Given an array of integers arr[] of size N and an integer, the task is to rotate the array elements to the left by d positions.
Examples:
Input:
N = 5, d = 2 ,arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
Output: 3 4 5 6 7 1 2
Input: N = 7, d=2 , arr[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2},
Output: 5 6 7 1 2 3 4
Approach 1 (Using temp array): This problem can be solved using the below idea:
After rotating d positions to the left, the first d elements become the last d elements of the array
- First store the elements from index d to N-1 into the temp array.
- Then store the first d elements of the original array into the temp array.
- Copy back the elements of the temp array into the original array
Illustration:
Suppose the give array is arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], d = 2.
First Step:
=> Store the elements from 2nd index to the last.
=> temp[] = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Second Step:
=> Now store the first 2 elements into the temp[] array.
=> temp[] = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2]
Third Steps:
=> Copy the elements of the temp[] array into the original array.
=> arr[] = temp[] So arr[] = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2]
Follow the steps below to solve the given problem.
- Initialize a temporary array(temp[n]) of length same as the original array
- Initialize an integer(k) to keep a track of the current index
- Store the elements from the position d to n-1 in the temporary array
- Now, store 0 to d-1 elements of the original array in the temporary array
- Lastly, copy back the temporary array to the original array
Below is the implementation of the above approach :
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to rotate array
void Rotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{ d=d%n;
// Storing rotated version of array
int temp[n];
// Keeping track of the current index
// of temp[]
int k = 0;
// Storing the n - d elements of
// array arr[] to the front of temp[]
for (int i = d; i < n; i++) {
temp[k] = arr[i];
k++;
}
// Storing the first d elements of array arr[]
// into temp
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) {
temp[k] = arr[i];
k++;
}
// Copying the elements of temp[] in arr[]
// to get the final rotated array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = temp[i];
}
}
// Function to print elements of array
void PrintTheArray(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int d = 2;
// Function calling
Rotate(arr, d, N);
PrintTheArray(arr, N);
return 0;
}
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Function to rotate array
static void Rotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{ d=d%n;
// Storing rotated version of array
int temp[] = new int[n];
// Keeping track of the current index
// of temp[]
int k = 0;
// Storing the n - d elements of
// array arr[] to the front of temp[]
for (int i = d; i < n; i++) {
temp[k] = arr[i];
k++;
}
// Storing the first d elements of array arr[]
// into temp
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) {
temp[k] = arr[i];
k++;
}
// Copying the elements of temp[] in arr[]
// to get the final rotated array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = temp[i];
}
}
// Function to print elements of array
static void PrintTheArray(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = arr.length;
int d = 2;
// Function calling
Rotate(arr, d, N);
PrintTheArray(arr, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ishankhandelwals.
def rotate(L, d, n):
d=d%n;
k = L.index(d)
new_lis = []
new_lis = L[k+1:]+L[0:k+1]
return new_lis
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
d = 2
N = len(arr)
# Function call
arr = rotate(arr, d, N)
for i in arr:
print(i, end=" ")
// Include namespace system
using System;
public class GFG
{
// Function to rotate array
public static void Rotate(int[] arr, int d, int n)
{ d=d%n;
// Storing rotated version of array
int[] temp = new int[n];
// Keeping track of the current index
// of temp[]
var k = 0;
// Storing the n - d elements of
// array arr[] to the front of temp[]
for (int i = d; i < n; i++)
{
temp[k] = arr[i];
k++;
}
// Storing the first d elements of array arr[]
// into temp
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++)
{
temp[k] = arr[i];
k++;
}
// Copying the elements of temp[] in arr[]
// to get the final rotated array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
arr[i] = temp[i];
}
}
// Function to print elements of array
public static void PrintTheArray(int[] arr, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Console.Write(arr[i].ToString() + " ");
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
var N = arr.Length;
var d = 2;
// Function calling
GFG.Rotate(arr, d, N);
GFG.PrintTheArray(arr, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ishankhandelwals.
function Rotate_and_Print(arr,d,n)
{
//Initializing array temp with size n
var temp=new Array(n);
d=d%n;
let k = 0;
// Storing the n - d elements of
// array arr[] to the front of temp[]
for (let i = d; i < n; i++) {
temp[k] = arr[i];
k++;
}
// Storing the first d elements of array arr[]
// into temp
for (let i = 0; i < d; i++) {
temp[k] = arr[i];
k++;
}
//Printing the temp array which stores the result
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
console.log(temp[i]+" ");
}
}
let arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ];
let n = arr.length;
let d = 2; //number of times rotating the array
Rotate_and_Print(arr, d, n);
//contributed by keerthikarathan123
Time complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Approach 2 (Rotate one by one): This problem can be solved using the below idea:
- At each iteration, shift the elements by one position to the left circularly (i.e., first element becomes the last).
