In this article, we will study remote sensing which has its importance in today’s era and helps in many ways in the monitoring and detection of the area’s physical characteristics with radiation and reflection. Remote – Something which is far away, Sensing – Getting information or getting data; remote sensing is getting or collecting information from far away or without being in contact with the object. The characteristics of an area are monitored with the radiation. It means it is the acquisition of information regarding any object without being in touch with that object- it means acquiring information from a distance, typically from aircraft or satellites.
This technology is used in various fields – geography, geology, hydrology, etc. It gives a large area of coverage to find information regarding the large area and more objects. To understand the weather assessment, large land area use, ocean use, and assessment are provided with this technology.
What is Remote Sensing?
Remote sensing is a technology for acquiring information about the earth’s surface without actually being in contact with it. This is done by sensing and recording reflection or emitted energy & processing, analyzing, and applying that information. In this technology, special cameras collect images from the objectives and then sense the images accordingly to provide information and sense things about the earth.
It is the science & art of obtaining information about an object, area, or phenomenon (earth’s surface) through the analysis of data acquired by a device that is not in direct contact with the object, area, or phenomena under the investigation. It helps in essential global matters such as climate change, global warming, etc.
In other words, remote sensing can be defined as the science and art of obtaining information about an object, area, or phenomenon through satellite. The science & art of acquiring information about an object without entering into contact with it, by sensing or recording the reflected or emitted energy and processing, analyzing, and applying that information in remote sensing.

Remote Sensing
There are a number of remote sensing satellites that different countries have launched into the space, in which some of them are:
- IRS (Indian remote sensing satellite)
- Sputnik 1 (Russia)
- Explorer 1 (USA)
By measuring the radiation that a region emits and reflects from a distance (usually from a satellite or aeroplane), remote sensing is the process of identifying and keeping track of the physical properties of a location. Remotely sensed photos are captured by specialized cameras and are used by scientists to “sense” the Earth.
Examples include: Without going to the ocean below, sonar equipment aboard ships may be utilized to take photographs of the seafloor; Observing changes in agriculture or woods, as well as the expansion of cities, over a period of years or decades.
Components
There are three essential components of remote sensing system –
- Remote sensing platforms
- Remote sensing sensors
- Remote sensing orbits
Remote Sensing Platforms
A platform is the vehicle or carrier for remote sensors. A platform is needed to hold the instrument and there are three types of platforms in Remote Sensing –
- Ground based platform
- Airborne platforms
- Space borne platform

Remote Sensing Platforms
1. Ground Based Platform
Ground based platform used to record detail information about the surface very closely. These are the ground level platforms such as cranes and towers. Some example of ground-based platform are:
- Ground vehicle
- Tower
- Air balloon
- Kite
The height of ground-based platform is up to 50 m or in the other words we can say that the ground-based platforms are found above 50 m from the Earth surface.
2. Airborne Platforms
They are used to collect very detailed images and facilities the collection of data over any portion of Earth’s surface at any time but it is very expensive platform as compared to ground-based platforms. The height of airborne platform is above 50 km from earth surface. These are the aerial platforms such as :
- Aeroplane
- High altitude aircraft
- Helicopters
3.Space Borne Platform
Some examples of space borne platform are as follows:
- Rocket satellite space shuttle whose height is 250 to 300 km above from the Earth surface
- Space station which whose height is 300 to 400 km
- Low level satellite which is also known as polar satellite whose height is 700 to 1500 km
- High level satellites which are also known as geostationary satellites whose height is 36000 km above the Earth’s surface.
Note: Satellites are objects which revolve around another object in this case the earth is another object.
Remote Sensing Sensors
Remote sensors collect data by collecting the energy which is reflected from the Earth, it is based on sensor technology to detect, in order to observe the target the sensors are needed and classify the object. The classification of sensors are as follows:
- Passive Sensors: They detect natural energy(radiation) that is emitted or reflected by the object or scene being observed. Reflected sunlight is the most common source of radiation measured by passive sensors. The passive sensors detect the energy which is reflected from the environment.
- Active sensors: They transmit their own signal and measure the energy that is reflected and transmitted back or scatter back from the target. For example, radar sonar. So in general , they provide their own source of energy to illuminate the object which they observe.
Remote Sensing Orbits
In remote sensing, orbits play one of the major components of remote sensing. The path followed by a satellite is referred to as its orbit. Orbit selection can vary in terms of altitude (their height above the Earth’s surface) and their orientation and rotation relative to the Earth. Overall, low earth orbit is the best orbit for the purpose of remote sensing which is commonly used for communication and remote sensing.
