Height of a generic tree from parent array
Last Updated :
22 Dec, 2022
We are given a tree of size n as array parent[0..n-1] where every index i in the parent[] represents a node and the value at i represents the immediate parent of that node. For root node value will be -1. Find the height of the generic tree given the parent links.
Examples:
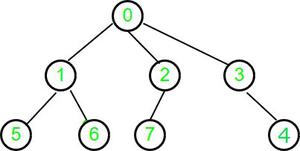
Input : parent[] = {-1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 1, 2}
Output : 2
Input : parent[] = {-1, 0, 1, 2, 3}
Output : 4
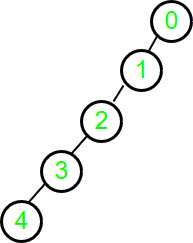
Here, a generic tree is sometimes also called an N-ary tree or N-way tree where N denotes the maximum number of child a node can have. In this problem, the array represents n number of nodes in the tree.
Approach 1: One solution is to traverse up the tree from the node till the root node is reached with node value -1. While Traversing for each node stores maximum path length.
The Time Complexity of this solution is O(n^2).
Approach 2: Build graph for N-ary Tree in O(n) time and apply BFS on the stored graph in O(n) time and while doing BFS store maximum reached level. This solution does two iterations to find the height of N-ary tree.
Implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAX 1001
using namespace std;
vector<int> adj[MAX];
int build_tree(int arr[], int n)
{
int root_index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] == -1)
root_index = i;
else {
adj[i].push_back(arr[i]);
adj[arr[i]].push_back(i);
}
}
return root_index;
}
int BFS(int start)
{
map<int, int> vis;
queue<pair<int, int> > q;
int max_level_reached = 0;
q.push({ start, 0 });
pair<int, int> p;
while (!q.empty()) {
p = q.front();
vis[p.first] = 1;
max_level_reached = max(max_level_reached,
p.second);
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < adj[p.first].size(); i++)
if (!vis[adj[p.first][i]])
q.push({ adj[p.first][i], p.second + 1 });
}
return max_level_reached;
}
int main()
{
int parent[] = { -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 };
int n = sizeof(parent) / sizeof(parent[0]);
int root_index = build_tree(parent, n);
int ma = BFS(root_index);
cout << "Height of N-ary Tree=" << ma;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 1001;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj =
new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
static int build_tree(int arr[], int n)
{
int root_index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == -1)
root_index = i;
else
{
adj.get(i).add(arr[i]);
adj.get(arr[i]).add(i);
}
}
return root_index;
}
static int BFS(int start)
{
Map<Integer, Integer> vis = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> q = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
int max_level_reached = 0;
q.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(start, 0 )));
ArrayList<Integer> p = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while(q.size() != 0)
{
p = q.get(0);
vis.put(p.get(0),1);
max_level_reached = Math.max(max_level_reached,p.get(1));
q.remove(0);
for(int i = 0; i < adj.get(p.get(0)).size(); i++)
{
if(!vis.containsKey(adj.get(p.get(0)).get(i)))
{
q.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(adj.get(p.get(0)).get(i), p.get(1)+1)));
}
}
}
return max_level_reached;
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
adj.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
int parent[] = { -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 };
int n = parent.length;
int root_index = build_tree(parent, n);
int ma = BFS(root_index);
System.out.println( "Height of N-ary Tree=" + ma);
}
}
|
Python3
from collections import deque
MAX = 1001
adj = [[] for i in range(MAX)]
def build_tree(arr, n):
root_index = 0
for i in range(n):
if (arr[i] == -1):
root_index = i
else:
adj[i].append(arr[i])
adj[arr[i]].append(i)
return root_index
def BFS(start):
vis = {}
q = deque()
max_level_reached = 0
q.append([start, 0])
p = []
while (len(q) > 0):
p = q.popleft()
vis[p[0]] = 1
max_level_reached = max(max_level_reached,
p[1])
for i in range(len(adj[p[0]])):
if (adj[p[0]][i] not in vis ):
q.append([adj[p[0]][i],
p[1] + 1])
return max_level_reached
if __name__ == '__main__':
