Difference between Single Bus Structure and Double Bus Structure
Last Updated :
21 Jul, 2022
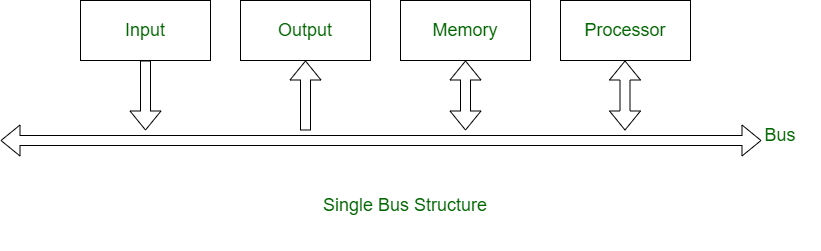
1. Single Bus Structure: In a single bus structure, one common bus is used to communicate between peripherals and microprocessors. It has disadvantages due to the use of one common bus.
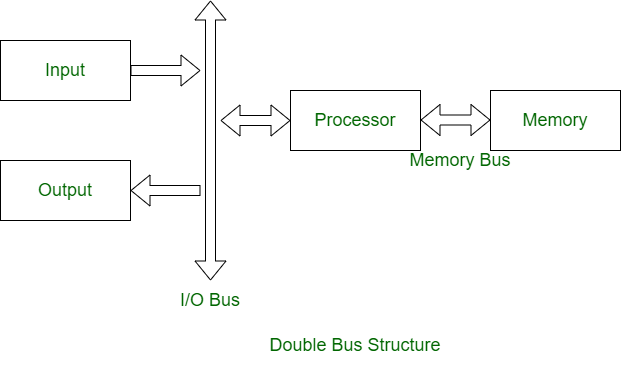
2. Double Bus Structure: In a double bus structure, one bus is used to fetch instructions while other is used to fetch data, required for execution. It is to overcome the bottleneck of a single bus structure.
Differences between Single Bus and Double Bus Structure :
| S. No. |
Single Bus Structure |
Double Bus Structure |
| 1. |
The same bus is shared by three units (Memory, Processor, and I/O units). |
The two independent buses link various units together. |
| 2. |
One common bus is used for communication between peripherals and processors. |
Two buses are used, one for communication from peripherals and the other for the processor. |
| 3. |
The same memory address space is utilized by I/O units. |
Here, the I/O bus is used to connect I/O units and processor and other one, memory bus is used to connect memory and processor. |
| 4. |
Instructions and data both are transferred in same bus. |
Instructions and data both are transferred in different buses. |
| 5. |
Its performance is low. |
Its performance is high. |
| 6. |
The cost of a single bus structure is low. |
The cost of a double bus structure is high. |
| 7. |
Number of cycles for execution is more. |
Number of cycles for execution is less. |
| 8. |
Execution of the process is slow. |
Execution of the process is fast. |
| 9. |
Number of registers associated are less. |
Number of registers associated are more. |
| 10. |
At a time single operand can be read from the bus. |
At a time two operands can be read. |
| 11. |
Advantages-
- Less expensive
- Simplicity
|
Advantages-
- Better performance
- Improves Efficiency
|
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...