Print all the permutation of length L using the elements of an array | Iterative
Last Updated :
22 Jun, 2022
Given an array of unique elements, we have to find all the permutations of length L using the elements of the array. Repetition of elements is allowed.
Examples:
Input: arr = { 1, 2 }, L=3
Output:
111
211
121
221
112
212
122
222
Input: arr = { 1, 2, 3 }, L=2
Output:
11
21
31
12
22
32
13
23
33
Approach:
- To form a sequence of length L with N number of elements, it is known that the i-th element of the sequence can be filled in N ways. So there will be
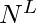 sequences
sequences - We will run a loop from 0 to
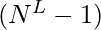 , for every i we will convert i from base 10 to base N. The digits of the converted number will represent the indices of the array
, for every i we will convert i from base 10 to base N. The digits of the converted number will represent the indices of the array - We can print all the
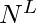 sequences in this way.
sequences in this way.
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void convert_To_Len_th_base(int n,
int arr[],
int len,
int L)
{
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
cout << arr[n % len];
n /= len;
}
cout << endl;
}
void print(int arr[],
int len,
int L)
{
for (int i = 0; i < (int)pow(len, L); i++) {
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, len, L);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int L = 2;
print(arr, len, L);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
static void convert_To_Len_th_base(int n, int arr[],
int len, int L)
{
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
{
System.out.print(arr[n % len]);
n /= len;
}
System.out.println();
}
static void print(int arr[], int len, int L)
{
for (int i = 0;
i < (int)Math.pow(len, L); i++)
{
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, len, L);
}
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
int len = arr.length;
int L = 2;
print(arr, len, L);
}
}
|
Python3
def convert_To_Len_th_base(n, arr, Len, L):
for i in range(L):
print(arr[n % Len], end = "")
n //= Len
print()
def printf(arr, Len, L):
for i in range(pow(Len, L)):
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, Len, L)
arr = [1, 2, 3]
Len = len(arr)
L = 2
printf(arr, Len, L)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static void convert_To_Len_th_base(int n, int []arr,
int len, int L)
{
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
{
Console.Write(arr[n % len]);
n /= len;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void print(int []arr, int len, int L)
{
for (int i = 0;
i < (int)Math.Pow(len, L); i++)
{
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, len, L);
}
}
public static void Main (String[] args)
{
int []arr = { 1, 2, 3 };
int len = arr.Length;
int L = 2;
print(arr, len, L);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function convert_To_Len_th_base( n, arr, len, L)
{
for ( i = 0; i < L; i++) {
document.write(parseInt(arr[n % len]));
n = parseInt(n / len);
}
document.write("<br>");
}
function print( arr, len, L)
{
for (var i = 0; i < parseInt(Math.pow(len, L)); i++) {
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, len, L);
}
}
var arr = [ 1, 2, 3 ];
var len = arr.length;
var L = 2;
print(arr, len, L);
</script>
|
Output: 11
21
31
12
22
32
13
23
33
Time Complexity: O(L*lenL), as we are using a loop to traverse pow(len,L) times and in each traversal, we are calling the function convert_To_Len_th_base which will cost O(L). Where L is the number of elements in the array.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), as we are not using any extra space.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...