Detect and Remove Loop in a Linked List
Last Updated :
02 Apr, 2024
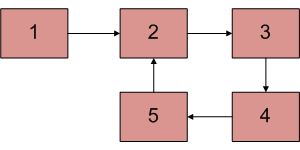
Write a function detectAndRemoveLoop() that checks whether a given Linked List contains a loop and if the loop is present then remove the loop and return true. If the list doesn’t contain a loop then it returns false. The below diagram shows a linked list with a loop. detectAndRemoveLoop() must change the below list to 1->2->3->4->5->NULL.
We also recommend reading the following post as a prerequisite to the solution discussed here.
Write a C function to detect a loop in a linked list
Before trying to remove the loop, we must detect it. Techniques discussed in the above post can be used to detect loops. To remove the loop, all we need to do is to get a pointer to the last node of the loop. For example, a node with value 5 in the above diagram. Once we have a pointer to the last node, we can make the next of this node NULL and the loop is gone.
We can easily use Hashing or Visited node techniques (discussed in the above-mentioned post) to get the pointer to the last node. The idea is simple: the very first node whose next is already visited (or hashed) is the last node.
We can also use the Floyd Cycle Detection algorithm to detect and remove the loop. In Floyd’s algo, the slow and fast pointers meet at a loop node. We can use this loop node to remove the cycle. There are following two different ways of removing the loop when Floyd’s algorithm is used for loop detection.
Method 1 (Check one by one) We know that Floyd’s Cycle detection algorithm terminates when fast and slow pointers meet at a common point. We also know that this common point is one of the loop nodes (2 or 3 or 4 or 5 in the above diagram). Store the address of this in a pointer variable say ptr2. After