Understanding Data Attribute Types | Qualitative and Quantitative
Last Updated :
11 Feb, 2024
When we talk about data mining, we usually discuss knowledge discovery from data. To learn about the data, it is necessary to discuss data objects, data attributes, and types of data attributes. Mining data includes knowing about data, finding relations between data. And for this, we need to discuss data objects and attributes.
Data objects are the essential part of a database. A data object represents the entity. Data Objects are like a group of attributes of an entity. For example, a sales data object may represent customers, sales, or purchases. When a data object is listed in a database they are called data tuples.
What are Data Attributes?
- Data attributes refer to the specific characteristics or properties that describe individual data objects within a dataset.
- These attributes provide meaningful information about the objects and are used to analyze, classify, or manipulate the data.
- Understanding and analyzing data attributes is fundamental in various fields such as statistics, machine learning, and data analysis, as they form the basis for deriving insights and making informed decisions from the data.
- Within predictive models, attributes serve as the predictors influencing an outcome. In descriptive models, attributes constitute the pieces of information under examination for inherent patterns or correlations.
We can say that a set of attributes used to describe a given object are known as attribute vector or feature vector.
Examples of data attributes include numerical values (e.g., age, height), categorical labels (e.g., color, type), textual descriptions (e.g., name, description), or any other measurable or qualitative aspect of the data objects.
Types of attributes:
This is the initial phase of data preprocessing involves categorizing attributes into different types, which serves as a foundation for subsequent data processing steps. Attributes can be broadly classified into two main types:
- Qualitative (Nominal (N), Ordinal (O), Binary(B)).
- Quantitative (Numeric, Discrete, Continuous)
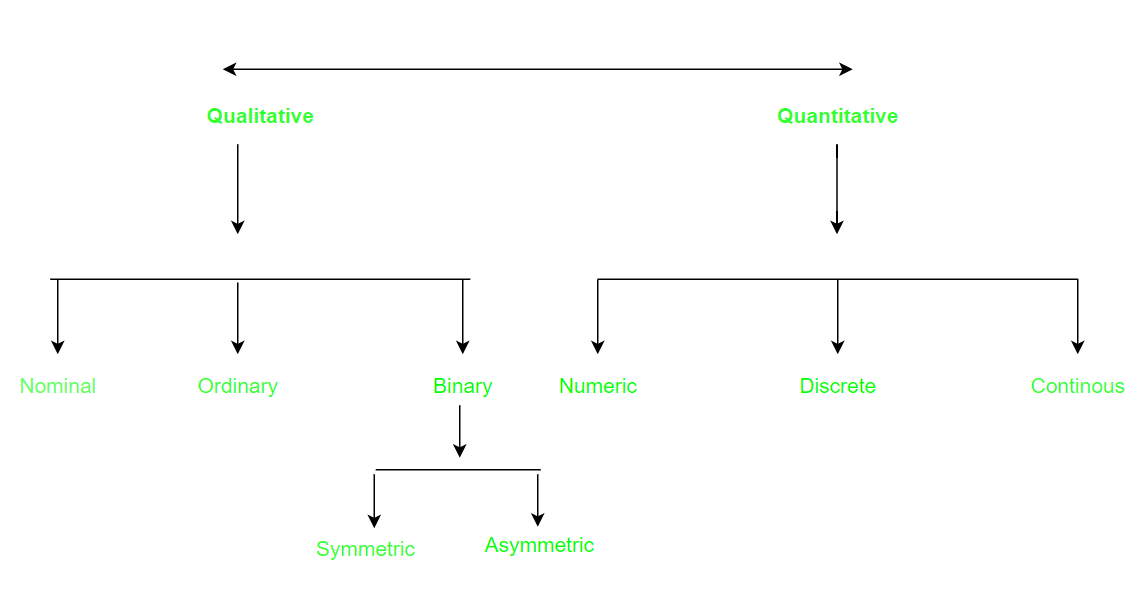
Qualitative Attributes:
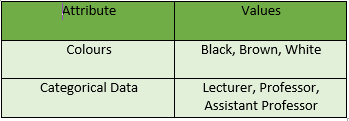
1. Nominal Attributes :
Nominal attributes, as related to names, refer to categorical data where the values represent different categories or labels without any inherent order or ranking. These attributes are often used to represent names or labels associated with objects, entities, or concepts.
