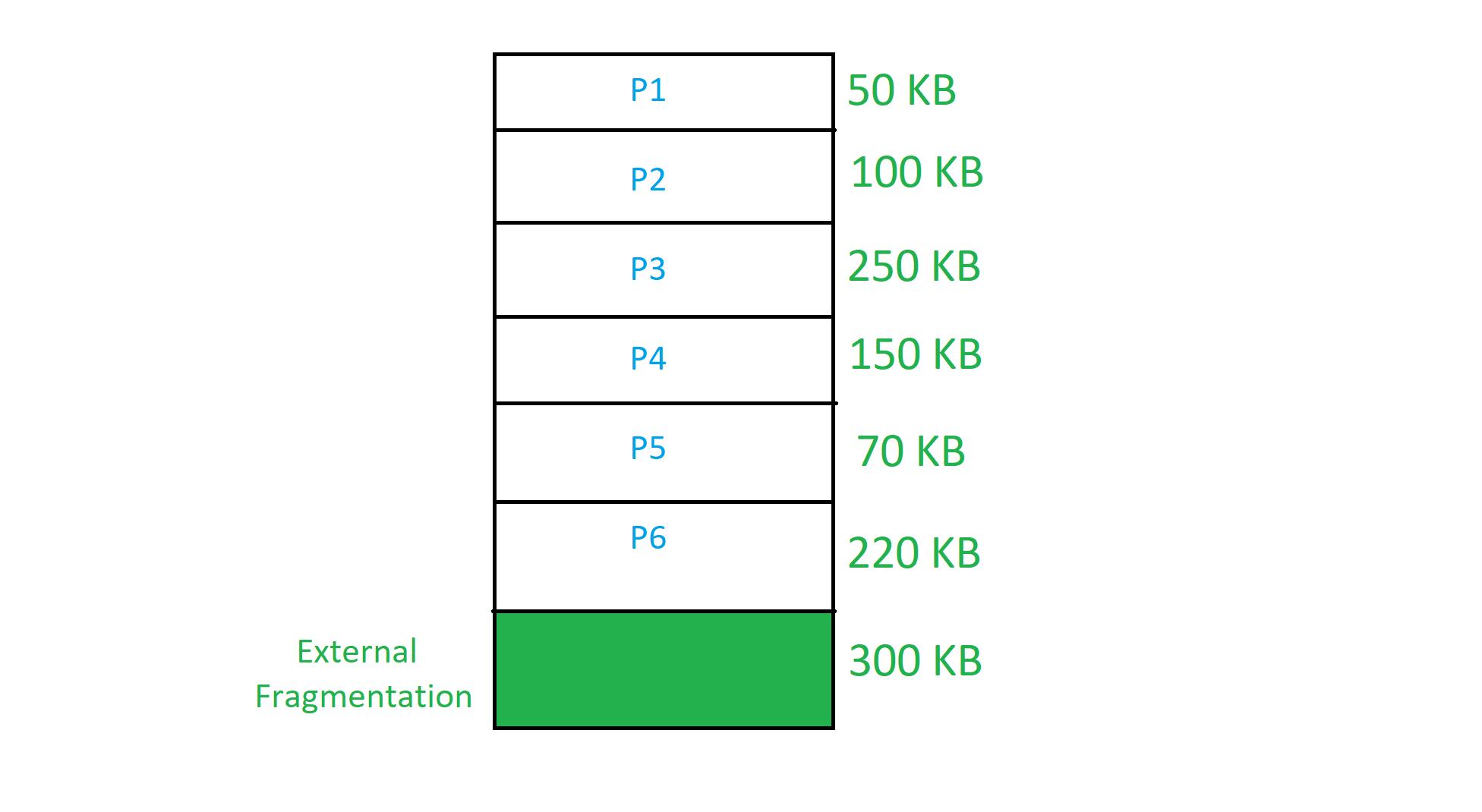 External Fragmentation is found in variable partition scheme. To overcome the problem of external fragmentation, compaction technique is used or non-contiguous memory management techniques are used.
External Fragmentation is found in variable partition scheme. To overcome the problem of external fragmentation, compaction technique is used or non-contiguous memory management techniques are used.
Solution of External Fragmentation
1. Compaction
Moving all the processes toward the top or towards the bottom to make free available memory in a single continuous place is called compaction. Compaction is undesirable to implement because it interrupts all the running processes in the memory.
Disadvantage of Compaction
- Page fault can occur.
- It consumes CPU time (overhead).
2. Non-contiguous memory allocation
- Physical address space: Main memory (physical memory) is divided into blocks of the same size called frames. frame size is defined by the operating system by comparing it with the size of the process.
- Logical Address space: Logical memory is divided into blocks of the same size called process pages. page size is defined by hardware system and these pages are stored in the main memory during the process in non-contiguous frames.
Advantages of Variable Partition Scheme
- Portion size = process size
- There is no internal fragmentation (which is the drawback of fixed partition schema).
- Degree of multiprogramming varies and is directly proportional to a number of processes.
Disadvantage Variable Partition Scheme
- External fragmentation is still there.
Advantages of Contiguous Memory Management
- It’s simple to monitor how many memory blocks are still available for use, which determines how many more processes can be allocated RAM.
- Considering that the complete file can be read from the disc in a single session, contiguous memory allocation offers good read performance.
- Contiguous allocation is simple to set up and functions well.
Disadvantages of Contiguous Memory Management
- Fragmentation is not a problem. Since new files can be written to the disk after older ones.
- To select the appropriate hole size while creating a new file, it needs know its final size.
- The extra space in the holes would need to be reduced or used once the disk is full.
FAQs on Contiguous Memory Management Techniques
Q.1: What are the memory management techniques?
Answer:
Four main memory management techniques of computers are paging, swapping, segmentation, and compaction
Q.2: What are the advantages of contiguous memory?
Answer:
- Contiguous memory requires less overhead.
- It is easy to implement.
- Contiguous memory allocation is an efficient technique.
Q.3: Is malloc memory contiguous?
Answer:
Yes, A contiguous blocks of main memory is allocates by malloc and deallocates it when no longer used.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...