- Perform this operation d times to rotate the elements to the left by d position.
Illustration:
Let us take arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], d = 2.
First Step:
=> Rotate to left by one position.
=> arr[] = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1}
Second Step:
=> Rotate again to left by one position
=> arr[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2}
Rotation is done by 2 times.
So the array becomes arr[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2}
Follow the steps below to solve the given problem.
- Rotate the array to left by one position. For that do the following:
- Store the first element of the array in a temporary variable.
- Shift the rest of the elements in the original array by one place.
- Update the last index of the array with the temporary variable.
- Repeat the above steps for the number of left rotations required.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to rotate an array by
// d elements
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/*Function to left rotate arr[] of size n by d*/
void Rotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
int p = 1;
while (p <= d) {
int last = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
}
arr[n - 1] = last;
p++;
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int d = 2;
// Function calling
Rotate(arr, d, N);
printArray(arr, N);
return 0;
}
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void rotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
int p = 1;
while (p <= d) {
int last = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
}
arr[n - 1] = last;
p++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = arr.length;
// Rotate 2 times
int d = 2;
// Function call
rotate(arr, d, N);
}
}
// contributed by keerthikarathan123
# Python program to rotate an array by d elements
# Function to left rotate arr[] of size n by d
def Rotate(arr, d, n):
p = 1
while(p <= d):
last = arr[0]
for i in range (n - 1):
arr[i] = arr[i + 1]
arr[n - 1] = last
p = p + 1
# Function to print an array
def printArray(arr, size):
for i in range (size):
print(arr[i] ,end = " ")
# Driver code
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
N = len(arr)
d = 2
# Function calling
Rotate(arr, d, N)
printArray(arr, N)
# This code is contributed by Atul_kumar_Shrivastava
// Include namespace system
using System;
public class GFG
{
public static void rotate(int[] arr, int d, int n)
{
var p = 1;
while (p <= d)
{
var last = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
}
arr[n - 1] = last;
p++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Console.Write(arr[i].ToString() + " ");
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
var N = arr.Length;
// Rotate 2 times
var d = 2;
// Function call
GFG.rotate(arr, d, N);
}
}
function printArray(arr,n,d)
{
let p = 1;
while (p <= d) {
let last = arr[0];
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
}
arr[n - 1] = last;
p++;
}
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
console.log(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
let arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ];
let n = arr.length;
let d=2; //number of times rotating the array
// Function calling
printArray(arr, n,d);
//contributed by keerthikarathan123
Time Complexity: O(N * d)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Approach 3 (A Juggling Algorithm): This is an extension of method 2.
Instead of moving one by one, divide the array into different sets where the number of sets is equal to the GCD of N and d (say X. So the elements which are X distance apart are part of a set) and rotate the elements within sets by 1 position to the left.
- Calculate the GCD between the length and the distance to be moved.
- The elements are only shifted within the sets.
- We start with temp = arr[0] and keep moving arr[I+d] to arr[I] and finally store temp at the right place.
Follow the below illustration for a better understanding
Illustration:
Each steps looks like following:
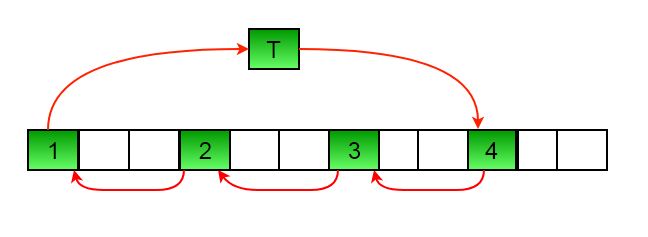
Let arr[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14} and d = 10
First step:
=> First set is {0, 5, 10}.
=> Rotate this set by d position in cyclic order
=> arr[0] = arr[0+10]
=> arr[10] = arr[(10+10)%15]
=> arr[5] = arr[0]
=> This set becomes {10,0,5}
=> Array arr[] = {10, 1, 2, 3, 4, 0, 6, 7, 8, 9, 5, 11, 12, 13, 14}
Second step:
=> Second set is {1, 6, 11}.
=> Rotate this set by d position in cyclic order.
=> This set becomes {11, 1, 6}
=> Array arr[] = {10, 11, 2, 3, 4, 0, 1, 7, 8, 9, 5, 6, 12, 13, 14}
Third step:
=> Second set is {2, 7, 12}.
=> Rotate this set by d position in cyclic order.
