Largest Sum Contiguous Subarray (Kadane’s Algorithm)
Last Updated :
26 Apr, 2024
Given an array arr[] of size N. The task is to find the sum of the contiguous subarray within a arr[] with the largest sum.
Example:
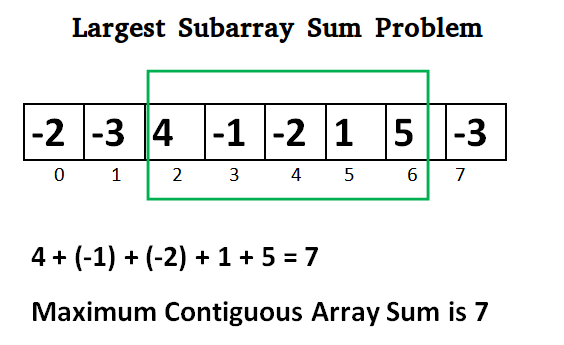
Input: arr = {-2,-3,4,-1,-2,1,5,-3}
Output: 7
Explanation: The subarray {4,-1, 2, 1, 5} has the largest sum 7.
Input: arr = {2}
Output: 2
Explanation: The subarray {2} has the largest sum 1.
Input: arr = {5,4,1,7,8}
Output: 23
Explanation: The subarray {5,4,1,7,8} has the largest sum 25.
Approach:
The idea of Kadane’s algorithm is to maintain a variable max_ending_here that stores the maximum sum contiguous subarray ending at current index and a variable max_so_far stores the maximum sum of contiguous subarray found so far, Everytime there is a positive-sum value in max_ending_here compare it with max_so_far and update max_so_far if it is greater than max_so_far.
So the main Intuition behind Kadane’s Algorithm is,
- The subarray with negative sum is discarded (by assigning max_ending_here = 0 in code).
- We carry subarray till it gives positive sum.
Pseudocode of Kadane’s algorithm:
Initialize:
max_so_far = INT_MIN
max_ending_here = 0
Loop for each element of the array
(a) max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i]
(b) if(max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here
(c) if(max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0
return max_so_far
Illustration of Kadane’s Algorithm:
Lets take the example: {-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3}
Note: in the image max_so_far is represented by Max_Sum and max_ending_here by Curr_Sum
-(2).jpg)
For i=0, a[0] = -2
- max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-2)
- Set max_ending_here = 0 because max_ending_here < 0
- and set max_so_far = -2
For i=1, a[1] = -3
- max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-3)
- Since max_ending_here = -3 and max_so_far = -2, max_so_far will remain -2
- Set max_ending_here = 0 because max_ending_here < 0
For i=2, a[2] = 4
- max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (4)
- max_ending_here = 4
- max_so_far is updated to 4 because max_ending_here greater than max_so_far which was -2 till now
For i=3, a[3] = -1
- max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-1)
- max_ending_here = 3
For i=4, a[4] = -2
- max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-2)
- max_ending_here = 1
For i=5, a[5] = 1
- max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (1)
- max_ending_here = 2
For i=6, a[6] = 5
- max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (5)
- max_ending_here =
- max_so_far is updated to 7 because max_ending_here is greater than max_so_far
For i=7, a[7] = -3
- max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-3)
- max_ending_here = 4
Follow the below steps to Implement the idea:
- Initialize the variables max_so_far = INT_MIN and max_ending_here = 0
- Run a for loop from 0 to N-1 and for each index i:
- Add the arr[i] to max_ending_here.
- If max_so_far is less than max_ending_here then update max_so_far to max_ending_here.
- If max_ending_here < 0 then update max_ending_here = 0
- Return max_so_far
Below is the Implementation of the above approach.
