A Function in maths is a special relation between the set of input values and the set of output values. In Function, each input value gives a particular output value. We represent a function in maths as, y = f(x) where x is the input value and for each x we get an output value as y.
In this article, we will learn about, functions in mathematics, their various types, examples, and others in detail.
What is a Function in Maths?
A function in mathematics is a relation between the input values (domain) and the output values (range) of the given sets such that no two variables from the domain sets are linked to the same variable in the range set. A simple example of a function in maths is f(x) = 2x which is defined on R→R, here any variable in the domain is related to only one variable in the range.
A function in mathematics has a domain, codomain, and range. The domain is the set of all the possible values of x and the range of the function is the set of all the output values of y. Range is the subset of codomain of a function. We can also say that a function in maths is a relation with a unique output and no two input value has similar output in a function which is the case for relation.
Function Definition
Function is a special relation or method connecting each member of set A to a unique member of set B via a defined relation. Set A is called the domain and set B is called the co-domain of the function. A function in mathematics from set A to set B is defined as,
f = {(a,b)| ∀ a ∈ A, b ∈ B}
Every function is a relation but every relation is not a function. The criteria for any relation to be considered a function as in function every element of set A has only one image in set B while in relation an element of set A can have more than one image in set B.
We define a functions in maths from non-empty set A to non-empty set B such that,
(a, b) ∈ f, then f(a) = b
where we called b as the image of a defined under the relation f.
Every element ‘a’ of set A has a unique image ‘b‘ in set B then it is a function.
Examples of Functions
A function in mathematics f is defined as, y = f(x) where x is the input value, and for each input value of x, we get a unique value of y. Various examples of the functions in maths defined on R→R are,
- y = f(x) = 3x + 4
- y = f(x) = sin x + 3
- y = f(x) = -3x2 + 3, etc
Condition for a Function
For any two non-empty sets A and B, a function f: A→B denotes that f is a function from A to B, where A is a domain and B is a co-domain.
For any element, a ∈ A, a unique element, b ∈ B is there such that (a,b) ∈ f. The unique element b which is related to a is denoted by f(a) and is read as f of a.
Vertical Line Test
Vertical line test is used to determine whether a curve is a function or not. If any curve cuts a vertical line at more than one point then the curve is not a function.

Representation of Functions in Math
We represent a function in mathematics as,
y = f(x) = x + 3
Here, the set of values of x is the domain of the function and the set of output values of y is the co-domain of the function. Here, the function is defined for all real numbers as it gives a unique value for each x but it is not always possible to get the output for each value of x in such case we define the function in two parts, this can be understood as
- f(x) = 1/(x – 2), where x ≠ 2
- f(x) = x2 where x ∈ {R}
We can define a function in mathematics as a machine that that takes some input and gives a unique output. The function f(x) = x2 is defined below as,

We can represent a function in math by the three method as,
- Set of Ordered Pairs
- Table Form
- Graphical Form
For instance, if we represent a function as, “f(x) = x3 ”
Another way to represent the same function is as the set of ordered pairs as,
f = {(1,1), (2,8), (3,27)}
In the above-mentioned set, the domain of the function is D = {1, 2, 3} and the range of the function is R = {1, 8, 27}

Identification of Function
Function is classified as a special type of relation in math. There are following rules which can be used to identify a function:
- A relation in which each input mapped to a unique output is a Function. This called one to one function.
- A relation in which two input(preimage) mapped to a single output is also a Function. This is many to one function.
- A relation in which one input is mapped two different output is not a function.
- A relation in which many inputs are mapped to many outputs following no specific rule is not a function.
Types of Function
Different Types of Functions are used to solve various types of mathematical problems especially related to curves and equations. There are three major types functions in mathematics that are based on the element mapping from set A to set B.
Injective function or One to One Function
The function in which each element of the domain has a distinct image in the codomain is called the Injective or One-to-One function.
f: A → B is said to be one-to-one or injective if the images of distinct elements of A under f are distinct, i.e.,
f(a1) = b1, f(a2) = b2
where a1, a2 ∈ A and b1, b2 ∈ B
Surjective functions or Onto Function
Surjective Function is the function in which every element of codomain has a pre-image in the domain. It is also called Onto Function which means each element of codomain is associated with each element of the domain. No element of codomain should have an empty relation. The number of elements of codomain and range is the same.
f: A → B is said to be onto, if every element of B is the image of some element of A under f, i.e., for every b ϵ B, there exists an element ‘a’ in A such that f(a) = b.
Bijective Function
If a function has properties of both Injective(One to One) and Surjective(Onto function) then the function is called a Bijective Function. In Bijective Function, each element of the domain is related to each element of the codomain and also there is one-to-one relation. This implies that number of elements of the codomain and range are the same and no element either in the domain or codomain has empty relation.