=> This set becomes {12, 2, 7}
=> Array arr[] = {10, 11, 12, 3, 4, 0, 1, 2, 8, 9, 5, 6, 7, 13, 14}
Fourth step:
=> Second set is {3, 8, 13}.
=> Rotate this set by d position in cyclic order.
=> This set becomes {13, 3, 8}
=> Array arr[] = {10, 11, 12, 13, 4, 0, 1, 2, 3, 9, 5, 6, 7, 8, 14}
Fifth step:
=> Second set is {4, 9, 14}.
=> Rotate this set by d position in cyclic order.
=> This set becomes {14, 4, 9}
=> Array arr[] = {10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
Follow the steps below to solve the given problem.
- Perform d%n in order to keep the value of d within the range of the array where d is the number of times the array is rotated and N is the size of the array.
- Calculate the GCD(N, d) to divide the array into sets.
- Run a for loop from 0 to the value obtained from GCD.
- Store the value of arr[i] in a temporary variable (the value of i denotes the set number).
- Run a while loop to update the values according to the set.
- After exiting the while loop assign the value of arr[j] as the value of the temporary variable (the value of j denotes the last element of the ith set).
Below is the implementation of the above approach :
C++
// C++ program to rotate an array by
// d elements
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/*Function to get gcd of a and b*/
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
else
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
/*Function to left rotate arr[] of size n by d*/
void leftRotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
/* To handle if d >= n */
d = d % n;
int g_c_d = gcd(d, n);
for (int i = 0; i < g_c_d; i++) {
/* move i-th values of blocks */
int temp = arr[i];
int j = i;
while (1) {
int k = j + d;
if (k >= n)
k = k - n;
if (k == i)
break;
arr[j] = arr[k];
j = k;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function calling
leftRotate(arr, 2, n);
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// C program to rotate an array by
// d elements
#include <stdio.h>
/* function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size);
/*Function to get gcd of a and b*/
int gcd(int a, int b);
/*Function to left rotate arr[] of size n by d*/
void leftRotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
int i, j, k, temp;
/* To handle if d >= n */
d = d % n;
int g_c_d = gcd(d, n);
for (i = 0; i < g_c_d; i++) {
/* move i-th values of blocks */
temp = arr[i];
j = i;
while (1) {
k = j + d;
if (k >= n)
k = k - n;
if (k == i)
break;
arr[j] = arr[k];
j = k;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
/*UTILITY FUNCTIONS*/
/* function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
/*Function to get gcd of a and b*/
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
else
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
leftRotate(arr, 2, 7);
printArray(arr, 7);
getchar();
return 0;
}
// Java program to rotate an array by
// d elements
import java.io.*;
class RotateArray {
/*Function to left rotate arr[] of size n by d*/
void leftRotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
/* To handle if d >= n */
d = d % n;
int i, j, k, temp;
int g_c_d = gcd(d, n);
for (i = 0; i < g_c_d; i++) {
/* move i-th values of blocks */
temp = arr[i];
j = i;
while (true) {
k = j + d;
if (k >= n)
k = k - n;
if (k == i)
break;
arr[j] = arr[k];
j = k;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
/*UTILITY FUNCTIONS*/
/* function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
/*Function to get gcd of a and b*/
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
else
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
RotateArray rotate = new RotateArray();
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
rotate.leftRotate(arr, 2, 7);
rotate.printArray(arr, 7);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
# Python3 program to rotate an array by
# d elements
# Function to left rotate arr[] of size n by d
def leftRotate(arr, d, n):
d = d % n
g_c_d = gcd(d, n)
for i in range(g_c_d):
# move i-th values of blocks
temp = arr[i]
j = i
while 1:
k = j + d
if k >= n:
k = k - n
if k == i:
break
arr[j] = arr[k]
j = k
arr[j] = temp
# UTILITY FUNCTIONS
# function to print an array
def printArray(arr, size):
for i in range(size):
print("% d" % arr[i], end=" ")
# Function to get gcd of a and b
def gcd(a, b):
if b == 0:
return a
else:
return gcd(b, a % b)
# Driver program to test above functions
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
n = len(arr)
d = 2
leftRotate(arr, d, n)
printArray(arr, n)
# This code is contributed by Shreyanshi Arun
// C# program for array rotation
using System;
class GFG {
/* Function to left rotate arr[]
of size n by d*/
static void leftRotate(int[] arr, int d, int n)
{
int i, j, k, temp;
/* To handle if d >= n */
d = d % n;
int g_c_d = gcd(d, n);
for (i = 0; i < g_c_d; i++) {
/* move i-th values of blocks */
temp = arr[i];
j = i;
while (true) {
k = j + d;
if (k >= n)
k = k - n;
if (k == i)
break;
arr[j] = arr[k];
j = k;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
/*UTILITY FUNCTIONS*/
/* Function to print an array */
static void printArray(int[] arr, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
/* Function to get gcd of a and b*/
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
else
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
leftRotate(arr, 2, 7);
printArray(arr, 7);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007
// JavaScript program to rotate an array by
// d elements
/*Function to get gcd of a and b*/
function gcd(a, b) {
if (b == 0)
return a;
else
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
/*Function to left rotate arr[] of size n by d*/
function leftRotate(arr, d, n) {
/* To handle if d >= n */
d = d % n;
let g_c_d = gcd(d, n);
for (let i = 0; i < g_c_d; i++) {
/* move i-th values of blocks */
let temp = arr[i];
let j = i;
while (1) {
let k = j + d;
if (k >= n)
k = k - n;
if (k == i)
break;
arr[j] = arr[k];
j = k;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// Function to print an array in a single line
function printArraySingleLine(arr, size) {
let result = "";
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {
result += arr[i] + " ";
}
console.log(result);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7];
let n = arr.length;
// Function calling
leftRotate(arr, 2, n);
printArraySingleLine(arr, n);
Please see the following posts for other methods of array rotation:
Block swap algorithm for array rotation
Reversal algorithm for array rotation
Please write comments if you find any bugs in the above programs/algorithms.
