The Architecture of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Last Updated :
07 May, 2024
Virtualization in cloud computing helps create virtual versions of hardware, such as desktop computers, with a virtual ecosystem of operating systems, storage, memory, and networking services. The virtualization architecture uses the same hardware to run multiple operating systems on the same machine and optimize their performance.
What is Virtualization?
Virtualization plays an important role and function in cloud computing. It helps in reducing the space or costs associated with the investment. This technology allows end users to run multiple desktop operating systems and applications simultaneously on the same hardware and software.
Virtualization in cloud computing simplifies the creation of virtual machines and makes it easier to run multiple machines. It also helps create a virtual ecosystem of server operating systems, multiple storage facilities, and multiple operating systems.
Cloud computing is an application or service associated with a virtual ecosystem. Such ecosystems can be public or private. Due to virtualization, the need for physical infrastructure can be reduced. The terms cloud computing and virtualization are now used interchangeably and are rapidly converging.
Important points of virtualization
There are some technologies in virtualization defined as follows:
- Virtual Machine: A virtual machine can be defined as a type of virtual machine that runs under the hypervisor of the computer.
- Hypervisor: It can be defined as a process running on real hardware. The virtual counterpart of the operating system is the underlying part that executes or emulates a virtual process.
- Container: They can be defined as a lightweight virtual machine that is a process of the same operating system (e.g. hypervisor).
- Virtualization software: This type of software helps in virtualizing the computer.
- Virtual Network: It is defined as a separate network and resides on the server. This type of network can be expanded to many servers.
What is Virtualization Architecture?
Virtualization Architecture is defined as a model that describes the concept of virtualization. The use of virtualization is important in cloud computing. In cloud computing, end users share data through an application called the cloud. However, end users can share their entire IT infrastructure with virtualization itself.

Architecture of the Virtualization
In the diagram above, virtualization includes virtual applications and virtual infrastructure services.
- The virtual application services help in application management, and the virtual infrastructure services can help in infrastructure management.
- Both services are integrated into the virtual data center or operating system. Virtual services can be used on any platform and programming environment. These services can be accessed from the local cloud or external cloud. In return, cloud users must pay a monthly or annual fee to the third party.
- This fee is paid to third parties for providing cloud services to end users, who in turn provide applications in different forms according to the needs of cloud end users.
- A hypervisor separates the operating system from the underlying hardware. It allows the host computer to run multiple virtual machines simultaneously and share the same computer resources.
Cloud computing and Virtualization Architecture
Virtualization in cloud computing helps create virtual versions of hardware such as desktop computers with a virtual ecosystem of operating systems, storage, memory, and networking services. Virtualization architecture uses the same hardware to run multiple operating systems on the same machine and optimize their performance.
Virtualization and virtualization architecture are important concepts in cloud computing. In fact, since the definition of cloud computing also includes virtual ecosystems, these terms are often used interchangeably. Whether the ecosystem is private (i.e., cloud) or public (public cloud), virtualization reduces the need for organizations to maintain physical (on-premises) infrastructure for their computing needs. With cloud computing and virtualization architecture, applications can be shared with many active users. With a public cloud like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure, these can be shared with multiple businesses.
Types of Virtualization Architectures
There are two main types of virtualization architectures: hosted and bare metal.
Hosted Architecture
In this type of configuration, first, the host operating system is installed on the hardware, then the software is installed. The software is a hypervisor or virtual machine (VM) that requires many guest operating systems or VMs to be installed on the hardware to set up the virtualization architecture. Once the hypervisor is in place, applications can be installed and run on the virtual machine as if they were installed on the physical machine.

Hosted Architecture
Bare Metal Architecture
In this architecture, the hypervisor is installed directly on the hardware, not on top of the operating system. Hypervisors and virtual machines are configured the same way as infrastructure. Bare metal virtualization architecture is designed for applications that provide real-time access or perform some form of data processing.
