Check if array contains contiguous integers with duplicates allowed
Last Updated :
08 Oct, 2023
Given an array Arr of N integers(duplicates allowed). Print “Yes” if it is a set of contiguous integers else print “No”.
Examples:
Input: Arr = { 5, 2, 3, 6, 4, 4, 6, 6 }
Output: Yes
The elements of array form a contiguous set of integers which is {2, 3, 4, 5, 6} so the output is Yes.
Input: Arr = { 10, 14, 10, 12, 12, 13, 15 }
Output: No
Approach:
- A similar approach is discussed here. It is recommended to go through it before moving further with this article.
- Find the max and min elements from the array.
- Update the array with the difference from the max element in the array.
- Traverse the array and do the following
- If 0 <= abs(arr[i])-1) < n and arr[abs(arr[i])-1)] > 0 means the element is positive (visited first time), make it negative by doing arr[abs(arr[i])-1] = -arr[abs(arr[i])-1].
- Else continue loop means either the value is already visited or out of range of the array
- Traverse the loop again and check if any element is positive means element has a difference greater than 1
break the loop and print “NO” - If no element is found positive, print “YES”
Below is the implementation code:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool check(int arr[], int n)
{
int k = INT_MIN;
int r = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
k = max(k, arr[i]);
r = min(r, arr[i]);
}
k += 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = k - arr[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (abs(arr[i]) - 1 < n
&& arr[abs(arr[i]) - 1] > 0) {
arr[abs(arr[i]) - 1]
= -arr[abs(arr[i]) - 1];
}
}
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k - r - 1; i++) {
if (arr[i] > 0) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
return flag == 0;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 5, 2, 3, 6, 4, 4, 6, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
if (check(arr, n))
cout << "Yes";
else
cout << "No";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static boolean check(int arr[], int n)
{
int k = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int r = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
k = Math.max(k, arr[i]);
r = Math.min(r, arr[i]);
}
k += 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = k - arr[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int abs_value = Math.abs(arr[i]);
if (abs_value - 1 < n &&
arr[abs_value - 1] > 0)
{
arr[abs_value - 1] = -arr[abs_value - 1];
}
}
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k - r - 1; i++)
{
if (arr[i] > 0)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
return flag == 0;
}
public static void main(String []args)
{
int arr[] = { 5, 2, 3, 6, 4, 4, 6, 6 };
int n = arr.length;
if (check(arr, n))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
|
Python3
def check(arr, n):
k = -10**9
r = 10**9
for i in range(n):
k = max(k, arr[i])
r = min(r, arr[i])
k += 1
for i in range(n):
arr[i] = k - arr[i]
for i in range(n):
if (abs(arr[i]) - 1 < n and
arr[abs(arr[i]) - 1] > 0):
arr[abs(arr[i]) - 1]= -arr[abs(arr[i]) - 1]
flag = 0
for i in range(k - r):
if (arr[i] > 0):
flag = 1
break
return flag == 0
arr = [5, 2, 3, 6, 4, 4, 6, 6]
n = len(arr)
if (check(arr, n)):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static bool check(int []arr, int n)
{
int k = int.MinValue;
int r = int.MaxValue;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
k = Math.Max(k, arr[i]);
r = Math.Min(r, arr[i]);
}
k += 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = k - arr[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (Math.Abs(arr[i]) - 1 < n &&
arr[(Math.Abs(arr[i]) - 1)] > 0)
{
arr[(Math.Abs(arr[i]) - 1)] = -
arr[(Math.Abs(arr[i])) - 1];
}
}
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k - r - 1; i++)
{
if (arr[i] > 0)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
return flag == 0;
}
static public void Main ()
{
int []arr = { 5, 2, 3, 6, 4, 4, 6, 6 };
int n = arr.Length;
if (check(arr, n))
Console.Write("Yes");
else
Console.Write("No");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function check(arr, n)
{
let k = Number.MIN_VALUE;
let r = Number.MAX_VALUE;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
k = Math.max(k, arr[i]);
r = Math.min(r, arr[i]);
}
k += 1;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = k - arr[i];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let abs_value = Math.abs(arr[i]);
if (abs_value - 1 < n
&& arr[abs_value - 1] > 0) {
arr[abs_value - 1]
= -arr[abs_value - 1];
}
}
let flag = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= k - r - 1; i++) {
if (arr[i] > 0) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
return flag == 0;
}
let arr = [ 5, 2, 3, 6, 4, 4, 6, 6 ];
let n = arr.length;
if (check(arr, n))
document.write("Yes");
else
document.write("No");
</script>
|
Output:
