How to Browse in Google Chrome Browser ?
Last Updated :
16 Oct, 2023
Google Chrome is one of the most popular web browsers globally, known for its speed, security, and user-friendly interface. It’s available on various platforms, including Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS. This guide will walk you through the types, features, benefits, and how to effectively use Google Chrome for a seamless browsing experience.
Types of Chrome Browser:
Google Chrome offers a consistent browsing experience across all platforms. However, there are variations tailored for specific devices, such as:
- Chrome for Desktop (Windows and macOS)
- Chrome for Android
- Chrome for iOS (iPhone and iPad)
Features of Chrome Browser:
- Speed: Chrome is renowned for its fast page loading and navigation.
- Security: It includes built-in features like Safe Browsing and automatic updates.
- Sync: You can sync your bookmarks, history, and settings across devices.
- Extensions: A vast library of extensions adds functionality and customization.
- Incognito Mode: Private browsing without saving your history.
- Tab Management: Organize and group tabs, and use tab previews.
- Omnibox: A combined search and address bar for quick access.
- Built-in PDF Viewer: Open and view PDFs without additional plugins.
- Voice Search: Search using your voice.
- Customization: Personalize your browser with themes and backgrounds.
- Developer Tools: Access a suite of developer-oriented features.
Benefits of Chrome Browser:
- Speedy Performance: Chrome’s rendering engine, Blink, ensures faster loading of web pages.
- Security: Frequent updates and built-in protection against malware.
- Cross-Platform Sync: Access your browsing data across multiple devices.
- Extensions: Enhance functionality and productivity.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy navigation and minimalistic design.
- Compatibility: Supports a wide range of web standards.
- Versatility: Use Chrome for browsing, as a development tool, or for research.
Uses of Chrome Browser:
- Daily Browsing: Use Chrome for everyday web surfing.
- Work and Productivity: Utilize extensions and bookmark sync for productivity.
- Web Development: Leverage developer tools for web debugging.
- Private Browsing: Choose incognito mode for anonymous browsing.
- Research: Organize your research using bookmarks and tab groups.
- Multimedia: Enjoy seamless streaming and playback of multimedia content.
Using Chrome Browser:
Download and Install
Step 1: Visit the Google Chrome website (www.google.com/chrome).
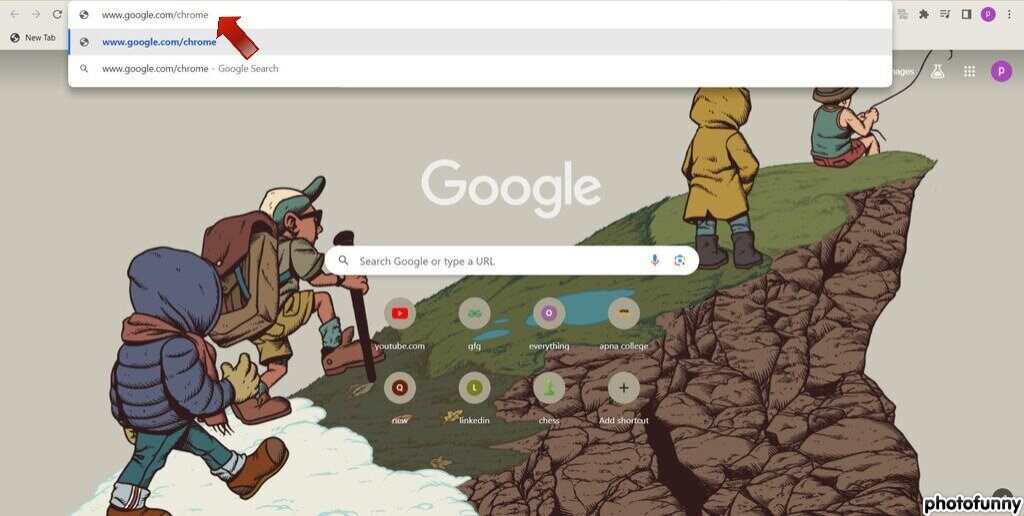
Step 2: Click “Download Chrome.”
.jpg)
Follow the on-screen instructions to install Chrome on your device.
Step 3: Launch Chrome
After installation, open Chrome by clicking its icon on your desktop or in your app drawer.
.jpg)
Navigation in Chrome Browser
Step 1:Learn to use the address bar (Omnibox) for searches and website URLs.