Based on the output values, the functions classified as odd and even functions. Let’s have a look on them
Odd Functions
Odd function is a type of function that exhibits symmetry about the origin. Specifically, if f(x) is an odd function, it exhibits that f(-x) = -f(x)
Even Function
Even function is a type of function that exhibits symmetry about the y-axis. Specifically, if f(x) is an even function, it exhibits that f(-x) = f(x)
What is a Function in Algebra?
A function in algebra is an equation for which any x that can be put into the equation will produce exactly one output such as y out of the equation. It is represented as y = f(x), where x is an independent variable and y is a dependent variable.
For example:
- y = 2x + 1
- y = 3x – 2
- y = 4y
- y = 5/x
Domain and Range of a Function
Domain and Range of a function are input and output value of a function respectively. For example let’s say we have a function given as f(x) = x2. Here, we can take all the real number as the input value of x and the output will be always a positive real number. Hence, its domain is set of all real numbers represented as R while its range is set of positive real numbers represented as R+
Composition of Functions
If f: A → B and g: B→ C be two functions. Then the composition of f and g is denoted as f(g) and it is defined as the function fog = f(g(x)) for x ∈ A.
Let’s take two functions f(x) = x + 3 and g(x) = 2x2
fog = f(g(x))
⇒ fog = f(2x2)
⇒ fog = 2x2 + 3
Learn More, Composition of Function
Algebra of Functions
Algebra of Functions involve the algebraic operations performed between two functions. The algebraic operation for two functions f(x) and g(x) defined on the real value of x are mentioned below:
- (f + g) (x) = f(x) + g(x)
- (f – g) (x) = f(x) – g(x)
- (f.g) (x) = f(x).g(x)
- (k f(x)) = k (f(x)); {For, k is a real number}
- (f/g)(x) = f(x) /g(x); {For g(x) ≠ 0}
What is a Function on a Graph?
A function can be easily represented on a graph. Any function on graph represent a curve (including straight line) in the x-y plane mapped for its input and corresponding output values.
To plot a function on a first find some points that lies on the function and then join these points according to the locus of the function. For example to graph the function (straight line) f(x) = y = 5x – 2 we need some point on the graph. To find the point the point on the graph we first take the random values of x and then find their corresponding values of y, as,
f(x) = y = 5x- 2
if x = 0, y = 5(0) – 2 = -2 ⇒ (x, y) = (0, -2)
if x = 1, y = 5(1) – 2 = 3 ⇒ (x, y) = (1, 3)
if x = 2, y = 5(2) – 2 = 8 ⇒ (x, y) = (2, 8)
Now joining these point we can get the graph of the function y = 5x – 2
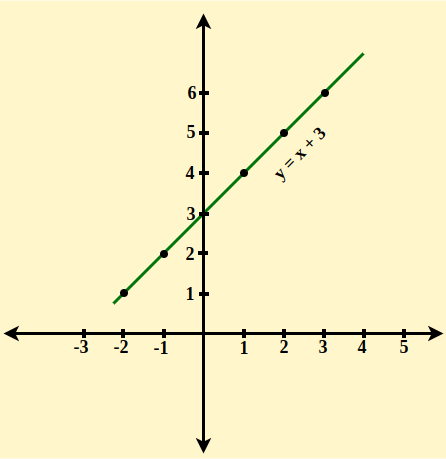
Graphing Functions
Knowing the values of x allows a function f(x) to be represented on a graph. Because y = f(x), we can find the associated value for y by starting with the values of x. As a result, we can plot a graph in a coordinate plane using x and y values. Consider the following scenario:
Assume y = x + 3
When x = 0, y = 3
Similarly,
- x = -2, y = -2 + 3 = 1
- x = -1, y = -1 + 3 = 2
- x = 1, y = 1 + 3 = 4
- x = 2, y = 2 + 3 = 5
- x = 3, y = 3 + 3 = 6
As a result, we may plot the graph for function x + 3 using these values.
Common Functions
Some Common Function that commonly used in mathematics are discussed below:
Real Function
Real function in maths refers to a function whose domain and range are subsets of the real numbers (denoted as ℝ). In simpler terms, a real function is a mathematical rule or relationship that assigns a real number value to each real number input.

Real Functions
Polynomial Function
The function in which the exponents of algebraic variables are non-negative integers is called a Polynomial Function. If the power of the variable is 1 it is called a linear function, if the power is 2 it is called a quadratic function, and if the power is 3 it is called a cubic function. Some examples of polynomial functions are mentioned below:
- y = x2
- y = 2x + 3
- y = 3x3
Polynomial Function can further classified into following types:
Linear function: Linear Function is those in which maximum power of variable is 1. The general Form of Linear Function is y = mx + c
Quadratic Function: Quadratic Function is those in which maximum power of variable is 2. General Form of quadratic function is, ax2 + bx + c = 0
Cubic Function: Cubic Function is those in which maximum power of variable is 3. General Form ax3 + bx2 + cx + d = 0
Inverse Function
Inverse Function is the function containing the inverse of another function. Let’s say we have a function y = f(x) then its inverse function will be x = f-1(y). In y = f(x), the domain is x and the range is y while in the case of x = f-1(y), the domain is y and the range is x. Thus we can say that the domain of the original function is the range of its inverse function and the range of the original function is the domain of the original function. Some examples of inverse functions are,
Area Function
Area function typically refers to a mathematical function that calculates the area of a geometric shape or region. The area function takes one or more parameters as input and returns the area of the corresponding shape. Some of the area functions are discussed below:
Area of Circle Function: Area of Circle (A) is a function of its radius(r) such that,
A = πr2
Area of Triangle Function: Area of Triangle (A) is a function of its base(b) and height(h) such that,
A = (bh)/2
Exponential Function
Exponential function is the one which is represented as f(x) = ex. It is often used to show rapid growth or decay.
