Data science is a field that involves analyzing and interpreting complex data to extract meaningful insights. Within this field, there are various roles that professionals can take on, each with its focus and responsibilities. These roles include positions such as Research Scientist, Data Scientist, Data Analyst, Machine Learning Engineer, Data Engineer, Business Intelligence Analyst, and Data Scientist/Consultant. Each role requires different skills and expertise, ranging from theoretical knowledge to practical application.
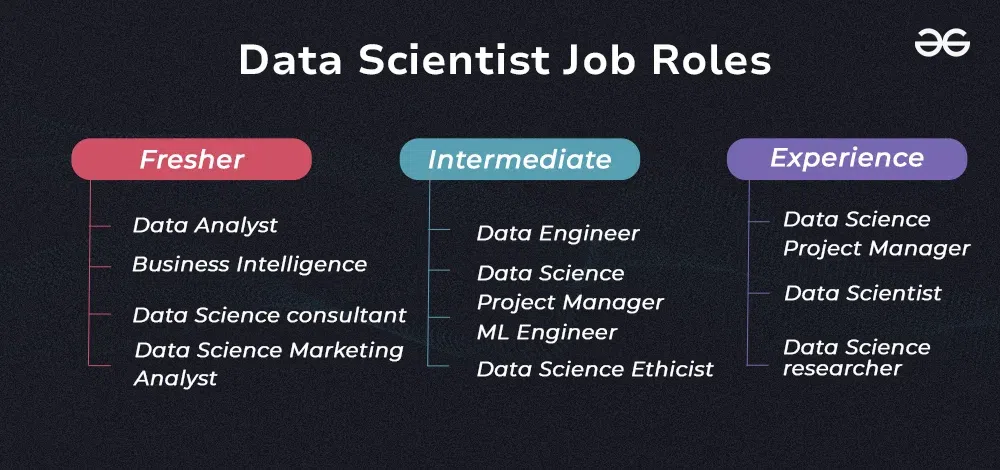
Types of Data Scientist Role
In this article we’ll delve into some of the Most Common Types of Data Scientist Roles to provide a better understanding of different professions and their scope in industry.
Types of Data Scientist Role
Data science encompasses a broad spectrum of roles that cater to different aspects of handling and analyzing data. Here’s a breakdown of the various types of data scientist roles:
1. Data Analyst
A data analyst is a professional who specializes in interpreting and analyzing data to extract valuable insights that can inform decision-making processes within an organization.
Responsibilities : Here’s a detailed explanation of the role:
- Data Collection and Cleaning: Data analysts are responsible for gathering data from various sources such as databases, spreadsheets, or APIs. They ensure that the collected data is accurate, complete, and free from errors by cleaning and preprocessing it. This involves identifying and correcting any inconsistencies or missing values in the data.
- Data Analysis: Once the data is cleaned and prepared, data analysts use statistical methods and analytical tools to analyze it. They identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data to uncover valuable insights. This analysis may involve calculating summary statistics, conducting exploratory data analysis, or performing more advanced statistical tests.
- Data Visualization: Data analysts often use data visualization techniques to communicate their findings effectively. They create charts, graphs, and dashboards to present the results of their analysis clearly and understandably. Visualization helps stakeholders, such as managers or executives, to interpret the data and make informed decisions based on the insights provided.
- Reporting: Data analysts are responsible for generating reports based on their analysis to share with stakeholders within the organization. These reports summarize key findings, highlight important trends, and provide recommendations for action. Reporting may involve creating written reports, slide presentations, or interactive dashboards depending on the needs of the audience.
- Decision Support: Ultimately, the goal of a data analyst is to provide decision support to stakeholders by offering insights derived from data analysis. Data analysts help organizations make data-driven decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations and actionable insights. They collaborate with other teams within the organization, such as marketing, finance, or operations, to address specific business challenges or opportunities.
2. Business Intelligence Analyst
Business intelligence analysts focus on extracting actionable insights from data to support business operations and strategy. They create reports, dashboards, and data visualizations to communicate findings to stakeholders effectively. Business intelligence analysts help organizations monitor performance, identify opportunities for growth, and optimize processes.
Responsibilities: Here’s a detailed explanation of the role:
- Data Analysis: Business Intelligence Analysts gather data from various sources within the organization and external sources, then analyze it to identify trends, patterns, and correlations. They use statistical analysis and data visualization techniques to present their findings in a clear and understandable manner.
- Reporting and Dashboard Creation: BI Analysts create reports and dashboards that summarize key metrics and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) for stakeholders. These reports help management and other decision-makers understand the current state of the business, track progress towards goals, and identify areas for improvement.
