What is a Broken Link? Identifying and Fixing Broken Link
Last Updated :
30 Jan, 2024
Broken link, also known as a dead link or a dangling link, refers to a hyperlink that points to a webpage, resource, or file that no longer exists or is unreachable. In other words, when you click on a broken link, you will encounter an error message or a “404 Not Found” page instead of being directed to the intended content.
What Is A Broken Link?

Broken link
A Broken link is a hyperlink that no longer functions or directs users to the intended content—instead of leading to a webpage or resource, clicking on a broken link results in an error message, commonly a “404 Not Found” page. Broken links can occur due to changes in URL, removal of content, typographical errors, server issues, or other factors, disrupting the seamless navigation of users through a website. Addressing broken links is crucial for maintaining a positive user experience and preserving the integrity of a website’s navigation structure. Additionally, search engines take into account the presence of broken links when assessing the overall health and relevance of a website for search rankings
Reasons For Broken Links
Broken links can occur for various reasons, and it’s essential for website owners to understand these reasons to prevent and address them effectively. Here are common reasons for broken links:
- Content Removal or Deletion:
- If a webpage or resource is removed or deleted, any links pointing to that content become broken.
- URL Changes:
- Changes in URL structure or permalink settings can result in broken links if the links are not updated accordingly.
- Typographical Errors:
- Simple typographical mistakes in URLs, such as misspellings or incorrect path specifications, can lead to broken links.
- Server Issues:
- Temporary or permanent server issues, such as server downtime or misconfigurations, can render a webpage or resource inaccessible, causing broken links.
- Expired Domain:
- If a website changes its domain or the domain expires, links pointing to the old domain become broken.
- Linking to External Resources:
- If a website links to external resources (on other websites), and those resources are moved, deleted, or no longer accessible, the links become broken.
- Incorrectly Formatted Links:
- Links that are incorrectly formatted, missing essential components (e.g., http:// or https://), can lead to broken links.
- Case Sensitivity:
- Some web servers are case-sensitive, and if the case of a URL is not correctly specified, it can result in broken links.
- Changes in Website Structure:
- If there are changes in the structure of a website (e.g., changes in folder organization), links may become broken if not updated.
- Image or File Deletion:
- If an image or file linked on a webpage is deleted, the link becomes broken, and users may see a missing image icon or encounter issues with file downloads.
Broken Link Error Codes
Let’s briefly understand some common error codes:
- 404 – Not Found: The requested page or resource is missing or mistyped.

HTTP 404
- 403 – Forbidden: The server refuses access, often due to permission issues.

403 forbidden request example
- 500 – Internal Server Error: A server-side problem affecting the request.

500 internal server error example
- 410 – Gone: Similar to 404 but indicates intentional removal.
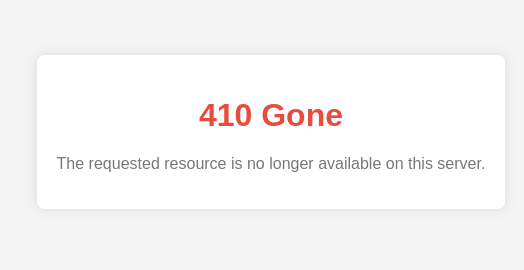
410 response
- 301 – Moved Permanently: Not an error, but a redirect indicating a permanent move.
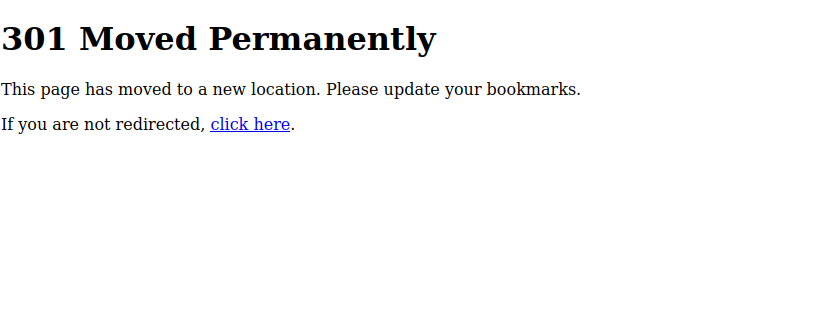
301 response example
How To Find Broken Links
Finding broken links on a website can be done using various tools and methods. Here are several approaches you can use:
- Online Broken Link Checkers:
- There are several online tools available that can scan your website and identify broken links. Some popular tools include:
- Google Search Console: If you have your website verified in Google Search Console, you can use the “Coverage” report to identify crawl errors, including broken links.
- W3C Link Checker: The W3C Link Checker allows you to check the links on a webpage or an entire website.

