Find Length of a Linked List (Iterative and Recursive)
Last Updated :
17 Aug, 2023
Write a function to count the number of nodes in a given singly linked list
Examples:
Input:
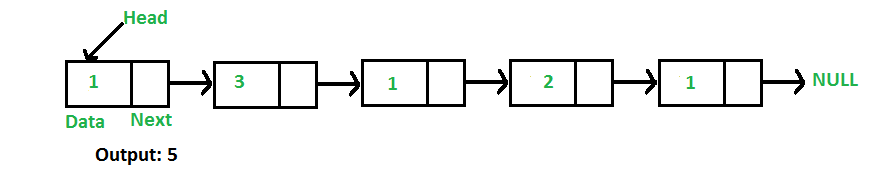
Input: 2->4->1->9->5->3->6
Output: 7
An iterative approach for finding the length of the linked list:
Follow the given steps to solve the problem:
- Initialize count as 0
- Initialize a node pointer, current = head.
- Do following while current is not NULL
- current = current -> next
- Increment count by 1.
- Return count
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int getCount(Node* head)
{
int count = 0;
Node* current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
count++;
current = current->next;
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
cout << "count of nodes is " << getCount(head);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int getCount(struct Node* head)
{
int count = 0;
struct Node* current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
count++;
current = current->next;
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
printf("count of nodes is %d", getCount(head));
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public int getCount()
{
Node temp = head;
int count = 0;
while (temp != null) {
count++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(1);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(1);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
System.out.println("Count of nodes is "
+ llist.getCount());
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def getCount(self):
temp = self.head
count = 0
while (temp):
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return count
if __name__ == '__main__':
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(1)
llist.push(3)
llist.push(1)
llist.push(2)
llist.push(1)
print("Count of nodes is :", llist.getCount())
|
C#
using System;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public int getCount()
{
Node temp = head;
int count = 0;
while (temp != null) {
count++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return count;
}
public static void Main()
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(1);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(1);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
Console.WriteLine("Count of nodes is "
+ llist.getCount());
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
var head;
function push(new_data) {
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
function getCount() {
var temp = head;
var count = 0;
while (temp != null) {
count++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return count;
}
push(1);
push(3);
push(1);
push(2);
push(1);
document.write("Count of nodes is " + getCount());
</script>
|
Output
count of nodes is 5
Time complexity: O(N), Where N is the size of the linked list
Auxiliary Space: O(1), As constant extra space is used.
A recursive approach for finding the length of the linked list:
Follow the given steps to solve the problem:
- If the head is NULL, return 0.
- Otherwise, return 1 + getCount(head->next)
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int getCount(Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL) {
return 0;
}
else {
return 1 + getCount(head->next);
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
cout << "Count of nodes is " << getCount(head);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public int getCountRec(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
return 1 + getCountRec(node.next);
}
public int getCount() { return getCountRec(head); }
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(1);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(1);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
System.out.println("Count of nodes is "
+ llist.getCount());
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def getCountRec(self, node):
if (not node):
return 0
else:
return 1 + self.getCountRec(node.next)
def getCount(self):
return self.getCountRec(self.head)
if __name__ == '__main__':
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(1)
llist.push(3)
llist.push(1)
llist.push(2)
llist.push(1)
print('Count of nodes is :', llist.getCount())
|
C#
using System;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public int getCountRec(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
return 1 + getCountRec(node.next);
}
public int getCount() { return getCountRec(head); }
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(1);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(1);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
Console.WriteLine("Count of nodes is "
+ llist.getCount());
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
var head;
function push( new_data) {
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
function getCountRec(node) {
if (node == null)
return 0;
return 1 + getCountRec(node.next);
}
function getCount() {
return getCountRec(head);
}
push(1);
push(3);
push(1);
push(2);
push(1);
document.write("Count of nodes is " + getCount());
</script>
|
Output
Count of nodes is 5
Time Complexity: O(N), As we are traversing the linked list only once.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), Extra space is used in the recursion call stack.
Recursive approach for finding the length of the linked list using constant space:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
The above recursive approach can be modified to make it a tail recursive function and thus our auxiliary space will become O(1)
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int getCount(Node* head, int count = 0)
{
if (head == NULL)
return count;
return getCount(head->next, count + 1);
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
cout << "Count of nodes is " << getCount(head);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public int getCountRec(Node node, int count)
{
if (node == null)
return count;
return getCountRec(node.next, 1 + count);
}
public int getCount() { return getCountRec(head, 0); }
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(1);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(1);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
System.out.println("Count of nodes is "
+ llist.getCount());
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def getCountRec(self, node, count=0):
if (not node):
return count
else:
return self.getCountRec(node.next, count+1)
def getCount(self):
return self.getCountRec(self.head)
if __name__ == '__main__':
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(1)
llist.push(3)
llist.push(1)
llist.push(2)
llist.push(1)
print('Count of nodes is :', llist.getCount())
|
C#
using System;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public int getCountRec(Node node, int count)
{
if (node == null)
return count;
return getCountRec(node.next, 1 + count);
}
public int getCount() { return getCountRec(head, 0); }
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(1);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(1);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
Console.WriteLine("Count of nodes is "
+ llist.getCount());
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
var head;
function push( new_data) {
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
function getCountRec(node,var count) {
if (node == null)
return count;
return getCountRec(node.next,count+1);
}
function getCount() {
return getCountRec(head,0);
}
push(1);
push(3);
push(1);
push(2);
push(1);
document.write("Count of nodes is " + getCount());
</script>
|
Output
Count of nodes is 5
Time Complexity: O(N), As we are traversing the list only once.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), In worst case the depth of recursion call stack will be N.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...