Logarithmic Function
Logarithmic function is a mathematical function that represents the inverse operation of exponentiation. It is represented as f(x) = log x.
Ceiling Function
Ceiling function, denoted as ⌈x⌉, rounds a real number x up to the nearest integer that is greater than or equal to x. In other words, it finds the smallest integer value that is greater than or equal to x.
Floor Function
Floor function, denoted as ⌊x⌋, rounds a real number x down to the nearest integer that is less than or equal to x. In other words, it finds the largest integer value that is less than or equal to x.
Modulus Function
Modulus function, also known as the absolute value function, returns the magnitude or “size” of a real number without regard to its sign. Modulus function is denoted as ∣x∣, where x is the input value.
Signum Function
Signum function, also known as the sign function or signum function, is a mathematical function that returns the sign of a real number. It indicates whether the number is positive, negative, or zero.
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions are mathematical functions that relate the angles of a right triangle to the lengths of its sides. The six primary trigonometric functions are sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan), cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot).
Complex Functions
Any function in which the input variable are complex function are called the complex function. A complex number is a number that can be plot on the complex plane. In a complex number we have real number and imaginary number. A complex number(z) is represented as, z= x + iy and a complex function is represented as, f(z) = P(x, y) + iQ(x, y)
Applications of Functions
When we say that a variable quantity y is a function of a variable quantity x, we indicate that y is dependent on x and that y’s value is determined by x’s value. This dependency can be expressed as follows: f = y (x).
- The radius of a circle can be used to calculate the area of a circle. The radius r affects area A. We declare that A is a function of r in the mathematic language of functions. We can write A = f(r) =π×r2
- A sphere’s volume V is a function of its radius. V = f(r) = 4/3×r3 denotes the dependence of V on r.
- Force is a function of the acceleration of a body of fixed mass m. F = g(a) = m×a.
Read More,
Examples on Function
Example 1: For two functions f and g are defined as, f(x) = x2 and g(x) = ln(2x). Find the composite function (gof )( x )
Solution:
Given:
(gof )( x ) = g (f (x))
[g (f (x)] = ln(2f(x))
= ln(2x2)
= 2 ln(√2x)
Thus, (gof)(x) = 2 ln(√2x)
Example 2: Find the output of the function g(t)= 6t2 + 5 at
Solution:
Given Function,
g(t)= 6t2 + 5t
g(0) = 6(0)2+5(0) = 0 + 0
g(0) = 0
g(2) = 6(2)2+5(2)
g(2) = 24 + 10
g(2) = 34
Example 3: The length of a rectangle is five times its breadth, express the area of the rectangle as a function of its length.
Solution:
Let, length of the rectangle be l and the breadth of the rectangle is, b
Now,
Area of Rectangle(A) = l × l/5 = l2/5
Thus, area of rectangle as the function of its length is,
A(l) = l2/5
Functions in Maths – FAQs
What is the Definition of a Function?
A relation f defined on a set A to another set B is called a function in math if each value of A has a unique value in set B.
How to Write a Function in Math?
The function f in mathematics is represented as f: A → B and is defined as, f(x) = x + 2. Here, for each unique value of x, we have a unique value of y.
How to Transform a Function?
We can easily transform a function to other functions by simply performing basic algebraic operations on the function. The different transformation of the function are, reflection, translation, rotation, etc.
What is a Rational Function?
A fraction function where the numerator and the denominator are polynomial functions is called the rational function. Some examples of the rational function are,
- f(x) = x2/(2x + 3)
- g(x) = (6x + 3)/(x – 1), etc.
What is a Linear Function?
An algebraic function in which each term of the function is either constant or has a power of one is called a linear function. Some examples of the linear function are,
- f(x) = 2x + 3
- g(x) = x – 5, etc.
What are Domain and Codomain of a Function?
If we define the function as, y = f(x). Then the domain of the x is all the values of x for which y results in a unique value. And the co-domain of y is the set of all the values of y for each value of x.
How do you Identify a Function in Maths?
If any input value(x) of the domain in a relation has more than one image (y) then these relation can never be a function. So if the value of x is repeated in the ordered pair then it is never a function.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...