Productivity in Ecosystem: Definition, Types & Diagram
Last Updated :
12 Jun, 2023
Productivity is an essential component of an ecosystem and is responsible for the sustenance of life in the ecosystem. The higher the productivity of an ecosystem, more is the energy available in that ecosystem. This energy that is available in the ecosystem keeps transferring from plants to animals and back to plants. The productivity of an ecosystem also influences the diversity of the ecosystem. An ecosystem with higher productivity has higher diversity as compared to an ecosystem with lesser productivity. The productivity of an ecosystem is responsible for the stability of an ecosystem.
What is Productivity?
Productivity can be defined as the energy supplied to a particular ecosystem in the form of biomass or the rate at which biomass is produced in an ecosystem. This energy produced by plants in an ecosystem makes up the productivity of the ecosystem. It can also be defined as the amount of organic matter accumulated in an ecosystem per unit volume per unit of time. Ecologists generally have a separate meaning of productivity. They consider it to be a process through which carbon assimilation takes place at a particular trophic level or in the complete ecosystem.
Units of Productivity
As we know that productivity is the amount of biomass per unit volume in a unit of time in an ecosystem, so the units can of productivity be derived from the units of mass, time, and, volume. Thus the units of productivity come out to be:
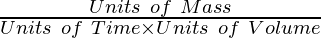
= gm-2d-1
Types of Productivity

The productivity of an ecosystem can be broadly classified into 2 types as follows:
Primary Productivity
The production of biomass by autotrophs such as plants is called primary productivity. In primary productivity, plants use water and carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight for photosynthesis and cooking. This results in the formation of both organic and inorganic substances. Primary productivity is also seen in some algae that use other chemical methods to obtain biomass. The tropical rainforest was the most productive ecosystem per unit area, the most productive ecosystem was the coral reef, and the least productive ecosystem was the deep lake ecosystem. Primary productivity depends on the types of plants growing in a given area. The annual net primary productivity of the entire biosphere is estimated at about 170 billion tonnes of organic matter. Of these 170 billion tonnes, the sea provides only 55 billion tonnes of productivity.
- Gross primary productivity: The total amount of fixed energy and organic matter consumed by respiration per unit of time in an ecosystem is called gross primary productivity (GPP). It can also be defined as the rate of formation of organic matter during photosynthesis. The GPP of an ecosystem depends on the rate of photosynthesis and environmental conditions. Plants use large amounts of GPP during respiration.
- Net primary productivity: As a significant amount of the GPP produced by the plants is consumed by plants themselves for respiration, the amount of energy that is left stored in plants is much less than GPP. This is termed as net primary productivity. This is the energy that plants can transfer to heterotrophs in the ecosystem. Thus, NPP can be defined as the difference between GPP and GPP lost during plant respiration.
Secondary Productivity
New organic matter is formed as heterotrophs or consumers consume organic matter from producers. The rate of formation of this biomass or organic matter is called secondary productivity. It is the result of energy transfer or energy flow in an ecosystem from one trophic level to another. It can also be referred to as the biomass growth of heterotrophs.
FAQs on Productivity
Q1: Define productivity.
Answer:
Ecosystem productivity can be defined as the energy supplied to a particular ecosystem in the form of biomass or the rate at which biomass is produced in an ecosystem.
Q2: Why do oceans contribute very little to the productivity of the ecosystem?
Answer:
Oceans have very low productivity due to which they contribute very little to the ecosystem. This is because the photosynthesis capacity of plants on land is much greater than that of the sea. This makes a huge difference to productivity on land and at sea. Lack of light in deep oceans is also one of the causes of the low productivity of oceans.
Q3: When will the productivity of all ecosystems be about the same?
Answer:
According to experts, when drought occurs, the productivity of all ecosystems becomes nearly the same, as plants adapt to the conditions by using water efficiently when drought occurs.
Q4: Calculate the net primary productivity if gross primary productivity from plants is 400J and 50J is spent in respiration.
Answer:
We know that net primary productivity (NPP) is the difference between GPP and respiration. Thus, it can be calculated as follows:
NPP = GPP – Respiration
NPP = 400J – 50J = 350J
Thus, the net primary productivity is 350J.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...