C++
// C++ program to print largest contiguous array sum
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maxSubArraySum(int a[], int size)
{
int max_so_far = INT_MIN, max_ending_here = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
if (max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0;
}
return max_so_far;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int a[] = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
// Function Call
int max_sum = maxSubArraySum(a, n);
cout << "Maximum contiguous sum is " << max_sum;
return 0;
}
// Java program to print largest contiguous array sum
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Kadane {
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
System.out.println("Maximum contiguous sum is "
+ maxSubArraySum(a));
}
// Function Call
static int maxSubArraySum(int a[])
{
int size = a.length;
int max_so_far = Integer.MIN_VALUE, max_ending_here
= 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
if (max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0;
}
return max_so_far;
}
}
def GFG(a, size):
max_so_far = float('-inf')
# Use float('-inf') instead of maxint
max_ending_here = 0
for i in range(0, size):
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i]
if max_so_far < max_ending_here:
max_so_far = max_ending_here
if max_ending_here < 0:
max_ending_here = 0
return max_so_far
# Driver function to check the above function
a = [-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3]
print("Maximum contiguous sum is", GFG(a, len(a)))
// C# program to print largest
// contiguous array sum
using System;
class GFG {
static int maxSubArraySum(int[] a)
{
int size = a.Length;
int max_so_far = int.MinValue, max_ending_here = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
if (max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0;
}
return max_so_far;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] a = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
Console.Write("Maximum contiguous sum is "
+ maxSubArraySum(a));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007_
<script>
// JavaScript program to find maximum
// contiguous subarray
// Function to find the maximum
// contiguous subarray
function maxSubArraySum(a, size)
{
var maxint = Math.pow(2, 53)
var max_so_far = -maxint - 1
var max_ending_here = 0
for (var i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i]
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here
if (max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0
}
return max_so_far
}
// Driver code
var a = [ -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 ]
document.write("Maximum contiguous sum is",
maxSubArraySum(a, a.length))
// This code is contributed by AnkThon
</script>
<?php
// PHP program to print largest
// contiguous array sum
function maxSubArraySum($a, $size)
{
$max_so_far = PHP_INT_MIN;
$max_ending_here = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $size; $i++)
{
$max_ending_here = $max_ending_here + $a[$i];
if ($max_so_far < $max_ending_here)
$max_so_far = $max_ending_here;
if ($max_ending_here < 0)
$max_ending_here = 0;
}
return $max_so_far;
}
// Driver code
$a = array(-2, -3, 4, -1,
-2, 1, 5, -3);
$n = count($a);
$max_sum = maxSubArraySum($a, $n);
echo "Maximum contiguous sum is " ,
$max_sum;
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
?>
OutputMaximum contiguous sum is 7
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Print the Largest Sum Contiguous Subarray:
To print the subarray with the maximum sum the idea is to maintain start index of maximum_sum_ending_here at current index so that whenever maximum_sum_so_far is updated with maximum_sum_ending_here then start index and end index of subarray can be updated with start and current index.
Follow the below steps to implement the idea:
- Initialize the variables s, start, and end with 0 and max_so_far = INT_MIN and max_ending_here = 0
- Run a for loop from 0 to N-1 and for each index i:
- Add the arr[i] to max_ending_here.
- If max_so_far is less than max_ending_here then update max_so_far to max_ending_here and update start to s and end to i .
- If max_ending_here < 0 then update max_ending_here = 0 and s with i+1.
- Print values from index start to end.