Yes
Time Complexity: 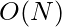
Space Complexity: 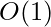 Extra Space
Extra Space
Approach 2: Using Hash Set
1. Taken an array arr[] to take input and called CheckContiguous() function.
2. In the CheckContiguous function, first creates an unordered_set to store the elements of the array.
3. It then starts by checking if there is a contiguous sequence of smaller integers than the first element of the array.
4. If yes, it keeps updating the counter variable ‘cnt’ and the current element ‘curr_elem’ until it reaches a number that is not present in the set.
6. Then it checks if there is a contiguous sequence of greater integers than the first element of the array.
7. If yes, it keeps updating the counter variable ‘cnt’ and the current element ‘curr_elem’ until it reaches a number that is not present in the set.
8. Finally, the function returns true if the count of contiguous integers is equal to the size of the set, else it returns false.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool CheckContiguous(int arr[], int n)
{
unordered_set<int> ust;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ust.insert(arr[i]);
int cnt = 1;
int curr_elem = arr[0] - 1;
while (ust.find(curr_elem) != ust.end()) {
cnt++;
curr_elem--;
}
curr_elem = arr[0] + 1;
while (ust.find(curr_elem) != ust.end()) {
cnt++;
curr_elem++;
}
return (cnt == (int)(ust.size()));
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 5, 2, 3, 6, 4, 4, 6, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
if (CheckContiguous(arr, n))
cout << "Yes";
else
cout << "No";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static boolean checkContiguous(int[] arr, int n) {
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
set.add(arr[i]);
int cnt = 1;
int curr_elem = arr[0] - 1;
while (set.contains(curr_elem)) {
cnt++;
curr_elem--;
}
curr_elem = arr[0] + 1;
while (set.contains(curr_elem)) {
cnt++;
curr_elem++;
}
return (cnt == set.size());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 5, 2, 3, 6, 4, 4, 6, 6 };
int n = arr.length;
if (checkContiguous(arr, n))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
|
Python3
def check_contiguous(arr, n):
ust = set(arr)
cnt = 1
curr_elem = arr[0] - 1
while curr_elem in ust:
cnt += 1
curr_elem -= 1
curr_elem = arr[0] + 1
while curr_elem in ust:
cnt += 1
curr_elem += 1
return cnt == len(ust)
arr = [5, 2, 3, 6, 4, 4, 6, 6]
n = len(arr)
if check_contiguous(arr, n):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
public static bool CheckContiguous(int[] arr, int n)
{
HashSet<int> set = new HashSet<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
set.Add(arr[i]);
int cnt = 1;
int curr_elem = arr[0] - 1;
while (set.Contains(curr_elem))
{
cnt++;
curr_elem--;
}
curr_elem = arr[0] + 1;
while (set.Contains(curr_elem))
{
cnt++;
curr_elem++;
}
return cnt == set.Count;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 5, 2, 3, 6, 4, 4, 6, 6 };
int n = arr.Length;
if (CheckContiguous(arr, n))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function checkContiguous(arr) {
const set = new Set(arr);
let cnt = 1;
let currElem = arr[0] - 1;
while (set.has(currElem)) {
cnt++;
currElem--;
}
currElem = arr[0] + 1;
while (set.has(currElem)) {
cnt++;
currElem++;
}
return cnt === set.size;
}
const arr = [5, 2, 3, 6, 4, 4, 6, 6];
if (checkContiguous(arr)) {
console.log("Yes");
} else {
console.log("No");
}
<script>
|
Time complexity: O(n), where n is the size of the input array.
Space complexity: O(n), as an unordered set to store the elements of the array, which can take up to n space in the worst case.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...