Class 12 RD Sharma Solutions – Chapter 6 Determinants Exercise Ex. 6.6 | Set 3
Last Updated :
21 Jul, 2021
Question 38. Write the value of the determinant 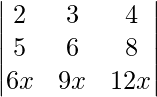 .
.
Solution:
We have,
A = 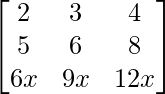
|A| = 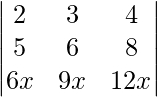
On taking 2x common from R3 we get,
|A| = 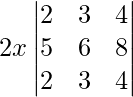
As R1 and R3 are identical we get
|A| = 0
Therefore, the value of the determinant is 0.
Question 39. If |A| = 2, where A is 2 × 2 matrix, find |adj A|.
Solution:
Given that |A| = 2 and the order of A matrix is 2 x 2
As we know that |adj A| = |A|n-1
Here the value of n is 2
So,
|adj A| = |2|2-1
= 2
Therefore, the value of the |adj A| is 2.
Question 40. What is the value of the determinant 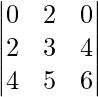 ?
?
Solution:
We have,
A = 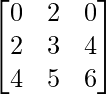
|A| = 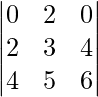
= 0(18 – 20) – 2(12 – 16) + 0(10 – 12)
= 0 + 8 + 0
= 8
Therefore, the value of the determinant is 8.
Question 41. For what value of x is the matrix 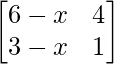 singular?
singular?
Solution:
As we know, a matrix is singular matrix, when the value of its determinant is 0.
Given that,
A = 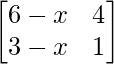
So,
|A| = 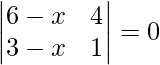
=> 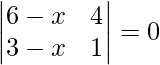
=> (6 – x) – 4(3 – x) = 0
=> 6 – x – 12 + 4x = 0
=> 3x – 6 = 0
=> 3x = 6
=> x = 6/3
=> x = 2
Therefore, the value of x is 2.
Question 42. A matrix A of order 3 × 3 is such that |A| = 4. Find the value of |2 A|.
Solution:
We have,
A matrix A is of order 3 × 3 so the value of n is 3.
And |A| = 4.
As we know,
=> |K A| = Kn |A|
So,
|2 A| = 23 (4)
= 8 (4)
= 32
Therefore, the value of |2 A| is 32.
Question 43. Evaluate: 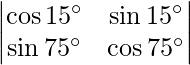 .
.
Solution:
We have,
A = 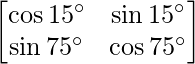
|A| = 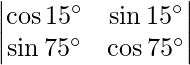
= cos 15° cos 75° – sin 15° sin 75°
As cos A cos B – sin A sin B = cos (A + B), we get
= cos (15° + 75°)
= cos 90°
= 0
Question 44. If A = 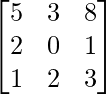 , write the cofactor of the element a32.
, write the cofactor of the element a32.
Solution:
We have,
A = 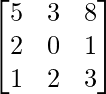
So, the minor of a32 is,
M32 = 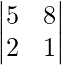
= 5 – 16
= -11
Now, the cofactor of a32 is,
A32 = (−1)3+2 M32
= 11
Therefore, the cofactor of element a32 is 11.
Question 45. If 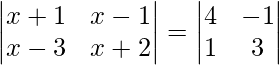 , then write the value of x.
, then write the value of x.
Solution:
We have,
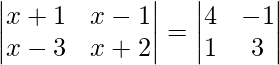
On expanding the determinants of both sides, we get
=> (x + 1) (x + 2) – (x – 1) (x – 3) = 12 + 1
=> x2 + 3x + 2 – x2 + 4x – 3 = 13
=> 7x – 1 = 13
=> 7x = 14
=> x = 2
Therefore, the value of x is 2.
Question 46. If 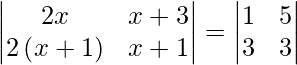 , then write the value of x.
, then write the value of x.
Solution:
We are given,
=> 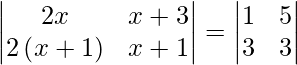
On expanding the determinants of both sides, we get
=> (2x) (x + 1) – 2 (x + 1) (x + 3) = 3 – 15
=> (x + 1) (2x – 2x – 6) = -12
=> -6x – 6 = – 12
=> -6x = -6
=> x = 1
Therefore, the value of x is 1.
Question 47. If 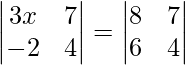 , find the value of x.
, find the value of x.
Solution:
We have,
=> 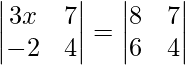
On expanding the determinants of both sides, we get
=> 12x + 14 = 32 – 42
=> 12x + 14 = -10
=> 12x = -24
=> x = -24/12
=> x = -2
Therefore, the value of x is -2.
Question 48. If 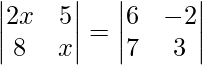 , write the value of x.
, write the value of x.
Solution:
Here, we have,
=> 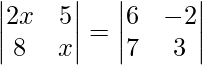
On expanding the determinants of both sides, we get
=> 2x2 – 40 = 18 + 14
=> 2x2 – 40 = 32
=> 2x2 = 72
=> x2 = 72/2
=> x2 = 36
=> x = ±6
Therefore, the value of x is ±6.
Question 49. If A is a 3 × 3 matrix, |A| ≠ 0 and |3A| = k |A| then write the value of k.
Solution:
We are given,
A is a 3 × 3 matrix.
Also |A| ≠ 0 and |3A| = k |A|.