Below is the Implementation of above approach:
C++
// C++ program to print largest contiguous array sum
#include <climits>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void maxSubArraySum(int a[], int size)
{
int max_so_far = INT_MIN, max_ending_here = 0,
start = 0, end = 0, s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here += a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here) {
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
start = s;
end = i;
}
if (max_ending_here < 0) {
max_ending_here = 0;
s = i + 1;
}
}
cout << "Maximum contiguous sum is " << max_so_far
<< endl;
cout << "Starting index " << start << endl
<< "Ending index " << end << endl;
}
/*Driver program to test maxSubArraySum*/
int main()
{
int a[] = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
maxSubArraySum(a, n);
return 0;
}
// Java program to print largest
// contiguous array sum
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void maxSubArraySum(int a[], int size)
{
int max_so_far = Integer.MIN_VALUE,
max_ending_here = 0, start = 0, end = 0, s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here += a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here) {
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
start = s;
end = i;
}
if (max_ending_here < 0) {
max_ending_here = 0;
s = i + 1;
}
}
System.out.println("Maximum contiguous sum is "
+ max_so_far);
System.out.println("Starting index " + start);
System.out.println("Ending index " + end);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a[] = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
int n = a.length;
maxSubArraySum(a, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by prerna saini
# Python program to print largest contiguous array sum
from sys import maxsize
# Function to find the maximum contiguous subarray
# and print its starting and end index
def maxSubArraySum(a, size):
max_so_far = -maxsize - 1
max_ending_here = 0
start = 0
end = 0
s = 0
for i in range(0, size):
max_ending_here += a[i]
if max_so_far < max_ending_here:
max_so_far = max_ending_here
start = s
end = i
if max_ending_here < 0:
max_ending_here = 0
s = i+1
print("Maximum contiguous sum is %d" % (max_so_far))
print("Starting Index %d" % (start))
print("Ending Index %d" % (end))
# Driver program to test maxSubArraySum
a = [-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3]
maxSubArraySum(a, len(a))
// C# program to print largest
// contiguous array sum
using System;
class GFG {
static void maxSubArraySum(int[] a, int size)
{
int max_so_far = int.MinValue, max_ending_here = 0,
start = 0, end = 0, s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here += a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here) {
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
start = s;
end = i;
}
if (max_ending_here < 0) {
max_ending_here = 0;
s = i + 1;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Maximum contiguous "
+ "sum is " + max_so_far);
Console.WriteLine("Starting index " + start);
Console.WriteLine("Ending index " + end);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] a = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
int n = a.Length;
maxSubArraySum(a, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by anuj_67.
<script>
// javascript program to print largest
// contiguous array sum
function maxSubArraySum(a , size) {
var max_so_far = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER, max_ending_here = 0, start = 0, end = 0, s = 0;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here += a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here) {
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
start = s;
end = i;
}
if (max_ending_here < 0) {
max_ending_here = 0;
s = i + 1;
}
}
document.write("Maximum contiguous sum is " + max_so_far);
document.write("<br/>Starting index " + start);
document.write("<br/>Ending index " + end);
}
// Driver code
var a = [ -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 ];
var n = a.length;
maxSubArraySum(a, n);
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
<?php
// PHP program to print largest
// contiguous array sum
function maxSubArraySum($a, $size)
{
$max_so_far = PHP_INT_MIN;
$max_ending_here = 0;
$start = 0;
$end = 0;
$s = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $size; $i++)
{
$max_ending_here += $a[$i];
if ($max_so_far < $max_ending_here)
{
$max_so_far = $max_ending_here;
$start = $s;
$end = $i;
}
if ($max_ending_here < 0)
{
$max_ending_here = 0;
$s = $i + 1;
}
}
echo "Maximum contiguous sum is ".
$max_so_far."\n";
echo "Starting index ". $start . "\n".