that start from the head of the Linked List and check for nodes one by one if they are reachable from ptr2. Whenever we find a node that is reachable, we know that this node is the starting node of the loop in the Linked List and we can get the pointer to the previous of this node.
Output:
Linked List after removing loop
50 20 15 4 10
Method 2 (Better Solution)
- This method is also dependent on Floyd’s Cycle detection algorithm.
- Detect Loop using Floyd’s Cycle detection algorithm and get the pointer to a loop node.
- Count the number of nodes in the loop. Let the count be k.
- Fix one pointer to the head and another to a kth node from the head.
- Move both pointers at the same pace, they will meet at the loop starting node.
- Get a pointer to the last node of the loop and make the next of it NULL.
Thanks to WgpShashank for suggesting this method.
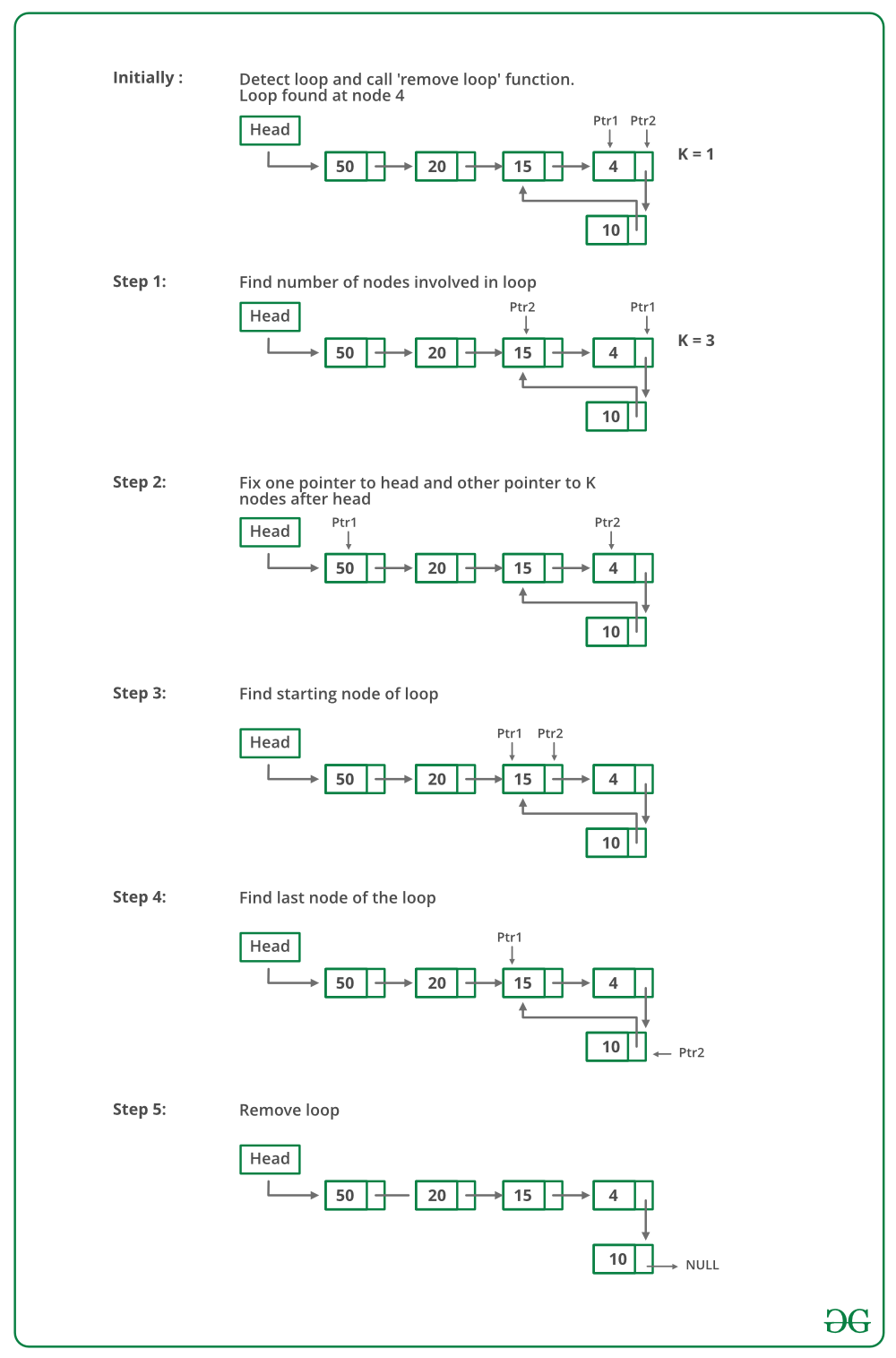
Below image is a dry run of the ‘remove loop’ function in the code :
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
/* Function to remove loop. */
void removeLoop(Node*, Node*);
/* This function detects and removes loop in the list
If loop was there in the list then it returns 1,
otherwise returns 0 */
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node* list)
{
Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
// Iterate and find if loop exists or not
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) {
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
/* If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then there
is a loop */
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
removeLoop(slow_p, list);
/* Return 1 to indicate that loop is found */
return 1;
}
}
/* Return 0 to indicate that there is no loop*/
return 0;
}
/* Function to remove loop.