Approach 4 (reversal algorithm):
- Reverse the First d Elements: Reverse the subarray containing the first d elements of the array.
- Reverse the Remaining Elements: Reverse the subarray containing the remaining elements of the array (from index d to the end).
- Reverse the Whole Array: Reverse the entire array
illustration :
Let us take arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], d = 2
n = length of arr
First Step:
=> Rotate first d elements
=> (first recursion call)
pick start = 0, end = d-1
=> (second recursion call)
pick start = d, end = n-1
=>(third recursion call) reverse whole array
pick start = 0, end = n-1
Second Step :
=> in reverse function use swapping technique
start = 0, end = 2
=> while(start < end)
arr[start] swap with arr[end]
increment start
decrement end
edge case :
when d is greater then array size d = d % n
code:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Function to reverse array elements from start to end
void reverse(vector<int>& arr, int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
// Function to left rotate array elements by d positions
void leftRotate(vector<int>& arr, int d) {
int n = arr.size();
d = d % n; // To handle case when d >= n
// Reverse the first d elements
reverse(arr, 0, d - 1);
// Reverse the remaining elements
reverse(arr, d, n - 1);
// Reverse the whole array
reverse(arr, 0, n - 1);
}
int main() {
vector<int> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int d = 2;
leftRotate(arr, d);
cout << "Array after left rotation:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int d = 2;
leftRotate(arr, d);
System.out.println("Array after left rotation:");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// Function to left rotate array elements by d positions
public static void leftRotate(int arr[], int d) {
int n = arr.length;
// To handle case when d >= n
d = d % n;
// Reverse the first d elements
reverse(arr, 0, d - 1);
// Reverse the remaining elements
reverse(arr, d, n - 1);
// Reverse the whole array
reverse(arr, 0, n - 1);
}
public static void reverse(int arr[], int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
// swapping of two numbers
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
}
# code
def reverse(arr, start, end):
"""
Function to reverse array elements from start to end
"""
while start < end:
arr[start], arr[end] = arr[end], arr[start]
start += 1
end -= 1
def left_rotate(arr, d):
"""
Function to left rotate array elements by d positions
"""
n = len(arr)
d = d % n # To handle case when d >= n
# Reverse the first d elements
reverse(arr, 0, d - 1)
# Reverse the remaining elements
reverse(arr, d, n - 1)
# Reverse the whole array
reverse(arr, 0, n - 1)
# Example usage
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
d = 2
left_rotate(arr, d)
print("Array after left rotation:", arr)
// Function to left rotate array elements by d positions
function leftRotate(arr, d) {
let n = arr.length;
// To handle case when d >= n
d = d % n;
// Reverse the first d elements
reverse(arr, 0, d - 1);
// Reverse the remaining elements
reverse(arr, d, n - 1);
// Reverse the whole array
reverse(arr, 0, n - 1);
}
// Function to reverse elements in the array from start to end index
function reverse(arr, start, end) {
while (start < end) {
// Swap elements at start and end indices
let temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
// Main function
function main() {
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let d = 2;
leftRotate(arr, d);
console.log("Array after left rotation: " + arr.join(" "));
}
// Execute main function
main();
OutputArray after left rotation:
3 4 5 1 2
Time complexity: O(N)
Space complexity: O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...