- Decision Support: BI Analysts provide decision support to stakeholders by translating complex data into actionable insights. They help stakeholders understand the implications of the data analysis and make informed decisions based on the insights provided. This may involve recommending strategic initiatives, identifying opportunities for cost savings or revenue growth, or optimizing business processes.
3. Data Science Consultant
Data scientists bridge the gap between data analysis and business strategy. They use advanced analytical techniques, such as machine learning and predictive modeling, to extract insights from data and solve complex problems. Data scientists also collaborate with stakeholders to understand business needs and develop data-driven solutions. As consultants, they may work with multiple clients across various industries to tackle diverse challenges related to data analysis and interpretation.
Responsibilities: Here’s a detailed explanation of the role:
- Data Analysis and Modeling: Data Scientist/Consultants analyze large datasets using statistical methods and machine learning techniques to extract meaningful insights. They develop predictive models, identify trends, and uncover patterns within the data to address specific business challenges or opportunities.
- Strategic Guidance: Data Scientist/Consultants provide strategic guidance to organizations based on their data analysis. They collaborate with stakeholders to understand business objectives and develop data-driven strategies and recommendations to achieve those objectives. This may involve identifying areas for optimization, forecasting future trends, or recommending new initiatives based on data insights.
- Communication and Collaboration: Data Scientist/Consultants communicate their findings and recommendations to stakeholders in a clear and understandable manner. They collaborate with cross-functional teams, including executives, managers, and subject matter experts, to ensure that data-driven insights are effectively integrated into decision-making processes across the organization.
4. Data Science Marketing Analyst
A Data Science Marketing Analyst blends marketing expertise with data science skills to extract customer insights and improve marketing campaigns.
Responsibilities: They use data science techniques to:
- Customer Segmentation: Divide the customer base into distinct groups based on shared characteristics. This allows for targeted marketing campaigns.
- Customer Behavior Analysis: Understand how customers interact with a brand or product, using data to predict future behavior.
- Marketing Campaign Optimization: Analyze the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and use data to optimize them for better results.
- Attribution Modeling: Identify which marketing channels are driving the most sales or conversions.
5. Data Engineer
A data engineer is a professional who designs, builds, and maintains the infrastructure required to manage and process large volumes of data within an organization.
Responsibilities: Here’s a detailed explanation of the role:
- Data Infrastructure Design: Data engineers are responsible for designing the architecture and infrastructure needed to store, process, and analyze data efficiently. They evaluate the organization’s data needs and design scalable solutions that can handle large volumes of data reliably. This involves selecting appropriate databases, data warehouses, and cloud services to meet the organization’s requirements.
- Data Pipeline Development: Data engineers build data pipelines that automate the process of ingesting, transforming, and loading data from various sources into the organization’s data storage systems. They design workflows that extract data from sources such as databases, APIs, or streaming platforms, transform it into a usable format, and load it into data warehouses or data lakes for analysis.
- Data Quality Assurance: Ensuring the quality and integrity of data is a crucial aspect of the data engineer’s role. Data engineers implement processes and checks to ensure that data is accurate, complete, and consistent. This may involve performing data validation, data cleansing, and error handling to identify and rectify any issues in the data.
6. Data Science Project Manager
A Data Science Project Manager is the glue that holds a data science project together. They are responsible for the overall success of the project, ensuring it’s delivered on time, within budget, and meets its goals.
Responsibilities: Here are some key aspects of their role:
- Project Planning & Execution: They define the project scope, break down tasks into a manageable timeline, and assign resources effectively. Think of them as the conductor of the data science orchestra.
- Stakeholder Management: They manage expectations and communicate progress to stakeholders, including business leaders, data scientists, and other team m mbers.
- Risk Management: They identify potential risks that could derail the project and develop mitigation plans to address them.
- Resource Management: They ensure the project has the right resources, including data scientists, engineers, and computing power.
- Technical Understanding: While they may not be coding themselves, they need a solid understanding of the data science process to make informed decisions.
7. Machine Learning Engineer
Machine learning engineers develop and deploy machine learning models to solve specific business problems. They work on tasks such as predictive modeling, pattern recognition, and natural language processing. Machine learning engineers need a strong understanding of algorithms and programming languages to build scalable and efficient machine learning solutions.
Responsibilities: Here’s a detailed explanation of the role:
- Model Development: Machine learning engineers develop algorithms and models that can learn from data and make predictions or decisions. They work on tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, and recommendation systems, using techniques such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
- Implementation and Deployment: Once a machine learning model is developed, machine learning engineers implement it into production environments. This involves integrating the model with existing systems, optimizing its performance, and deploying it to make predictions or automate decision-making processes in real-time.
