Side-Side-Side or SSS is a fundamental rule in congruency of triangles. If the three sides of a triangle are equal to the corresponding three sides of any other triangle, then the two triangles are called congruent.
Definition of SSS
SSS Criterion, which stands for Side-Side-Side congruence postulate, is a rule in geometry which says that if all three sides of one triangle are equal to the three corresponding sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
In simpler terms, if you have two triangles, and the lengths of all their respective sides are equal, then those triangles are the same shape and size. This also means that all their angles will be the same.
For example, if you look at the triangles below and find that side AC is equal to side PQ, side CB is equal to side PR, and side AB is equal to side QR, then you can say that the two triangles are congruent.

So, in geometry notation, we write ∆ABC ≅ ∆XYZ, indicating that triangle ABC is congruent to triangle XYZ.
Congruence and Similarityof Triangle
Two figures are said to be congruent if they have the same shape and size.
Two figures having the same shape (and not necessarily the same size) are called similar figures.
All congruent figures are similar but the similar figures need not be congruent.
Two triangles are similar, if
- Their corresponding angles are equal
- Their corresponding sides are in the same ratio (or proportion).
The symbol ‘⁓’ stands for ‘is similar to’. The symbol ‘≅’ stands for ‘is congruent to’.
Two triangles are congruent if the sides and angles of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides and angles of the other triangle. Congruence of Triangles is proved using various rules.
- Note: It is necessary to correctly write the correspondence of vertices to write the congruence of triangles in symbolic form.
What is SSS Congruence Rule?
Theorem (SSS Congruency Rule):
If three sides of a triangle are equal to the three sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
The above theorem means that if all the three sides of a triangle are same as all the three corresponding sides of another triangle, then both the triangles have all 3 corresponding equal and all angles to be equal too as corresponding parts of congruent triangles.
SSS congruence rule is one of the ways to verify two or more triangles are exactly the same. By ‘same’ we mean that the triangles have all three corresponding sides equal to that of one another and that all the corresponding angles are equal too.
SSS Criterion
SSS stands for Side – Side – Side.
By SSS, we mean that we need to consider all three sides of the the given triangle to compare two given triangles to check for their congruency or similarity.
SSS Congruence Rule Proof
To prove the SSS congruence rule, pick any side of the first triangle and measure it. Match it with all three sides of the other triangle and check if it matches any side. If it does mark a line on the respective sides of both triangles.
Keep doing the step for all three sides of the first triangle. This proves SSS congruence rule. Incase no side of second triangle matches any one side of first triangle, then both triangles are not congruent.
SSS Similarity Condition
If in two triangles, the sides of one triangle are proportional to (i.e., in the same ratio of ) the sides of the other triangle, then their corresponding angles are equal and hence the two triangles are similar.
This criterion is referred to as the SSS (Side–Side–Side) similarity criterion for two triangles.
SSS similarity formula is,
(Side 1 of triangle 1)/(Side 1 of triangle 2) = (Side 2 of triangle 1)/(Side 2 of triangle 2) = (Side 3 of triangle 1)/(Side 3 of triangle 2) = constant
The symbol ‘⁓’ stands for ‘is similar to’.
Say we have two triangles, ΔABC and ΔXYZ.
According to SSS similarity criterion,

SSS Similarity Condition
if PQ/ED = QR/DF = AC/XZ then ΔABC ~ ΔXYZ.
From this result, we can can say that, ∠P = ∠E, ∠Q = ∠D and ∠R = ∠F
How to Apply SSS Congruence Rule?
To check if you can apply the SSS Congruence Rule to prove whether triangles are congruent, check the given and the triangles.
If it is given or if you can measure or verify all three sides of a triangle to be equal to the corresponding three sides of another triangle, then you can apply the SSS Congruence Rule to prove them to be congruent to each other.
Examples on SSS Congruence Rule
Example 1: Given: AB = DE, BC = EF, and AC = DF. To prove: ∆ABC ≅ ∆DEF.