loop_node --> Pointer to one of the loop nodes
head --> Pointer to the start node of the linked list */
void removeLoop(Node* loop_node, Node* head)
{
Node* ptr1 = loop_node;
Node* ptr2 = loop_node;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
unsigned int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1->next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2->next != ptr1)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2->next = NULL;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList(Node* node)
{
// Print the list after loop removal
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* head = new Node(50);
head->next = new Node(20);
head->next->next = new Node(15);
head->next->next->next = new Node(4);
head->next->next->next->next = new Node(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
cout << "Linked List after removing loop \n";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// Java program to detect and remove loop in linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
Node slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null && fast != null
&& fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same point then loop
// is present
if (slow == fast) {
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
void removeLoop(Node loop, Node head)
{
Node ptr1 = loop;
Node ptr2 = loop;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
int k = 1, i;
Node prevNode = ptr1;
while (ptr1.next != ptr2) {
// keeping track beforeing moving next
prevNode = ptr1;
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
k++;
}
prevNode.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
System.out.println(
"Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
// A C# program to detect and remove loop in linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
Node slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same
// point then loop is present
if (slow == fast) {
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
void removeLoop(Node loop, Node head)
{
Node ptr1 = loop;
Node ptr2 = loop;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1.next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2.next != ptr1) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = list.head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(list.head);
Console.WriteLine("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(list.head);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
<script>
// Javascript program to detect and
// remove loop in linked list
var head;
class Node
{
constructor(x)
{
this.data = x;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
function detectAndRemoveLoop(node)
{
var slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null &&
fast != null &&
fast.next != null)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same
// point then loop is present
if (slow == fast)
{
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
function removeLoop(loop, head)
{
var ptr1 = loop;
var ptr2 = loop;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
var k = 1, i;
while (ptr1.next != ptr2)
{
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to
// k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for(i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1)
{
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2.next != ptr1)
{
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
function printList(node)
{
while (node != null)
{
document.write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
head = new Node(50);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
document.write("Linked List after removing loop : ");
printList(head);
// This code is contributed by todaysgaurav
</script>
# Python program to detect and remove loop in linked list
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def detectAndRemoveLoop(self):
slow_p = fast_p = self.head
while(slow_p and fast_p and fast_p.next):
slow_p = slow_p.next
fast_p = fast_p.next.next
# If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then
# there is a loop
if slow_p == fast_p:
self.removeLoop(slow_p)
# Return 1 to indicate that loop is found
return 1
# Return 0 to indicate that there is no loop
return 0
# Function to remove loop
# loop_node --> pointer to one of the loop nodes
# head --> Pointer to the start node of the linked list
def removeLoop(self, loop_node):
ptr1 = loop_node
ptr2 = loop_node
# Count the number of nodes in loop
k = 1
while(ptr1.next != ptr2):
ptr1 = ptr1.next
k += 1
# Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = self.head
# And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = self.head
for i in range(k):
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Move both pointers at the same place
# they will meet at loop starting node
while(ptr2 != ptr1):
ptr1 = ptr1.next
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Get pointer to the last node
while(ptr2.next != ptr1):
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Set the next node of the loop ending node
# to fix the loop
ptr2.next = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print the LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print(temp.data, end = ' ')
temp = temp.next
# Driver program
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(10)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(20)
llist.push(50)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next
llist.detectAndRemoveLoop()
print("Linked List after removing loop")
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
OutputLinked List after removing loop
50 20 15 4 10
Time Complexity: O(N), Where N is the number of nodes in the tree
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Method 3 (Optimized Method 2: Without Counting Nodes in Loop)
We do not need to count the number of nodes in Loop. After detecting the loop, if we start the slow pointer from the head and move both slow and fast pointers at the same speed until fast don’t meet, they would meet at the beginning of the loop.
How does this work?
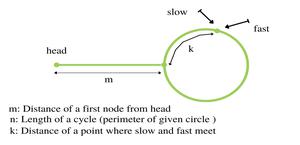
Let slow and fast meet at some point after Floyd’s Cycle finding algorithm. The below diagram shows the situation when the cycle is found.
Situation when cycle is found
We can conclude below from the above diagram
Distance traveled by fast pointer = 2 * (Distance traveled
by slow pointer)
(m + n*x + k) = 2*(m + n*y + k)
Note that before meeting the point shown above, fast
was moving at twice speed.
x --> Number of complete cyclic rounds made by
fast pointer before they meet first time
y --> Number of complete cyclic rounds made by
slow pointer before they meet first time
From the above equation, we can conclude below
m + k = (x-2y)*n
Which means m+k is a multiple of n.
Thus we can write, m + k = i*n or m = i*n - k.
Hence, distance moved by slow pointer: m, is equal to distance moved by fast pointer:
i*n - k or (i-1)*n + n - k (cover the loop completely i-1 times and start from n-k).
So if we start moving both pointers again at same speed such that one pointer (say slow) begins from head node of linked list and other pointer (say fast) begins from meeting point. When the slow pointer reaches the beginning of the loop (has made m steps), the fast pointer would have made also moved m steps as they are now moving at the same pace. Since m+k is a multiple of n and fast starts from k, they would meet at the beginning. Can they meet before also? No because slow pointer enters the cycle first time after m steps.