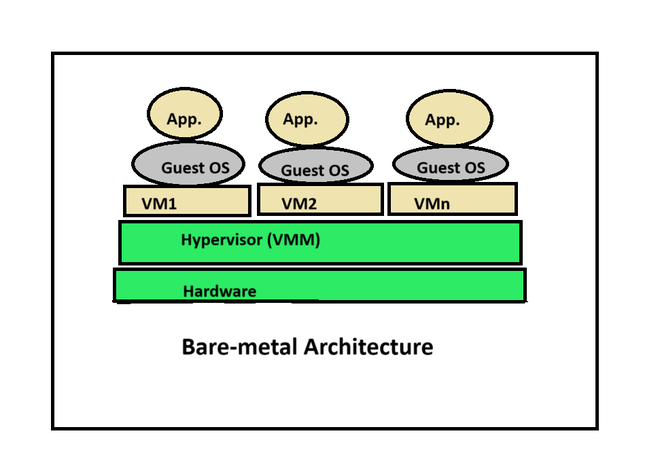
Bare-metal Architecture
More about Hypervisors in Virtualization Architecture
Virtualization is hypervisor based. A hypervisor separates the operating system and applications from the underlying computer hardware so that the host computer can run multiple virtual machines as guests and share physical resources such as network processor, memory space, and network bandwidth. A hypervisor allocates memory or storage services and distributes some of these services to each virtual machine according to the needs of the virtualization architecture.
- Type 1 hypervisors: Sometimes called bare metal hypervisors, run directly on top of the host system hardware. The bare metal hypervisor provides a high level of control and management. Their direct access to system hardware provides better performance, scalability and stability. Examples include: Microsoft Hyper-V, Citrix XenServer, VMware ESXi.
- Type 2 hypervisors: (also called management hypervisors) are installed on the host operating system rather than directly on the hardware like Type 1 hypervisors. All guest operating systems or virtual machines run on top of the hypervisor. The simplicity of the host operation is known to facilitate the installation and management of the project. But adding a layer of layering can limit functionality and introduce a security vulnerability. Example: VMware Workstation Pro, VMware Fusion, Oracle VirtualBox, Oracle Solaris Zones, Oracle VM Server for x86.
Benefits of a Virtualization Architecture
- Virtualization architecture provides cloud-native organizations with a flexible, cost-effective, and versatile way to run multiple virtual machines or systems using a single service or host. As a result, it provides efficient and economical deployment and reduces IT infrastructure costs.
- Since the host computer user can limit the number of users of virtual resources, the environment provides better control while also reducing energy and resource consumption.
- Virtualization also enables remote, anytime, anywhere access, which is essential for remote or isolated locations.
- It also reduces the need for physical equipment such as servers, resulting in more uptime and fewer interruptions, better error management, and more efficient and capable product balance. Resources can be replaced or removed as needed, providing business teams with greater scalability and agility.
- All major cloud service providers offer virtualization solutions based on a one-time payment model. This ensures that organizations only pay for resources that are actually used, not for resources that are not used or have no capacity or potential. As a result, they have more control over the weather budget and spending.
- Virtualization is also beneficial from a security perspective. You can configure tasks, devices, applications, etc. on each virtual machine. There may be more than one guest user who can run it. This extraction helps protect sensitive or business-critical data.
Virtualization and Containerization
The alternative to hypervisor-based virtualization in cloud computing is containerization. For example, operating system virtualization is an important volume-based virtualization approach. In this architecture, the operating system is set up to act as multiple separate systems, allowing distributed applications to be deployed and run without having to turn on the entire virtual machine for each system. Instead, multiple isolated machines (called volumes) run on a single host, each accessing a single key.
Like virtual machines, container is a way to create virtual packages. Essentially, a container is a lightweight virtual machine that is part of the same operating system instance or hypervisor. But virtualization is a way to run multiple operating systems on a single physical server. Containerization, on the other hand, is a way of running multiple applications on the same machine in a virtual machine. VMs are best suited for applications that require full-scale performance. Containers are a better choice for short-term projects that need to reduce the number of servers used by multiple applications.
Conclusion
Virtualization and virtualization architecture are important concepts in cloud computing. Virtualization and cloud computing work together to ensure you have the highest level of computing intelligence. It enables applications to be shared across multiple network threads between different companies and active users.
Virtualization in Cloud Computing – FAQs
How is virtualization becoming the foundation of cloud computing?
Cloud providers create and manage their own data centers. They create different virtual environments using basic hardware.
How does virtualization reduce costs?
Instead of running a single application on a single server, single server can be used to support multiple virtual machines, each running its own operating system and applications. This results in significantly higher hardware recycling rates and lower maintenance costs.
Is a virtualization platform needed to use the cloud?
Virtualization is used to deliver cloud service models including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Installing a virtualization platform is easier, more cost-effective, and more efficient.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...