"Ending index " . $end . "\n";
}
// Driver Code
$a = array(-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3);
$n = sizeof($a);
maxSubArraySum($a, $n);
// This code is contributed
// by ChitraNayal
?>
OutputMaximum contiguous sum is 7
Starting index 2
Ending index 6
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Largest Sum Contiguous Subarray using Dynamic Programming:
For each index i, DP[i] stores the maximum possible Largest Sum Contiguous Subarray ending at index i, and therefore we can calculate DP[i] using the mentioned state transition:
- DP[i] = max(DP[i-1] + arr[i] , arr[i] )
Below is the implementation:
C++
// C++ program to print largest contiguous array sum
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void maxSubArraySum(int a[], int size)
{
vector<int> dp(size, 0);
dp[0] = a[0];
int ans = dp[0];
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
dp[i] = max(a[i], a[i] + dp[i - 1]);
ans = max(ans, dp[i]);
}
cout << ans;
}
/*Driver program to test maxSubArraySum*/
int main()
{
int a[] = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
maxSubArraySum(a, n);
return 0;
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
// Function to find the largest contiguous array sum
public static void maxSubArraySum(int[] a) {
int size = a.length;
int[] dp = new int[size]; // Create an array to store intermediate results
dp[0] = a[0]; // Initialize the first element of the intermediate array with the first element of the input array
int ans = dp[0]; // Initialize the answer with the first element of the intermediate array
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
// Calculate the maximum of the current element and the sum of the current element and the previous result
dp[i] = Math.max(a[i], a[i] + dp[i - 1]);
// Update the answer with the maximum value encountered so far
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i]);
}
// Print the maximum contiguous array sum
System.out.println(ans);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
maxSubArraySum(a); // Call the function to find and print the maximum contiguous array sum
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivamgupta310570
# Python program for the above approach
def max_sub_array_sum(a, size):
# Create a list to store intermediate results
dp = [0] * size
# Initialize the first element of the list with the first element of the array
dp[0] = a[0]
# Initialize the answer with the first element of the array
ans = dp[0]
# Loop through the array starting from the second element
for i in range(1, size):
# Choose the maximum value between the current element and the sum of the current element
# and the previous maximum sum (stored in dp[i - 1])
dp[i] = max(a[i], a[i] + dp[i - 1])
# Update the overall maximum sum
ans = max(ans, dp[i])
# Print the maximum contiguous subarray sum
print(ans)
# Driver program to test max_sub_array_sum
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Sample array
a = [-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3]
# Get the length of the array
n = len(a)
# Call the function to find the maximum contiguous subarray sum
max_sub_array_sum(a, n)
# This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli
using System;
class MaxSubArraySum {
// Function to find and print the maximum sum of a
// subarray
static void FindMaxSubArraySum(int[] arr, int size)
{
// Create an array to store the maximum sum of
// subarrays
int[] dp = new int[size];
// Initialize the first element of dp with the first
// element of arr
dp[0] = arr[0];
// Initialize a variable to store the final result
int ans = dp[0];
// Iterate through the array to find the maximum sum
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
// Calculate the maximum sum ending at the
// current position
dp[i] = Math.Max(arr[i], arr[i] + dp[i - 1]);
// Update the final result with the maximum sum
// found so far
ans = Math.Max(ans, dp[i]);
}
// Print the maximum sum of the subarray
Console.WriteLine(ans);
}
// Driver program to test FindMaxSubArraySum
static void Main()
{
// Example array
int[] arr = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
// Calculate and print the maximum subarray sum
FindMaxSubArraySum(arr, arr.Length);
}
}
// Javascript program to print largest contiguous array sum
// Function to find the largest contiguous array sum
function maxSubArraySum(a) {
let size = a.length;
// Create an array to store intermediate results
let dp = new Array(size);
// Initialize the first element of the intermediate array with the first element of the input array
dp[0] = a[0];
// Initialize the answer with the first element of the intermediate array
let ans = dp[0];
for (let i = 1; i < size; i++) {
// Calculate the maximum of the current element and the sum of the current element and the previous result
dp[i] = Math.max(a[i], a[i] + dp[i - 1]);
// Update the answer with the maximum value encountered so far
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i]);
}
// Print the maximum contiguous array sum
console.log(ans);
}
let a = [-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3];
// Call the function to find and print the maximum contiguous array sum
maxSubArraySum(a);
Practice Problem:
Given an array of integers (possibly some elements negative), write a C program to find out the *maximum product* possible by multiplying ‘n’ consecutive integers in the array where n ? ARRAY_SIZE. Also, print the starting point of the maximum product subarray.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...