Enumeration (or enum) in C
Last Updated :
24 May, 2022
Enumeration (or enum) is a user defined data type in C. It is mainly used to assign names to integral constants, the names make a program easy to read and maintain.
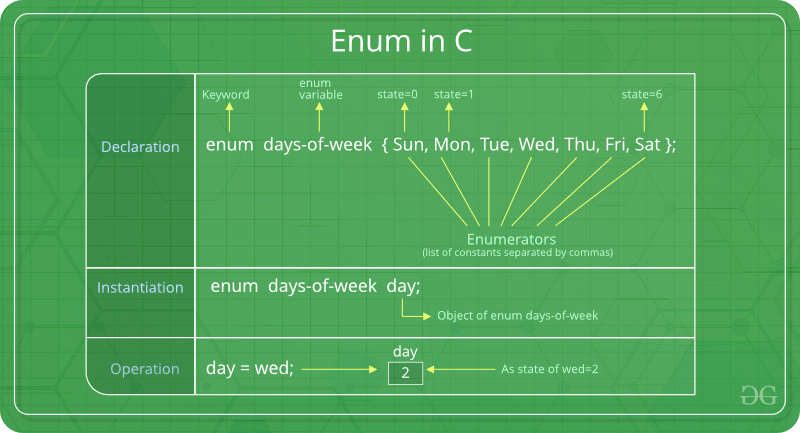
Hereby mistake, the state of wed is 2, it should be 3. Please refer to the same example below for a better understanding.
enum State {Working = 1, Failed = 0};
The keyword ‘enum’ is used to declare new enumeration types in C and C++. Following is an example of enum declaration.
// The name of enumeration is "flag" and the constant
// are the values of the flag. By default, the values
// of the constants are as follows:
// constant1 = 0, constant2 = 1, constant3 = 2 and
// so on.
enum flag{constant1, constant2, constant3, ....... };
Variables of type enum can also be defined. They can be defined in two ways:
// In both of the below cases, "day" is
// defined as the variable of type week.
enum week{Mon, Tue, Wed};
enum week day;
// Or
enum week{Mon, Tue, Wed}day;
C
#include<stdio.h>
enum week{Mon, Tue, Wed, Thur, Fri, Sat, Sun};
int main()
{
enum week day;
day = Wed;
printf("%d",day);
return 0;
}
|
Output:
2
In the above example, we declared “day” as the variable and the value of “Wed” is allocated to day, which is 2. So as a result, 2 is printed.
Another example of enumeration is:
C
#include<stdio.h>
enum year{Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul,
Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec};
int main()
{
int i;
for (i=Jan; i<=Dec; i++)
printf("%d ", i);
return 0;
}
|
Output:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
In this example, the for loop will run from i = 0 to i = 11, as initially the value of i is Jan which is 0 and the value of Dec is 11.
Interesting facts about initialization of enum.
1. Two enum names can have same value. For example, in the following C program both ‘Failed’ and ‘Freezed’ have same value 0.
C
#include <stdio.h>
enum State {Working = 1, Failed = 0, Freezed = 0};
int main()
{
printf("%d, %d, %d", Working, Failed, Freezed);
return 0;
}
|
Output:
1, 0, 0
2. If we do not explicitly assign values to enum names, the compiler by default assigns values starting from 0. For example, in the following C program, sunday gets value 0, monday gets 1, and so on.
C
#include <stdio.h>
enum day {sunday, monday, tuesday, wednesday, thursday, friday, saturday};
int main()
{
enum day d = thursday;
printf("The day number stored in d is %d", d);
return 0;
}
|
Output:
The day number stored in d is 4
3. We can assign values to some name in any order. All unassigned names get value as value of previous name plus one.
C
#include <stdio.h>
enum day {sunday = 1, monday, tuesday = 5,
wednesday, thursday = 10, friday, saturday};
int main()
{
printf("%d %d %d %d %d %d %d", sunday, monday, tuesday,
wednesday, thursday, friday, saturday);
return 0;
}
|
Output:
1 2 5 6 10 11 12
4. The value assigned to enum names must be some integral constant, i.e., the value must be in range from minimum possible integer value to maximum possible integer value.
5. All enum constants must be unique in their scope. For example, the following program fails in compilation.
C
enum state {working, failed};
enum result {failed, passed};
int main() { return 0; }
|
Output:
Compile Error: 'failed' has a previous declaration as 'state failed'
Exercise:
Predict the output of following C programs
Program 1:
C
#include <stdio.h>
enum day {sunday = 1, tuesday, wednesday, thursday, friday, saturday};
int main()
{
enum day d = thursday;
printf("The day number stored in d is %d", d);
return 0;
}
|
Program 2:
C
#include <stdio.h>
enum State {WORKING = 0, FAILED, FREEZED};
enum State currState = 2;
enum State FindState() {
return currState;
}
int main() {
(FindState() == WORKING)? printf("WORKING"): printf("NOT WORKING");
return 0;
}
|
Enum vs Macro
We can also use macros to define names constants. For example we can define ‘Working’ and ‘Failed’ using following macro.
C
#define Working 0
#define Failed 1
#define Freezed 2
|
There are multiple advantages of using enum over macro when many related named constants have integral values.
a) Enums follow scope rules.
b) Enum variables are automatically assigned values. Following is simpler
CPP
enum state {Working, Failed, Freezed};
|
Introduction part of this article is contributed by Piyush Vashistha.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...