parent = [-1, 0, 1, 2, 3]
n = len(parent)
root_index = build_tree(parent, n)
ma = BFS(root_index)
print("Height of N-ary Tree=",
ma)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
static int MAX = 1001;
static List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>();
static int build_tree(int[] arr, int n)
{
int root_index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == -1)
root_index = i;
else
{
adj[i].Add(arr[i]);
adj[arr[i]].Add(i);
}
}
return root_index;
}
static int BFS(int start)
{
Dictionary<int, int> vis = new Dictionary<int, int>();
List<List<int>> q= new List<List<int>>();
int max_level_reached = 0;
q.Add(new List<int>(){start, 0});
List<int> p = new List<int>();
while(q.Count != 0)
{
p = q[0];
vis.Add(p[0], 1);
max_level_reached = Math.Max(max_level_reached, p[1]);
q.RemoveAt(0);
for(int i = 0; i < adj[p[0]].Count; i++)
{
if(!vis.ContainsKey(adj[p[0]][i]))
{
q.Add(new List<int>(){adj[p[0]][i], p[1] + 1 });
}
}
}
return max_level_reached;
}
static public void Main ()
{
for(int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
adj.Add(new List<int>());
}
int[] parent = { -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 };
int n = parent.Length;
int root_index = build_tree(parent, n);
int ma = BFS(root_index);
Console.Write("Height of N-ary Tree=" + ma);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let MAX = 1001;
let adj = [];
function build_tree(arr,n)
{
let root_index = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == -1)
root_index = i;
else
{
adj[i].push(arr[i]);
adj[arr[i]].push(i);
}
}
return root_index;
}
function BFS(start)
{
let vis = new Map();
let q = [];
let max_level_reached = 0;
q.push([start, 0 ]);
let p = [];
while(q.length != 0)
{
p = q[0];
vis.set(p[0],1);
max_level_reached =
Math.max(max_level_reached,p[1]);
q.shift();
for(let i = 0; i < adj[p[0]].length; i++)
{
if(!vis.has(adj[p[0]][i]))
{
q.push([adj[p[0]][i], p[1]+1]);
}
}
}
return max_level_reached;
}
for(let i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
adj.push([]);
}
let parent = [ -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 ];
let n = parent.length;
let root_index = build_tree(parent, n);
let ma = BFS(root_index);
document.write( "Height of N-ary Tree=" + ma);
</script>
|
Output:
Height of N-ary Tree=4
Time Complexity: O(n) which converges to O(n) for very large n.
Auxiliary Space: O(n), we are using an adjacency list to store the tree in memory. The size of the adjacency list is proportional to the number of nodes in the tree, so the space complexity of the algorithm is O(n).
Approach 3:
We can find the height of the N-ary Tree in only one iteration. We visit nodes from 0 to n-1 iteratively and mark the unvisited ancestors recursively if they are not visited before till we reach a node which is visited, or we reach the root node. If we reach the visited node while traversing up the tree using parent links, then we use its height and will not go further in recursion.
Explanation For Example 1:

- For node 0: Check for Root node is true,
Return 0 as height, Mark node 0 as visited
- For node 1: Recur for an immediate ancestor, i.e 0, which is already visited
So, Use its height and return height(node 0) +1
Mark node 1 as visited
- For node 2: Recur for an immediate ancestor, i.e 0, which is already visited
So, Use its height and return height(node 0) +1
Mark node 2 as visited
- For node 3: Recur for an immediate ancestor, i.e 0, which is already visited
So, Use its height and return height(node 0) +1
Mark node 3 as visited
- For node 4: Recur for an immediate ancestor, i.e 3, which is already visited
So, Use its height and return height(node 3) +1
Mark node 3 as visited
- For node 5: Recur for an immediate ancestor, i.e 1, which is already visited
So, Use its height and return height(node 1) +1
Mark node 5 as visited
- For node 6: Recur for an immediate ancestor, i.e 1, which is already visited
So, Use its height and return height(node 1) +1
Mark node 6 as visited
- For node 7: Recur for an immediate ancestor, i.e 2, which is already visited
So, Use its height and return height(node 2) +1
- Mark node 7 as visited
Hence, we processed each node in the N-ary tree only once.
Implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fillHeight(int p[], int node, int visited[],
int height[])
{
if (p[node] == -1) {
visited[node] = 1;
return 0;
}
if (visited[node])
return height[node];
visited[node] = 1;
height[node] = 1 + fillHeight(p, p[node],
visited, height);
return height[node];
}
int findHeight(int parent[], int n)
{
int ma = 0;
int visited[n];
int height[n];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
memset(height, 0, sizeof(height));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!visited[i])
height[i] = fillHeight(parent, i,
visited, height);
ma = max(ma, height[i]);
}
return ma;
}
int main()
{
int parent[] = { -1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 1, 2 };
int n = sizeof(parent) / sizeof(parent[0]);
cout << "Height of N-ary Tree = "
<< findHeight(parent, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int fillHeight(int p[], int node,
int visited[], int height[])
{
if (p[node] == -1)
{
visited[node] = 1;
return 0;
}
if (visited[node] == 1)
return height[node];
visited[node] = 1;
height[node] = 1 + fillHeight(p, p[node],
visited, height);
return height[node];
}
static int findHeight(int parent[], int n)
{
int ma = 0;
int []visited = new int[n];
int []height = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
visited[i] = 0;
height[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (visited[i] != 1)
height[i] = fillHeight(parent, i,
visited, height);
ma = Math.max(ma, height[i]);
}
return ma;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int parent[] = { -1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 1, 2 };
int n = parent.length;
System.out.println("Height of N-ary Tree = " +
findHeight(parent, n));
}
}
|
Python3
def fillHeight(p, node, visited, height):
if (p[node] == -1):
visited[node] = 1
return 0
if (visited[node]):
return height[node]
visited[node] = 1
height[node] = 1 + fillHeight(p, p[node],
visited, height)
return height[node]
def findHeight(parent, n):
ma = 0
visited = [0] * n
height = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
if (not visited[i]):
height[i] = fillHeight(parent, i,
visited, height)
ma = max(ma, height[i])
return ma
if __name__ == '__main__':
parent = [-1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 1, 2]
n = len(parent)
print("Height of N-ary Tree =",
findHeight(parent, n))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int fillHeight(int []p, int node,
int []visited,
int []height)
{
if (p[node] == -1)
{
visited[node] = 1;
return 0;
}
if (visited[node] == 1)
return height[node];
visited[node] = 1;
height[node] = 1 + fillHeight(p, p[node],
visited, height);
return height[node];
}
static int findHeight(int []parent, int n)
{
int ma = 0;
int []visited = new int[n];
int []height = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
visited[i] = 0;
height[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (visited[i] != 1)
height[i] = fillHeight(parent, i,
visited, height);
ma = Math.Max(ma, height[i]);
}
return ma;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []parent = { -1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 1, 2 };
int n = parent.Length;
Console.WriteLine("Height of N-ary Tree = " +
findHeight(parent, n));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function fillHeight(p, node, visited, height)
{
if (p[node] == -1)
{
visited[node] = 1;
return 0;
}
if (visited[node] == 1)
return height[node];
visited[node] = 1;
height[node] = 1 + fillHeight(p, p[node],
visited, height);
return height[node];
}
function findHeight(parent,n)
{
let ma = 0;
let visited = new Array(n);
let height = new Array(n);
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
visited[i] = 0;
height[i] = 0;
}
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (visited[i] != 1)
height[i] = fillHeight(parent, i,
visited, height);
ma = Math.max(ma, height[i]);
}
return ma;
}
let parent = [ -1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 1, 2 ];
let n = parent.length;
document.write("Height of N-ary Tree = " +
findHeight(parent, n));
</script>
|
Output:
Height of N-ary Tree = 2
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(n), this is because we need to store the visited and height arrays which are of size n.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...