Shortest cycle in an undirected unweighted graph
Last Updated :
18 Mar, 2022
Given an undirected unweighted graph. The task is to find the length of the shortest cycle in the given graph. If no cycle exists print -1.
Examples:
Input:
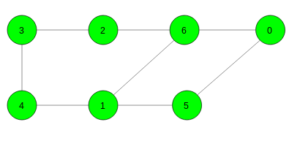
Output: 4
Cycle 6 -> 1 -> 5 -> 0 -> 6
Input:
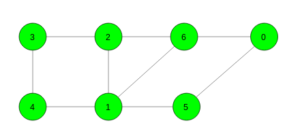
Output: 3
Cycle 6 -> 1 -> 2 -> 6
Prerequisites: Dijkstra
Approach: For every vertex, we check if it is possible to get the shortest cycle involving this vertex. For every vertex first, push current vertex into the queue and then it’s neighbours and if the vertex which is already visited comes again then the cycle is present.
Apply the above process for every vertex and get the length of the shortest cycle.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 100200
vector<int> gr[N];
void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].push_back(y);
gr[y].push_back(x);
}
int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
int ans = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
vector<int> dist(n, (int)(1e9));
vector<int> par(n, -1);
dist[i] = 0;
queue<int> q;
q.push(i);
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int child : gr[x]) {
if (dist[child] == (int)(1e9)) {
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
par[child] = x;
q.push(child);
}
else if (par[x] != child and par[child] != x)
ans = min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
if (ans == INT_MAX)
return -1;
else
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int n = 7;
Add_edge(0, 6);
Add_edge(0, 5);
Add_edge(5, 1);
Add_edge(1, 6);
Add_edge(2, 6);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
Add_edge(4, 1);
cout << shortest_cycle(n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static final int N = 100200;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector<Integer>[] gr = new Vector[N];
static void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].add(y);
gr[y].add(x);
}
static int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, (int) 1e9);
int[] par = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(par, -1);
dist[i] = 0;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(i);
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
int x = q.poll();
for (int child : gr[x])
{
if (dist[child] == (int) (1e9))
{
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
par[child] = x;
q.add(child);
} else if (par[x] != child && par[child] != x)
ans = Math.min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
if (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
return -1;
else
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
gr[i] = new Vector<>();
int n = 7;
Add_edge(0, 6);
Add_edge(0, 5);
Add_edge(5, 1);
Add_edge(1, 6);
Add_edge(2, 6);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
Add_edge(4, 1);
System.out.println(shortest_cycle(n));
}
}
|
Python3
from sys import maxsize as INT_MAX
from collections import deque
N = 100200
gr = [0] * N
for i in range(N):
gr[i] = []
def add_edge(x: int, y: int) -> None:
global gr
gr[x].append(y)
gr[y].append(x)
def shortest_cycle(n: int) -> int:
ans = INT_MAX
for i in range(n):
dist = [int(1e9)] * n
par = [-1] * n
dist[i] = 0
q = deque()
q.append(i)
while q:
x = q[0]
q.popleft()
for child in gr[x]:
if dist[child] == int(1e9):
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x]
par[child] = x
q.append(child)
elif par[x] != child and par[child] != x:
ans = min(ans, dist[x] +
dist[child] + 1)
if ans == INT_MAX:
return -1
else:
return ans
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 7
add_edge(0, 6)
add_edge(0, 5)
add_edge(5, 1)
add_edge(1, 6)
add_edge(2, 6)
add_edge(2, 3)
add_edge(3, 4)
add_edge(4, 1)
print(shortest_cycle(n))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static readonly int N = 100200;
static List<int>[] gr = new List<int>[N];
static void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].Add(y);
gr[y].Add(x);
}
static int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
int ans = int.MaxValue;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int[] dist = new int[n];
fill(dist, (int) 1e9);
int[] par = new int[n];
fill(par, -1);
dist[i] = 0;
List<int> q = new List<int>();
q.Add(i);
while (q.Count!=0)
{
int x = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
foreach (int child in gr[x])
{
if (dist[child] == (int) (1e9))
{
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
par[child] = x;
q.Add(child);
} else if (par[x] != child && par[child] != x)
ans = Math.Min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
if (ans == int.MaxValue)
return -1;
else
return ans;
}
static int[] fill(int []arr, int val)
{
for(int i = 0;i<arr.GetLength(0);i++)
arr[i] = val;
return arr;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
gr[i] = new List<int>();
int n = 7;
Add_edge(0, 6);
Add_edge(0, 5);
Add_edge(5, 1);
Add_edge(1, 6);
Add_edge(2, 6);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
Add_edge(4, 1);
Console.WriteLine(shortest_cycle(n));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var N = 100200;
var gr = Array.from(Array(N),()=>Array());
function Add_edge(x, y)
{
gr[x].push(y);
gr[y].push(x);
}
function shortest_cycle(n)
{
var ans = 1000000000;
for(var i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
var dist = Array(n).fill(1000000000);
var par = Array(n).fill(-1);
dist[i] = 0;
var q = [];
q.push(i);
while (q.length!=0)
{
var x = q[0];
q.shift();
for(var child of gr[x])
{
if (dist[child] == 1000000000)
{
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
par[child] = x;
q.push(child);
} else if (par[x] != child && par[child] != x)
ans = Math.min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
if (ans == 1000000000)
return -1;
else
return ans;
}
function fill(arr, val)
{
for(var i = 0;i<arr.length;i++)
arr[i] = val;
return arr;
}
var n = 7;
Add_edge(0, 6);
Add_edge(0, 5);
Add_edge(5, 1);
Add_edge(1, 6);
Add_edge(2, 6);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
Add_edge(4, 1);
document.write(shortest_cycle(n));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O( |V| * (|V|+|E|)) for a graph G=(V, E)
Memory Complexity: O(V^2) for a graph G=(V, E)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...