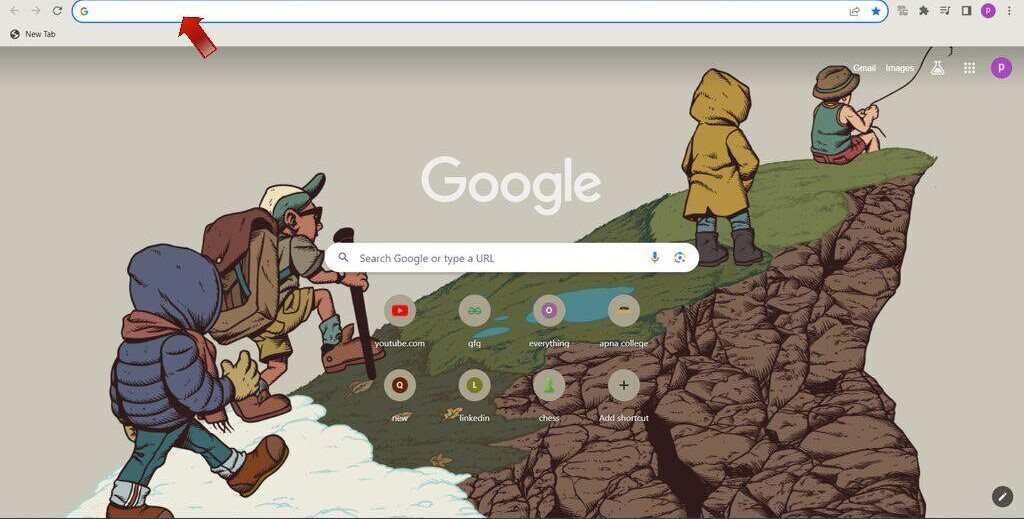
Step 2: Explore the menu, settings, and bookmarks.
.jpg)
Tabs and Tab Management in Chrome Browser
Step 1: Open a new tab by clicking the “+” icon or pressing Ctrl/Cmd + T.
.jpg)
Step 2: Close a tab with the “X” or use Ctrl/Cmd + W.
.jpg)
Step 3:Right-click on a tab to manage it, including pinning ,grouping or to mute .
.jpg)
Adding Extensions in Chrome Browser
Step 1: Visit the Chrome Web Store (chrome.google.com/webstore).
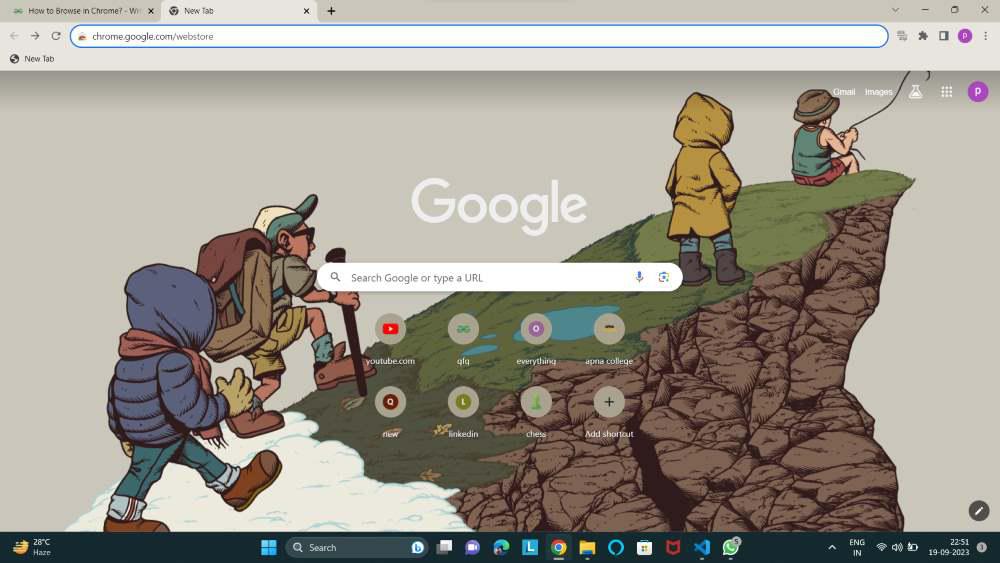
Step 2: Search and install extensions to enhance functionality.
Read Aloud: You can use extensions like “Read Aloud” to have Chrome read web content aloud. Install the extension from the Chrome Web Store, select text, and click the extension icon.
.jpg)
Customization – Sync Across Devices in Chrome
Sign in to Chrome with your Google account to sync data.
.jpg)
Developer Tools of Chrome Browser
Opening Developer Tools:
Right-click on a web page element.
Select “Inspect” to open the “Elements” panel.

Developer Tools Panels:
- Console: View and debug JavaScript errors
Use console.log() for debugging.
Run JavaScript commands in the Console.
- Elements: Inspect and modify HTML/CSS.
- Sources: Debug JavaScript code, set breakpoints, and more.
- Network: Monitor network requests and responses.
- Performance: Analyze web page performance.
- Application: Inspect storage, cookies, and service workers.
- Lighthouse: Audit web page for performance, SEO, and accessibility.
Keyboard Shortcuts of Chrome for Windows/Linux:
- Open Developer Tools: Ctrl+Shift+I or F12.
- Toggle Console: Ctrl+Shift+J.
- Toggle DevTools Panel: Ctrl+1 to Ctrl+8.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...