System Bus Design
Last Updated :
02 Apr, 2023
Definition:
The electrically conducting path along which data is transmitted inside any digital electronic device. A Computer bus consists of a set of parallel conductors, which may be conventional wires, copper tracks on a PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD, or microscopic aluminum trails on the surface of a silicon chip. Each wire carries just one bit, so the number of wires determines the most significant data WORD the bus can transmit: a bus with eight wires can carry only 8-bit data words and hence defines the device as an 8-bit device.
- The bus is a communication channel.
- The characteristic of the bus is shared transmission media.
- The limitation of a bus is only one transmission at a time.
- A bus used to communicate between the major components of a computer is called a System bus.
Computer:
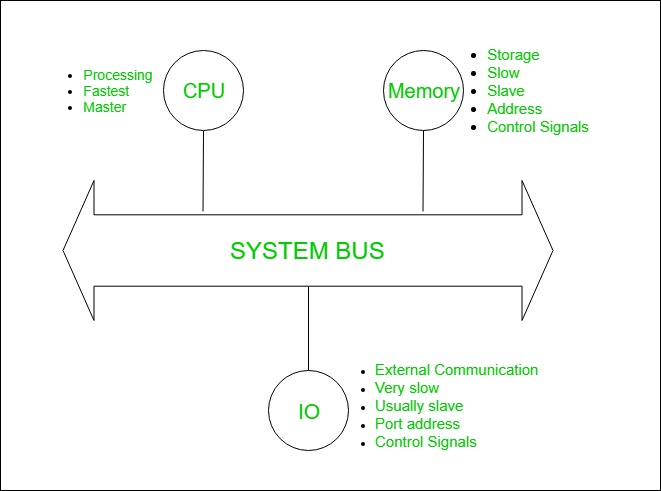
System bus contains 3 categories of lines used to provide the communication between the CPU, memory and IO named as:
1. Address lines (AL)
2. Data lines (DL)
3. Control lines (CL)
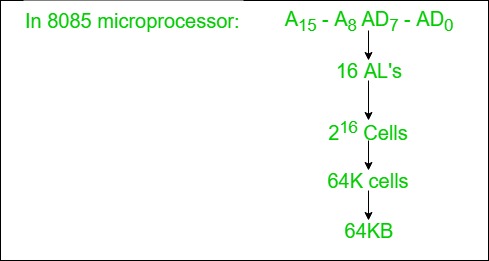
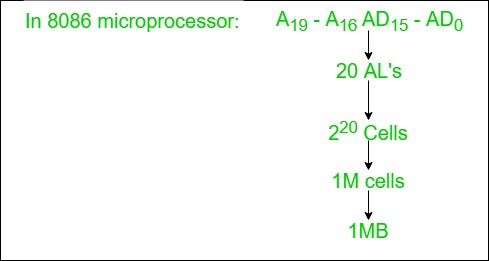
1. Address Lines:
- Used to carry the address to memory and IO.
- Unidirectional.
- Based on the width of an address bus we can determine the capacity of a main memory
Example:
2. Data Lines:
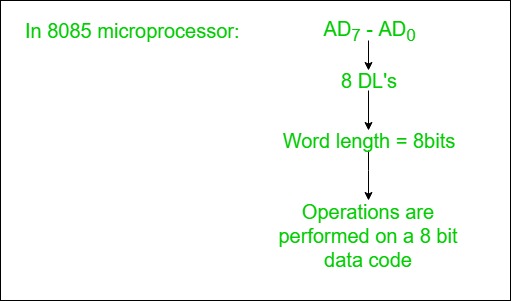
- Used to carry the binary data between the CPU, memory and IO.
- Bidirectional.
- Based on the width of a data bus we can determine the word length of a CPU.
- Based on the word length we can determine the performance of a CPU.
Example:
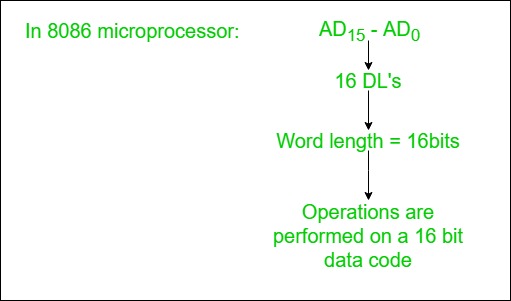
3. Control Lines:
- Used to carry the control signals and timing signals
- Control signals indicate the type of operation.
- Timing Signals are used to synchronize the memory and IO operations with a CPU clock.
- Typical Control Lines may include Memory Read/Write, IO Read/Write, Bus Request/Grant, etc.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...