- Continuous Improvement: Machine learning engineers are responsible for monitoring the performance of deployed models and continuously improving them over time. This may involve retraining models with new data, fine-tuning model parameters, or experimenting with different algorithms to achieve better results.
8. Data Science Ethicist
A Data Science Ethicist is a relatively new and evolving role. They focus on the ethical implications of data science projects, ensuring they are used responsibly and don’t cause harm.
Responsibilities: Here are some of their key areas of focus:
- Bias Detection & Mitigation: Data can be biased, and data science models can perpetuate that bias. A data science ethicist helps identify and mitigate bias in data and algorithms.
- Privacy Protection: Data science projects often involve sensitive data. The ethicist ensures data privacy regulations are followed and user privacy is protected.
- Algorithmic Fairness: They ensure algorithms are fair and don’t discriminate against certain groups. This might involve fairness audits or impact assessments.
- Transparency & Explainability: Data science models can be complex “black boxes”. The ethicist helps make models more transparent and understandable, so their decisions can be scrutinized.
9. Data Science Product Manager
A Data Science Product Manager is a unique role that bridges the gap between business, technology, and data. They are the glue that holds together the data science side of a product.
Responsibilities: Here’s what they typically do:
- Understanding Business Needs and User Experience: They listen to stakeholders and understand the business goals for a data science product. They also empathize with the target user and ensure the product is designed for their needs.
- Translating Needs into Data Solutions: Data Science PMs take those business goals and translate them into actionable data science projects. They identify what data is needed, how it will be used, and the success metrics for the product.
- Prioritizing the Backlog: There are always more data science projects than resources. The Data Science PM prioritizes the backlog, deciding which projects to tackle first based on their potential impact and feasibility.
- Collaboration is Key: They work closely with data scientists, data engineers, designers, and other stakeholders to ensure everyone is aligned on the product vision and goals.
- Communication is King: Data Science PMs need to communicate effectively with both technical and non-technical audiences. They explain complex data concepts to business leaders and translate technical jargon for users.
10. Data Scientist
A Data Scientist is the core technical expert on a data science project.
Responsibilities: They are responsible for the technical aspects of the project, using their programming skills and knowledge of machine learning to:
- Data Wrangling & Cleaning: They prepare the data for analysis, ensuring it’s accurate and usable for modeling.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): They get to know the data, identifying patterns, trends, and potential relationships.
- Model Building & Training: They develop and train machine learning models to solve specific problems or make predictions.
- Model Evaluation & Improvement: They evaluate how well the model performs and make adjustments to improve its accuracy.
- Communication & Visualization: They explain their findings and the model’s results to technical and non-technical audiences.
11. Data Science Researcher
A Data Science Researcher pushes the boundaries of the field, developing new methods, algorithms, and tools for data science. They are often employed by universities, research labs, or large tech companies.
Responsibilities: Here’s what a data science researcher might do:
- Fundamental Research: They investigate new theoretical concepts and approaches to data science problems.
- Algorithm Development: They develop new machine learning algorithms or improve existing ones.
- Publishing & Peer Review: They publish their research findings in academic journals and present them at conferences, contributing to the advancement of the field.
- Collaboration: They often collaborate with other researchers, data scientists, and computer scientists.
Types Of Data Scientist Roles – FAQ’s
1. What skills do I need to become a Data Analyst?
To become a data analyst, you’ll need strong analytical skills, proficiency in programming languages like SQL and Python, knowledge of statistical methods, and the ability to interpret data effectively. Additionally, having experience with data visualization tools and databases can be beneficial.
2. What’s the difference between a Data analyst and a Data scientist?
While both roles involve working with data, data analysts primarily focus on analyzing existing data to uncover insights and support decision-making, whereas data scientists often use advanced statistical and machine learning techniques to develop predictive models and solve complex problems.
3. What does a Data Engineer do?
Data engineers are responsible for building and maintaining the infrastructure needed to store, process, and analyze large volumes of data. They design data pipelines, ensure data quality and reliability, and collaborate with data scientists and analysts to ensure that data is accessible and usable for analysis.
4. How can I transition into a career in Data Science?
Transitioning into a career in data science often requires gaining relevant skills and experience. Consider pursuing online courses, bootcamps, or degree programs in data science or related fields. Additionally, gaining hands-on experience through internships, projects, or Kaggle competitions can help you build a strong portfolio and make yourself more attractive to employers.
5. What industries hire Data Scientists?
Data scientists are in demand across various industries, including technology, finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and manufacturing. Any industry that generates or collects data can benefit from hiring data scientists to analyze that data and extract valuable insights to drive business decisions and innovation.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...