C++
// C++ program to detect and remove loop
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect and remove loop in a linked list that
// may contain loop
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node* head)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node without loop
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return;
Node *slow = head, *fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps ahead respectively.
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast && fast->next) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = head;
// this check is needed when slow and fast both meet
// at the head of the LL eg: 1->2->3->4->5 and then
// 5->next = 1 i.e the head of the LL
if (slow == fast)
while (fast->next != slow)
fast = fast->next;
else {
while (slow->next != fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast->next = NULL; /* remove loop */
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = new Node(50);
head->next = new Node(20);
head->next->next = new Node(15);
head->next->next->next = new Node(4);
head->next->next->next->next = new Node(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
printf("Linked List after removing loop \n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// C++ program to detect and remove loop
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ", head->key);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Function to detect and remove loop in a linked list that
// may contain loop
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node* head)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node without loop
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return;
Node *slow = head, *fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps ahead respectively.
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast && fast->next) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = head;
// this check is needed when slow and fast both meet
// at the head of the LL eg: 1->2->3->4->5 and then
// 5->next = 1 i.e the head of the LL
if (slow == fast)
while (fast->next != slow)
fast = fast->next;
else {
while (slow->next != fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast->next = NULL; /* remove loop */
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = head;
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
printf("Linked List after removing loop \n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
// Java program to detect
// and remove loop in linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (node == null || node.next == null)
return;
Node slow = node, fast = node;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = node;
if (slow != fast) {
while (slow.next != fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast.next = null; /* remove loop */
}
/* This case is added if fast and slow pointer meet at first position. */
else {
while(fast.next != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
}
fast.next = null;
}
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
// C# program to detect and remove loop in linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
public Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (node == null || node.next == null)
return;
Node slow = node, fast = node;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = node;
while (slow.next != fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast.next = null; /* remove loop */
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = list.head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(list.head);
Console.WriteLine("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(list.head);
}
}
<script>
// javascript program to detect
// and remove loop in linked list
var head;
class Node
{
constructor(x)
{
this.data = x;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
function detectAndRemoveLoop(node) {
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (node == null || node.next == null)
return;
var slow = node, fast = node;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = node;
if (slow != fast) {
while (slow.next != fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast.next = null; /* remove loop */
}
/* This case is added if fast and
slow pointer meet at first position. */
else {
while (fast.next != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
}
fast.next = null;
}
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
function printList(node) {
while (node != null) {
document.write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
head = new Node(50);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
document.write("Linked List after removing loop : ");
printList(head);
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
</script>
# Python program to detect and remove loop
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def detectAndRemoveLoop(self):
if self.head is None:
return
if self.head.next is None:
return
slow_p = self.head
fast_p = self.head
while(slow_p and fast_p and fast_p.next):
slow_p = slow_p.next
fast_p = fast_p.next.next
# If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then
# there is a loop
if slow_p == fast_p:
slow_p = self.head
# Finding the beginning of the loop
while (slow_p.next != fast_p.next):
slow_p = slow_p.next
fast_p = fast_p.next
# Sinc fast.next is the looping point
fast_p.next = None # Remove loop
# Utility function to print the LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print(temp.data, end = ' ')
temp = temp.next
# Driver program
llist = LinkedList()
llist.head = Node(50)
llist.head.next = Node(20)
llist.head.next.next = Node(15)
llist.head.next.next.next = Node(4)
llist.head.next.next.next.next = Node(10)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next
llist.detectAndRemoveLoop()
print("Linked List after removing loop")
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
OutputLinked List after removing loop
50 20 15 4 10
Time Complexity: O(N), Where N is the number of nodes in the tree
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Method 4 Hashing: Hash the address of the linked list nodes
We can hash the addresses of the linked list nodes in an unordered map and just check if the element already exists in the map. If it exists, we have reached a node that already exists by a cycle, hence we need to make the last node’s next pointer NULL.