W3C Broken link checker
- Browser Extensions:
- Browser extensions like “Check My Links” for Google Chrome can help identify broken links on a webpage. These extensions highlight broken links and provide information about the HTTP status codes.
Browser Extensions
- Command Line Tools:
- For more technical users, command line tools like
wget or curl can be used to crawl a website and check for broken links. For example, you can use wget with the --spider option to simulate a web spider and check for broken links.

CMD Tools
- Content Management System (CMS) Plugins:
- If your website is built on a CMS like WordPress, there are plugins available that can automatically check for broken links. Examples include “Broken Link Checker” for WordPress.
- Site Crawlers:
- Dedicated website crawling tools, such as Screaming Frog SEO Spider or Xenu’s Link Sleuth, can analyze your entire website for broken links. These tools provide detailed reports on broken links, redirects, and other issues.
- Manually Check Links:
- Manually reviewing your website’s content and clicking on each link to verify its functionality can be time-consuming, but it allows for a thorough inspection.
- Regular Monitoring:
- Set up regular monitoring for broken links, either manually or using automated tools, to ensure that new broken links are promptly identified and fixed.
How To Fix Broken Links?
Fixing broken links involves identifying the broken links on your website and updating them to point to the correct URLs or removing them if the content is no longer available. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to fix broken links:
1. Identify Broken Links:
Manual Check:
- Manually review your website’s content and click on each link to identify broken ones.
- Check for broken links in critical areas, such as navigation menus, important pages, and sitemaps.
Online Tools:
Browser Extensions:
- Use browser extensions like “Check My Links” for Google Chrome, which highlights broken links on a webpage.
2. Update or Remove Broken Links:
Once you’ve identified broken links, take the following actions:
Update Links:
- If the content still exists but has a new URL, update the link with the correct URL.
- Ensure that the updated URLs are accessible and functional.
Remove Links:
- If the linked content no longer exists or is irrelevant, consider removing the broken links.
- Removing broken links can improve user experience and prevent search engines from penalizing your site.
3. Redirects:
Implement Redirects:
- If the linked content has been moved to a new location, consider setting up redirects.
- Use 301 redirects (permanent) for moved or updated content.
4. Regular Maintenance:
Schedule Regular Checks:
- Regularly check for broken links on your website. This can be done manually or using automated tools.
- Set up periodic checks to identify and fix new broken links promptly.
5. Use Relative Paths:
Use Relative Paths:
- When linking to pages within your own website, use relative paths instead of absolute URLs. Relative paths are less prone to breaking when content is moved.
6. Implement Custom 404 Page:
Custom 404 Page:
- Create a custom 404 error page that provides helpful information and navigation options for users who encounter broken links.
- This enhances the user experience and encourages users to stay on your site.
7. Monitor Analytics:
Analyze User Behavior:
- Monitor your website analytics to understand user behavior when encountering broken links.
- Identify high-traffic pages with broken links for priority fixing.
8. Use Webmaster Tools:
Utilize Webmaster Tools:
- Regularly check webmaster tools for insights into crawl errors and broken links reported by search engines.
By regularly monitoring and addressing broken links, you can enhance user experience, maintain a healthy website, and positively impact your site’s search engine rankings.
Conclusion
Maintaining a website’s link structure is crucial for a positive user experience and SEO performance. Broken links disrupt this structure, impacting ranking and traffic. By understanding the causes and proactively identifying and fixing broken links, website owners can ensure smooth navigation, user satisfaction, and a strong online presence. Regular audits and proactive maintenance are key to avoiding the pitfalls of broken links.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...