Types of remote sensing orbits are as follows:
- Geostationary orbits
- Polar Orbit
- Sun -Synchronous
1. Geostationary Orbit
Satellites at very high altitudes, which view the same portion of the Earth’s surface at all times have geostationary orbits. These geostationary satellites, at altitudes of approximately 36,000 kilometers, revolve at speeds which match the rotation of the Earth so they seem stationary, relative to the Earth’s surface. This allows the satellites to observe and collect information continuously over specific areas. Weather and communications satellites commonly have these types of orbits.
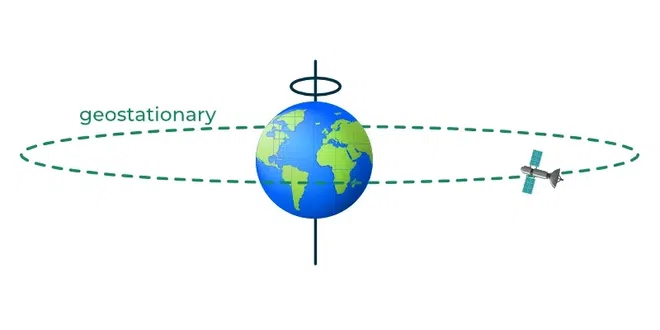
Geostationary Orbits
2. Polar Orbit
A polar orbit travels north-south over the poles and takes approximately an hour and a half for a full rotation. As a result, a satellite can observe the entire Earth’s surface (off-nadir) in the time span of 24 hours. Almost all the satellites that are in a polar orbit are at lower altitudes. Plus, they are often used for applications such as monitoring crops, forests and even global security.
.webp)
Polar Orbit
3. Sun-Synchronous Orbit
These orbits allow a satellite to pass over a section of the Earth. Since there are 365 days in a year and 360 degrees in a circle, it means that the satellite has to shift its orbit by approximately one degree per day. These satellites orbit at an altitude between 700 to 800 km.
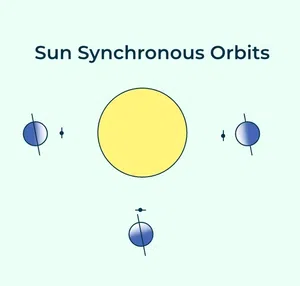
Sun Synchronous Orbit
Types of Remote Sensing
There are two type of remote sensing sensors which is based on the sensors are as follows:
- Passive sensors
- Active sensors
Passive Sensors
Passive sensors detect natural energy(radiation) that is emitted or reflected by the object or scene being observed. Reflected sunlight is the most common source of radiation measured by passive sensors. Sensing done via active sensors is called active sensing. For excitation, they often need extra electrical power. Only when the energy that naturally occurs is available can passive sensors be utilized to detect it, during the day can passive sensors gather data, electromagnetic energy is measured by the passive sensor.
The passive sensor is defenseless against an invading force. Sensors that are passive wait patiently for data requests. As a result of the stimulation, the passive sensor’s transducer causes a change in a passive electrical quantity like capacitance, resistance, or inductance.
The passive sensor measures utilizing EM radiation that is naturally emitted within its field of view. Satellites used for remote sensing, such as SPOT-1 and LANDSAT-1, are examples of passive sensors.
Active Sensors
Active sensors transmit their own signal and measure the energy that is reflected and transmitted back or scatter back from the target. For example, radar sonar. Sensing done via passive sensors is called passive sensing. A transducer that is an active sensor directly produces electric current or voltage in response to external stimulus. The active sensor produces its own electromagnetic (EM) energy, transmits it toward the earth, and then collects energy reflected back from the planet. Electromagnetic (EM) radiation that has been received is used for measurement.
They self-destructs during hijack attempts and can take measurements at any time. Electromagnetic energy is measured and transmitted by active sensors. Regardless of whether the on-duty employees want the data or not, an active sensor actively communicates measurement to ground stations. It provides their own energy source for illumination. Example of active sensor like communication satellite, earth observation satellite, LISS -1, etc.
Working
The various process involved in remote sensing is given as follows:
- Energy source – The first requirement for remote sensing is to have an energy source which illuminate or provide electromagnetic energy to the target of interest.
- Radiation and atmosphere – As the energy travels from its source to the target, it will come in contact with or interact with the atmosphere it passes through; this interaction may take place a second as the energy travels from the target to the sensor.
- Interaction with the target – Once the energy makes it way to the target through the atmosphere, it interacts with the target depending upon the properties of both the target & radiation
- Recording of energy by the sensors – After the energy has been scattered by, emitted from the target, we require a sensor (remote-not in contact with the target) to collect and record the electromagnetic radiation.
- Transmission, reception and processing –The energy required by the sensors has to be transmitted, often in electronic form, to receive and processing section where the data are produced into an image (hard copy & digital).
- Interpretation and analysis –The proceed image is interpreted in two types visually and digitally. To extract information about the target which was illuminated.
- Application – The final element of remote sensing process is achieved when we apply the information – we have been able to extract from the imagery about the target in order to better understand and reveal some new information.