Let us considered A = 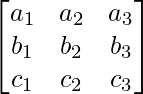
3A = 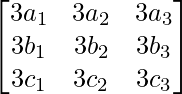
|3A| = 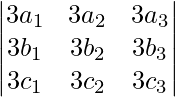
On taking 3 common from each row we get,
= 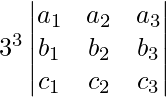
= 27 |A|
Therefore, the value of k is 27.
Question 50. Write the value of the determinant 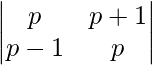 .
.
Solution:
We have,
A = 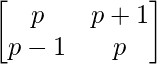
|A| = 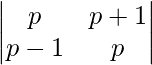
On expanding the determinant we have,
= p2 – (p + 1) (p – 1)
= p2 – (p2 – 1)
= p2 – p2 + 1
= 1
Therefore, the value of the determinant is 1.
Question 51. Write the value of the determinant 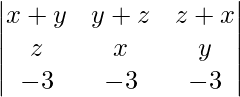 .
.
Solution:
We have,
A = 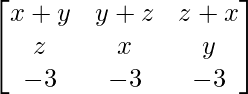
|A| = 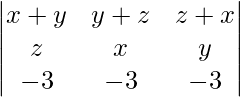
On applying R1 -> R1 + R2 we get,
= 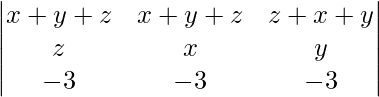
On taking x + y + z common from R1 we have,
= 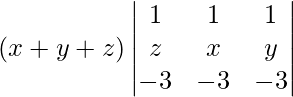
On applying R3 -> R3 + 3 R1 we get,
= 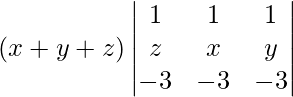
= 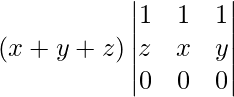
On expanding along the last row we get,
= 0
Therefore, the value of the determinant is 0.
Question 52. If A = 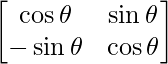 , then for any natural number, find the value of Det(An).
, then for any natural number, find the value of Det(An).
Solution:
Given that, A = 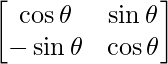
=> A2 = 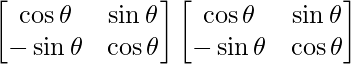
= 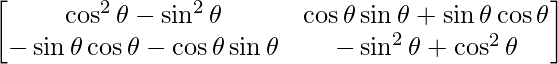
= 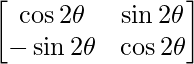
Similarly, An = 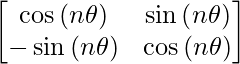
So,
|An| = 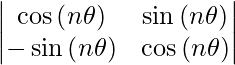
= (cos nθ) (cos nθ) + (sin nθ) (sin nθ)
= cos2 (nθ) + sin2 (nθ)
= 1
Therefore, Det(An) = 1.
Question 53. Find the maximum value of 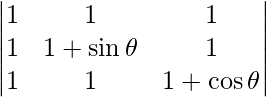 .
.
Solution:
We have,
A = 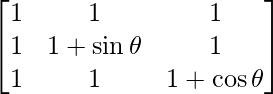
|A| = 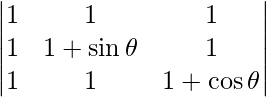
On applying R2 -> R2 – R1 and R3 -> R3 – R1, we get
|A| = 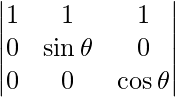
= sin θ cos θ
= (sin 2θ)/2
We know that −1 ≤ sin2θ ≤ 1.
So, the maximum value of |A| = (1/2) (1)
= 1/2
Therefore, the maximum value is 1/2.
Question 54. If x ∈ N and 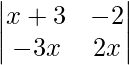 = 8, then find the value of x.
= 8, then find the value of x.
Solution:
Here we have,
A = 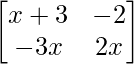
|A| = 8
On expansion we get,
=> (x + 3) (2x) – (-2) (-3x) = 8
=> 2 x2 + 6x – 6x = 8
=> 2 x2 = 8
=> 2x2 – 8 = 0
=> x2 – 4 = 0
=> x2 = 4
As x ∈ N, we get
=> x = 2
Therefore, the value of x is 2.
Question 55. If 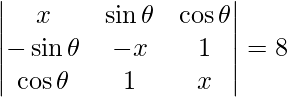 , write the value of x.
, write the value of x.
Solution:
We have,
A = 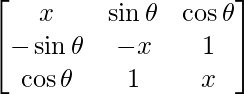
|A| = 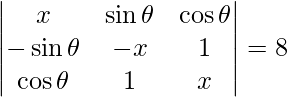
=> 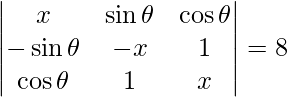
On expanding along R1, we get
=> x (-x2 – 1) – sin θ (-x sin θ – cos θ) + cos θ (-sin θ + x cos θ) = 8
=> -x3 – x + x sin2 θ + sin θ cos θ – sin θ cos θ + x cos2 θ = 8
=> -x3 – x + x (sin2 θ + cos2 θ) = 8
=> -x3 – x + x = 8
=> x3 + 8 = 0
=> x = -2
Therefore, the value of x is -2.
Question 56. If A is a 3 × 3 invertible matrix, then what will be the value of k if det(A–1) = (det A)k.
Solution:
Given that A is a 3 × 3 invertible matrix.
So, we know that
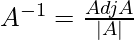
Therefore we get,
=> 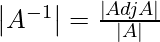
As we know that, 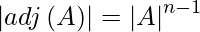
= 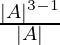
= 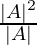
= |A|
|A-1| = |Ak|, we get
=> k = 1
Therefore, the value of k is 1.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...