SSS Congruence Example 1
Solution:
It is given in the question and hence, we know that the three sides of both the triangles are of the same size and length.
If we superimpose both the triangles, DE will be placed on AB, EF will be placed on BC, and DF will be placed on AC.
Which makes it
AB = DE [side]
BC = EF [side]
and AC = DF [side]
Therefore, we can say that ∆ABC ≅ ∆DEF
Hence proved.
Example 2: ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle and the line segment AD is the angle bisector of ∠A. Prove that ∆ADB ≅ ∆ADC.
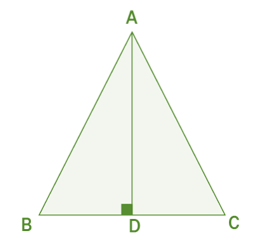
SSS Congruence Example 2
Solution:
We are given that ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle
Therefore, AB = AC [side]
The side AD is common in both the triangles ∆ADB and ∆ADC.
Therefore, AD = AD [side]
As the line segment AD is the angle bisector of the angle A then it divides the line segment BC into two equal parts BD and CD.
Therefore, BD =CD and AB = AC [side]
Hence, according to the SSS congruence rule, the two triangles are congruent.
∴ ∆ADB ≅ ∆ADC
Example 3: Two points P and Q are on the opposite sides of the line segment AB. The points P and Q are equidistant from points A and B. Can you prove that ∆PAQ is congruent to the ∆PBQ?

SSS Congruence Example 3
Solution:
As the two points, P and Q are equidistant from the endpoints of the line segment AB.
Therefore, AP =BP and AQ = BQ
Now the side PQ is common in both the triangles ∆PAQ and ∆PBQ.
Therefore according to the SSS postulate, the two triangles are congruent.
∴ ∆PAQ ≅ ∆PBQ
Example 4: In the given figure, AB = BC and AD = CD. Show that BD bisects AC at right angles.

SSS Congruence Example 4
Solution:
Here, we need to prove that ∠BEA = ∠BEC = 90° and AE = EC.
In ∆ABD and ∆CBD,
It is given that,
AB = BC [side 1]
AD = CD [side 2]
and since BD is common for both triangles,
hence BD = BD [side 3]
By SSS congruency rule both triangles are congruent.
∴ ∆ABD ≅ ∆CBD
As we know that CPCT are equal, hence ∠ABD = ∠CBD
Now, in ∆ABE and ∆CBE,
It is given in question, AB = BC [side 1]
We proved above that ∠ABD = ∠CBD [angle]
and since BE is common for both triangles, BE = BE [side 2]
By SAS congruency rule both triangles are congruent.
∴ ∆ABE≅ ∆CBE
As we know that CPCT are equal, hence ∠BEA = ∠BEC
And since ∠BEA and ∠BEC are linear pairs,
∠BEA +∠BEC = 180°
2(∠BEA) = 180° (∵∠BEA = ∠BEC)
∠BEA = 180°/2 = 90° = ∠BEC
As we know that CPCT are equal, hence AE = EC
Hence, BD is a perpendicular bisector of AC.
Hence proved.
Practice Questions on SSS Congruence Rule
Question 1: Triangle PQR is an isosceles triangle and the line segment PM is the angle bisector of the angle P. Prove that ∆PMR is congruent to the ∆PMQ?
Question 2: Two points A and B are on the opposite sides of the line segment PQ. The points A and B are equidistant from points P and Q. Prove that ∆PAQ is congruent to the ∆PBQ?
FAQs on SSS Congruence Rule
What does SSS stands for?
SSS congruency condition stands for Side-Side-Side rule.
What are the Rules of Congruency?
There are 5 main rules of congruency for triangles:
- SSS Criterion: Side-Side-Side
- SAS Criterion: Side-Angle-Side
- ASA Criterion: Angle-Side- Angle
- AAS Criterion: Angle-Angle-Side
- RHS Criterion: Right angle- Hypotenuse-Side
What is SSS congruency of triangles?
If all the three sides of one triangle are equivalent to the corresponding three sides of the second triangle, then the two triangles are said to be congruent by SSS rule.
What is difference between SAS and SSS?
SAS and SSS congruence rules are the triangle congruence rules.
- Full form of SAS is “side-angle-side”.
- Full form of SSS is “side-side-side.”
- In the SAS, two sides and the angle between them in a triangle are equal to the corresponding two sides and the angle between them in another triangle.
- In the SSS, all three sides of one triangle are equal to the three corresponding sides of another triangle.
What does CPCT in math mean?
Full form of CPCT is Corresponding parts of Congruent triangles. After proving triangles as congruent, the remaining dimensions of the triangles can be predicted without actually measuring the sides and angles of a triangle.
What is SSS, SAS, ASA, and AAS?
The 4 different triangle congruence theorems are:
- SSS(Side-Side-Side)
- SAS(Side-Angle-Side)
- ASA(Angle-Side-Angle)
- AAS(Angle-Angle-Side)
What is the Side Side Side Rule?
SSS rule states that, “if three sides of one triangle are equal to three sides of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent.”
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...