sciPy stats.gmean() function | Python
Last Updated :
19 Aug, 2021
scipy.stats.gmean(array, axis=0, dtype=None) calculates the geometric mean of the array elements along the specified axis of the array (list in python).
It’s formula –
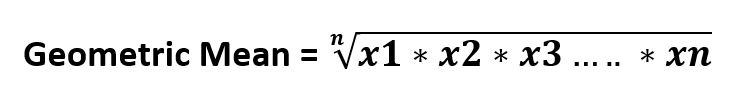
Parameters :
array: Input array or object having the elements to calculate the geometric mean.
axis: Axis along which the mean is to be computed. By default axis = 0
dtype: It sets the type of returned element.
Returns : Geometric mean of the array elements based on the set parameters.
Code #1:
Python3
from scipy.stats.mstats import gmean
arr1 = gmean([1, 3, 27])
print("Geometric Mean is :", arr1)
|
Output:
Geometric Mean is : 4.32674871092
Code #2: With multi-dimensional data
Python3
from scipy.stats.mstats import gmean
arr1 = [[1, 3, 27],
[3, 4, 6],
[7, 6, 3],
[3, 6, 8]]
print("Geometric Mean is :", gmean(arr1))
print("\nGeometric Mean is with default axis = 0 : \n",
gmean(arr1, axis = 0))
print("\nGeometric Mean is with default axis = 1 : \n",
gmean(arr1, axis = 1))
|
Output:
Geometric Mean is : [ 2.81731325 4.55901411 7.89644408]
Geometric Mean is with default axis = 0 :
[ 2.81731325 4.55901411 7.89644408]
Geometric Mean is with default axis = 1 :
[ 4.32674871 4.16016765 5.01329793 5.24148279]
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...