Program to implement Inverse Interpolation using Lagrange Formula
Last Updated :
27 Dec, 2021
Given task is to find the value of x for a given y of an unknown function y = f(x) where values of some points (x, y) pairs are given.
Let, y = f(x) be an unknown function where x in an independent variable.
For different values of x, say 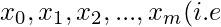 [Tex]x_k, k=0, 1, 2, 3…m) [/Tex]values of respective
[Tex]x_k, k=0, 1, 2, 3…m) [/Tex]values of respective  [Tex]y_k = f(x_k), k=0, 1, 2, 3…m) [/Tex]given.
[Tex]y_k = f(x_k), k=0, 1, 2, 3…m) [/Tex]given.
The process of finding the value of the independent variable x for a given value of y lying between two tabulated values with the help of the given set of observation for an unknown function is known as Inverse Interpolation.
This is often used to check whether the correctness of output y for an unknown function f i.e how much argument x for this output y differs from the original input.
The problem of inverse interpolation can be solved using Lagrange’s Formula.
Lagrange’s Formula:
The formula for inverse interpolation is similar to interpolation formula but few changes.
Here to solve the problem of inverse interpolation the places of x and y are interchanged. The formula for inverse interpolation is:
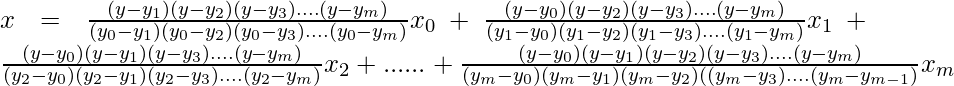
This method can even be used when the points are unequally spaced. Here x is expressed as a function of y.
Examples:
Input: Find the value of x where y = 4.5 and the given points are:
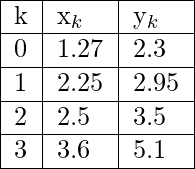
Output: 2.79501
Explanation: Here num of data points given = 4 and y = 4.5
So, putting the values of all x and y in the inverse interpolation formula given above we get,

From here we get,
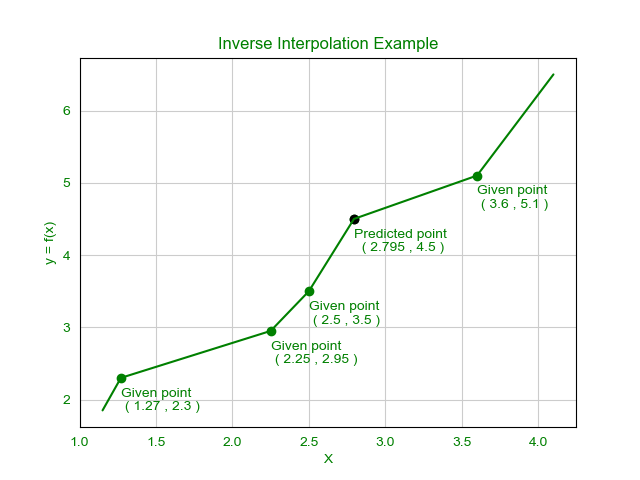
The value of x = 2.79501 where the value of y = 4.5
Graph:
Algorithm:
Here, data is a list of points consisting of x and y and n is the num of data points.
STEP – 1 : Initialize the final value x = 0
STEP – 2 : FOR i = 1 to n do
STEP – 3 : Initialize xi = data[i].x
STEP – 4 : FOR j = 1 to n do
STEP – 5 : IF i != j do
STEP – 6 : Multiply xi by ( y – data[j].y ) and divide by ( data[i].y – data[j].y )
ENDIF
ENDFOR
STEP – 7 : Add xi to x
ENDFOR
STEP – 8 : Return final value of x
STEP – 9 : END
Implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Data {
double x, y;
};
double inv_interpolate(Data d[], int n, double y)
{
double x = 0;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
double xi = d[i].x;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (j != i) {
xi = xi
* (y - d[j].y)
/ (d[i].y - d[j].y);
}
}
x += xi;
}
return x;
}
int main()
{
Data d[] = { { 1.27, 2.3 },
{ 2.25, 2.95 },
{ 2.5, 3.5 },
{ 3.6, 5.1 } };
int n = 4;
double y = 4.5;
cout << "Value of x at y = 4.5 : "
<< inv_interpolate(d, n, y);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static class Data
{
double x, y;
public Data(double x, double y)
{
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
};
static double inv_interpolate(Data []d, int n, double y)
{
double x = 0;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
double xi = d[i].x;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (j != i)
{
xi = xi
* (y - d[j].y)
/ (d[i].y - d[j].y);
}
}
x += xi;
}
return x;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Data []d = { new Data( 1.27, 2.3 ),
new Data( 2.25, 2.95 ),
new Data( 2.5, 3.5 ),
new Data( 3.6, 5.1 ) };
int n = 4;
double y = 4.5;
System.out.printf("Value of x at y = 4.5 : %.5f"
, inv_interpolate(d, n, y));
}
}
|
Python3
class Data:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
def inv_interpolate(d: list, n: int,
y: float) -> float:
x = 0
for i in range(n):
xi = d[i].x
for j in range(n):
if j != i:
xi = (xi * (y - d[j].y) /
(d[i].y - d[j].y))
x += xi
return x
if __name__ == "__main__":
d = [Data(1.27, 2.3),
Data(2.25, 2.95),
Data(2.5, 3.5),
Data(3.6, 5.1)]
n = 4
y = 4.5
print("Value of x at y = 4.5 :",
round(inv_interpolate(d, n, y), 5))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
class Data
{
public double x, y;
public Data(double x, double y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
};
static double inv_interpolate(Data []d,
int n, double y)
{
double x = 0;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
double xi = d[i].x;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (j != i)
{
xi = xi * (y - d[j].y) /
(d[i].y - d[j].y);
}
}
x += xi;
}
return x;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Data []d = {new Data(1.27, 2.3),
new Data(2.25, 2.95),
new Data(2.5, 3.5),
new Data(3.6, 5.1)};
int n = 4;
double y = 4.5;
Console.Write("Value of x at y = 4.5 : {0:f5}",
inv_interpolate(d, n, y));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Data {
constructor(x , y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
};
function inv_interpolate( d , n , y)
{
var x = 0;
var i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
var xi = d[i].x;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (j != i) {
xi = xi * (y - d[j].y) / (d[i].y - d[j].y);
}
}
x += xi;
}
return x;
}
var d = [ new Data(1.27, 2.3), new Data(2.25, 2.95), new Data(2.5, 3.5), new Data(3.6, 5.1) ];
var n = 4;
var y = 4.5;
document.write("Value of x at y = 4.5 : ", inv_interpolate(d, n, y).toFixed(5));
</script>
|
Output: Value of x at y = 4.5 : 2.79501
Complexity: The time complexity of the given solution is O(n^2) and space complexity is O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...