- Electromagnetic radiation — electromagnetic radiation refers to the waves of the electromagnetic field, propagating through space, carrying electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.

Remote Sensing
Uses
Following are the major categories of problems wherein remote sensing is used:
- If there is forest fire then remote sensing can be used to map the area where fire is and accordingly supplies can be given by rapid forces to dismiss the fire.
- Even clouds are been tracked via remote sensing in places like UAE to support artificial rain.
- Volcanic eruption and losses from them are also monitored.
- Deforestation and growth of cities are also monitored using remote sensing.
- Discovery of unseen land terrains, oceans and other biomes can be done.
Advantages , Disadvantages and Applications
Some of the Advantages , Disadvantages and Applications are as follows:
Advantages
- Remote sensing allows coverage of very large areas which enables regional surveys on a variety of themes and identification of extremely large features.
- Remote sensing allows Repetitive coverage which comes in handy when collecting data on dynamic themes such as water, agricultural fields and so on.
- Remote sensing allows for easy collection of data over a variety of scales and resolutions.
- A single image captured through remote sensing can be analyzed and interpreted for use in various applications and purposes. There is no limitation on the extent of information that can be gathered from a single remotely sensed image.
- Remotely sensed data can easily be processed and analyzed fast using a computer and the data utilized for various purposes.
- Remote sensing is Unobstructed especially if the sensor is passively recording the electromagnetic energy reflected from or emitted by the phenomena of interest. This means that passive remote sensing does not disturb the object or the area of interest.
- Data collected through remote sensing is analyzed at the laboratory which minimizes the work that needs to be done on the field.
- Remote sensing allows for map revision at a small to medium scale which makes it a bit cheaper and faster.
- It is easier to locate floods or forest fire that has spread over a large region which makes it easier to plan a rescue mission easily and fast.
- Remote sensing is a relatively cheap and constructive method reconstructing a base map in the absence of detailed land survey methods.
Disadvantages
- Remote sensing is a fairly expensive method of analysis especially when measuring or analyzing smaller areas.
- Remote sensing requires a special kind of training to analyze the images. It is therefore expensive in the long run to use remote sensing technology since extra training must be accorded to the users of the technology.
- It is expensive to analyze repetitive photographs if there is need to analyze different aspects of the photography features.
- It is humans who select what sensor needs to be used to collect the data, specify the resolution of the data and calibration of the sensor, select the platform that will carry the sensor and determine when the data will be collected. Because of this, it is easier to introduce human error in this kind of analysis.
- Powerful active remote sensing systems such as radars that emit their own electromagnetic radiation can be intrusive and affect the phenomenon being investigated.
- The instruments used in remote sensing may sometimes be un-calibrated which may lead to un-calibrated remote sensing data.
- The image being analyzed may sometimes be interfered by other phenomena that are not being measured and this should also be accounted for during analysis.
- Remote sensing technology is sometimes oversold to the point where it feels like it is a panacea that will provide all the solution and information for conducting physical, biological or scientific research.
- The information provided by remote sensing data may not be complete and may be temporary.
- Sometimes large-scale engineering maps cannot be prepared from satellite data which makes remote sensing data collection incomplete.
Application
There are various places where remote sensing plays an important role are:
- In Agriculture : it is used for Crop type classification , Crop condition assessment ,Crop yield estimation , Mapping of soil characteristics, Mapping of soil management practices and so on.
- Forestry: Remote sensing application in forestry includes, Forest cover, Type of forest , Vegetation density , Deforestation , Forest fires , Biomass estimation.
- Geology: Remote sensing applications in geology includes: Bedrock mapping, Lithological mapping, Structural mapping, Mineral exploration, Hydrocarbon exploration , Environmental geology ,etc.
- Hydrology: Remote sensing applications of hydrology includes, Wetlands mapping and monitoring, Soil moisture estimation, Measuring snow thickness, etc.
- Sea Ice: Remote sensing applications of sea ice includes, Ice concentration , Iceberg detection and tracking and so on.
Conclusion
Here we study about the concept of remote sensing in detail version which helps in may aspects to get information regarding some matter .This technology is used in many ways as mentioned above in the examples and in many fields .Special cameras are used for detecting the images and we can say that it provides proper global perspective in its own way. It helps in detection of various matters , special cameras collect the images and then sense things about the Earth , which helps to know more about it. Also it helps to deal with the learning and teaching experience related to the real world problems.
Remote Sensing – Frequently Asked Questions
What is required for remote sensing?
Energy source or illumination is the most important thing which is required for the process of remote sensing .
Is GPS a remote sensing tool ?
GPS is a remote sensing tool which monitors the seal level and ice melts – to measure earth’s gravity field.
Which types of satellites are used in remote sensing?
Low altitude satellites gives good resolution of data of the regions of the Earth , whereas polar satellites are mostly used in it.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...