Assignment Operators in C
Last Updated :
20 Mar, 2024
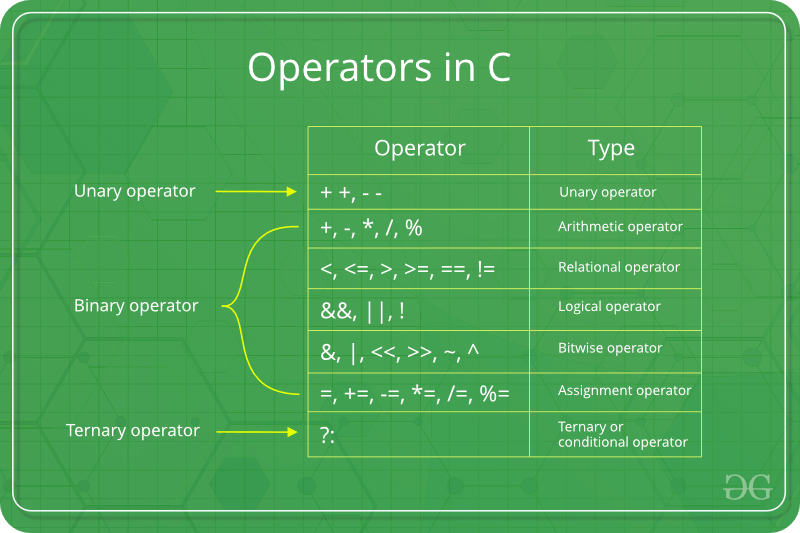
Assignment operators are used for assigning value to a variable. The left side operand of the assignment operator is a variable and right side operand of the assignment operator is a value. The value on the right side must be of the same data-type of the variable on the left side otherwise the compiler will raise an error.
Different types of assignment operators are shown below:
1. “=”: This is the simplest assignment operator. This operator is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. Example:
a = 10;
b = 20;
ch = 'y';
2. “+=”: This operator is combination of ‘+’ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first adds the current value of the variable on left to the value on the right and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
(a += b) can be written as (a = a + b)
If initially value stored in a is 5. Then (a += 6) = 11.
3. “-=” This operator is combination of ‘-‘ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first subtracts the value on the right from the current value of the variable on left and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
(a -= b) can be written as (a = a - b)
If initially value stored in a is 8. Then (a -= 6) = 2.
4. “*=” This operator is combination of ‘*’ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first multiplies the current value of the variable on left to the value on the right and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
(a *= b) can be written as (a = a * b)
If initially value stored in a is 5. Then (a *= 6) = 30.
5. “/=” This operator is combination of ‘/’ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first divides the current value of the variable on left by the value on the right and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
(a /= b) can be written as (a = a / b)
If initially value stored in a is 6. Then (a /= 2) = 3.
Below example illustrates the various Assignment Operators:
C
// C program to demonstrate
// working of Assignment operators
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// Assigning value 10 to a
// using "=" operator
int a = 10;
printf("Value of a is %d\n", a);
// Assigning value by adding 10 to a
// using "+=" operator
a += 10;
printf("Value of a is %d\n", a);
// Assigning value by subtracting 10 from a
// using "-=" operator
a -= 10;
printf("Value of a is %d\n", a);
// Assigning value by multiplying 10 to a
// using "*=" operator
a *= 10;
printf("Value of a is %d\n", a);
// Assigning value by dividing 10 from a
// using "/=" operator
a /= 10;
printf("Value of a is %d\n", a);
return 0;
}
OutputValue of a is 10
Value of a is 20
Value of a is 10
Value of a is 100
Value of a is 10
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...