Example :
2. Binary Attributes: Binary attributes are a type of qualitative attribute where the data can take on only two distinct values or states. These attributes are often used to represent yes/no, presence/absence, or true/false conditions within a dataset. They are particularly useful for representing categorical data where there are only two possible outcomes. For instance, in a medical study, a binary attribute could represent whether a patient is affected or unaffected by a particular condition.
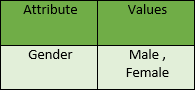
- Symmetric:In a symmetric attribute, both values or states are considered equally important or interchangeable. For example, in the attribute “Gender” with values “Male” and “Female,” neither value holds precedence over the other, and they are considered equally significant for analysis purposes.
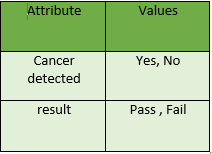
- Asymmetric: An asymmetric attribute indicates that the two values or states are not equally important or interchangeable. For instance, in the attribute “Result” with values “Pass” and “Fail,” the states are not of equal importance; passing may hold greater significance than failing in certain contexts, such as academic grading or certification exams
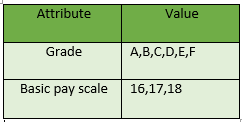
3. Ordinal Attributes : Ordinal attributes are a type of qualitative attribute where the values possess a meaningful order or ranking, but the magnitude between values is not precisely quantified. In other words, while the order of values indicates their relative importance or precedence, the numerical difference between them is not standardized or known.
Example:
Quantitative Attributes:
1. Numeric: A numeric attribute is quantitative because, it is a measurable quantity, represented in integer or real values. Numerical attributes are of 2 types: interval, and ratio-scaled.
- An interval-scaled attribute has values, whose differences are interpretable, but the numerical attributes do not have the correct reference point, or we can call zero points. Data can be added and subtracted at an interval scale but can not be multiplied or divided. Consider an example of temperature in degrees Centigrade. If a day’s temperature of one day is twice of the other day we cannot say that one day is twice as hot as another day.
- A ratio-scaled attribute is a numeric attribute with a fix zero-point. If a measurement is ratio-scaled, we can say of a value as being a multiple (or ratio) of another value. The values are ordered, and we can also compute the difference between values, and the mean, median, mode, Quantile-range, and Five number summary can be given.
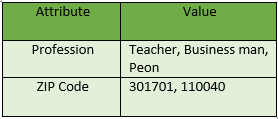
2. Discrete : Discrete data refer to information that can take on specific, separate values rather than a continuous range. These values are often distinct and separate from one another, and they can be either numerical or categorical in nature.
Example:
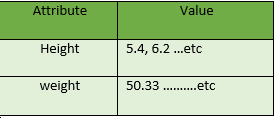
3. Continuous: Continuous data, unlike discrete data, can take on an infinite number of possible values within a given range. It is characterized by being able to assume any value within a specified interval, often including fractional or decimal values.
Example :
What is a target attribute?
A target attribute, also known as a target variable or response variable, is a specific attribute or column in a dataset that represents the outcome or prediction target in a supervised learning problem. In supervised learning, the goal is typically to predict or model the value of the target attribute based on the values of other attributes, known as predictor variables or features.
For example, in a dataset of housing prices, the target attribute might be the sale price of houses, while the predictor variables could include attributes such as the number of bedrooms, the square footage, and the location. The target attribute is what the model aims to predict or estimate based on the input features.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Q. What are data types of attributes?
Data types of attributes refer to the categories that describe the nature of the values they can take on within a dataset, including qualitative types such as nominal and ordinal, and quantitative types such as discrete and continuous.
Q. What is the difference between nominal and ordinal attributes?
Nominal attributes represent categories without any inherent order or ranking, while ordinal attributes have a meaningful sequence or ranking between values, but the magnitude between values is not precisely known.
Q. How do discrete and continuous attributes differ?
Discrete attributes represent countable values or whole numbers, while continuous attributes can take on any value within a range and are typically associated with measurements.
Q. What are attributes in warehouse?
In a data warehouse, attributes typically refer to the descriptive characteristics or properties of data entities, such as dimensions or features, which are used for analysis, reporting, and decision-making.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...