C++
// C++ program to detect and remove loop
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
void hashAndRemove(Node* head)
{
// hash map to hash addresses of the linked list nodes
unordered_map<Node*, int> node_map;
// pointer to last node
Node* last = NULL;
while (head != NULL) {
// if node not present in the map, insert it in the map
if (node_map.find(head) == node_map.end()) {
node_map[head]++;
last = head;
head = head->next;
}
// if present, it is a cycle, make the last node's next pointer NULL
else {
last->next = NULL;
break;
}
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = new Node(50);
head->next = new Node(20);
head->next->next = new Node(15);
head->next->next->next = new Node(4);
head->next->next->next->next = new Node(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
// printList(head);
hashAndRemove(head);
printf("Linked List after removing loop \n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// Java program to detect and remove loop in a linked list
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedList {
static Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Returns true if the loop is removed from the linked
// list else returns false.
static boolean removeLoop(Node h)
{
HashSet<Node> s = new HashSet<Node>();
Node prev = null;
while (h != null) {
// If we have already has this node
// in hashmap it means there is a cycle and we
// need to remove this cycle so set the next of
// the previous pointer with null.
if (s.contains(h)) {
prev.next = null;
return true;
}
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, insert it in hash
else {
s.add(h);
prev = h;
h = h.next;
}
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.head = new Node(50);
llist.head.next = new Node(20);
llist.head.next.next = new Node(15);
llist.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
llist.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next;
if (removeLoop(llist.head)) {
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop");
llist.printList(llist.head);
}
else
System.out.println("No Loop found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Animesh Nag.
// C# program to detect and remove loop in a linked list
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class LinkedList {
public Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Returns true if the loop is removed from the linked
// list else returns false.
bool removeLoop(Node h)
{
HashSet<Node> s = new HashSet<Node>();
Node prev = null;
while (h != null) {
// If we have already has this node
// in hashmap it means there is a cycle and we
// need to remove this cycle so set the next of
// the previous pointer with null.
if (s.Contains(h)) {
prev.next = null;
return true;
}
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, insert it in hash
else {
s.Add(h);
prev = h;
h = h.next;
}
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void Main()
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = list.head.next.next;
if (list.removeLoop(list.head)) {
Console.WriteLine("Linked List after removing loop");
list.printList(list.head);
}
else
Console.WriteLine("No Loop found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by ihritik
<script>
// javascript program to detect and remove loop in a linked list class LinkedList {
/* Linked list Node */
class Node {
constructor(x) {
this.data = x;
this.next = null;
}
}
var head; // head of list
// Function to print the linked list
function printList(node) {
while (node != null) {
document.write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Returns true if the loop is removed from the linked
// list else returns false.
function removeLoop(h)
{
var s = new Set();
var prev = null;
while (h != null)
{
// If we have already has this node
// in hashmap it means there is a cycle and we
// need to remove this cycle so set the next of
// the previous pointer with null.
if (s.has(h)) {
prev.next = null;
return true;
}
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, insert it in hash
else {
s.add(h);
prev = h;
h = h.next;
}
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
head = new Node(50);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
/* Create loop for testing */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
if (removeLoop(head)) {
document.write("Linked List after removing loop<br/>");
printList(head);
} else
document.write("No Loop found");
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def print_list(self, node):
# Function to print the linked list
while node:
print(node.data, end=' ')
node = node.next
print()
@staticmethod
def remove_loop(h):
# Function to remove loop from linked list and return True if removed, False otherwise
s = set()
prev = None
while h:
# If node is already in the set, remove the loop
if h in s:
prev.next = None
return True
# Add node to the set and move forward
s.add(h)
prev = h
h = h.next
return False
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
llist = LinkedList()
llist.head = Node(50)
llist.head.next = Node(20)
llist.head.next.next = Node(15)
llist.head.next.next.next = Node(4)
llist.head.next.next.next.next = Node(10)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next
if LinkedList.remove_loop(llist.head):
print("Linked List after removing loop:")
llist.print_list(llist.head)
else:
print("No Loop found")
OutputLinked List after removing loop
50 20 15 4 10
Time Complexity: O(N), Where N is the number of nodes in the tree.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), Where N is the number of nodes in the tree (due to hashing).
Please write comments if you find the above codes/algorithms incorrect, or find other ways to solve the same problem
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...