scipy stats.kurtosistest() function | Python
Last Updated :
01 Nov, 2019
scipy.stats.kurtosistest(array, axis=0) function test whether the given data set has normal kurtosis (Fisher or Pearson) or not.
What is Kurtosis ?
It is the fourth central moment divided by the square of the variance. It is a measure of the “tailedness” i.e. descriptor of shape of probability distribution of a real-valued random variable. In simple terms, one can say it is a measure of how heavy tail is compared to a normal distribution.
Its formula –
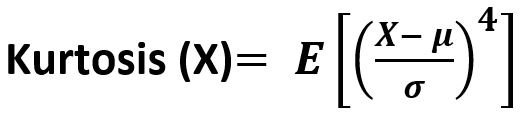
Parameters :
array : Input array or object having the elements.
axis : Axis along which the kurtosistest is to be computed. By default axis = 0.
Returns : Z-score (Statistics value) and P-value for the normally distributed data set.
Code #1:
from scipy.stats import kurtosistest
import numpy as np
import pylab as p
x1 = np.linspace( -5, 5, 1000 )
y1 = 1./(np.sqrt(2.*np.pi)) * np.exp( -.5*(x1)**2 )
p.plot(x1, y1, '*')
print( '\nKurtosis for normal distribution :\n', kurtosistest(y1))
|
Output :
 Kurtosis for normal distribution :
KurtosistestResult(statistic=-2.2557936070461615, pvalue=0.024083559905734513)
Kurtosis for normal distribution :
KurtosistestResult(statistic=-2.2557936070461615, pvalue=0.024083559905734513)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...