Preorder Traversal of Binary Tree
Last Updated :
15 Apr, 2024
Preorder traversal is defined as a type of tree traversal that follows the Root-Left-Right policy where:
- The root node of the subtree is visited first.
- Then the left subtree is traversed.
- At last, the right subtree is traversed.
Preorder traversal
Algorithm for Preorder Traversal of Binary Tree
The algorithm for preorder traversal is shown as follows:
Preorder(root):
- Follow step 2 to 4 until root != NULL
- Write root -> data
- Preorder (root -> left)
- Preorder (root -> right)
- End loop
How does Preorder Traversal of Binary Tree work?
Consider the following tree:
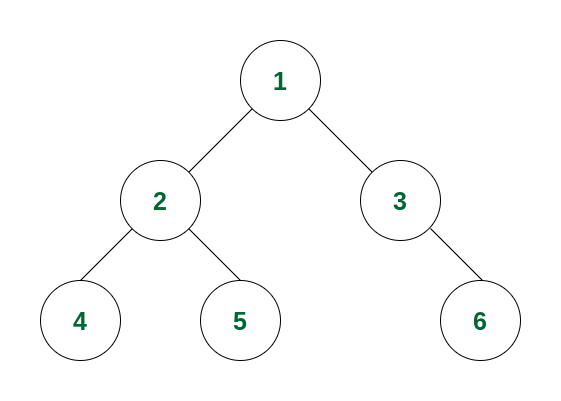
Example of Binary Tree
If we perform a preorder traversal in this binary tree, then the traversal will be as follows:
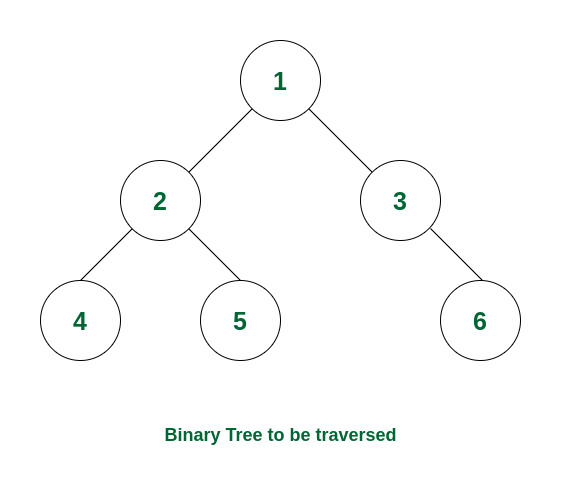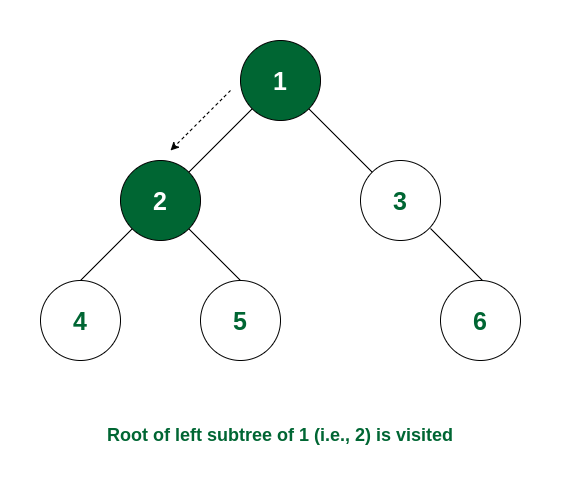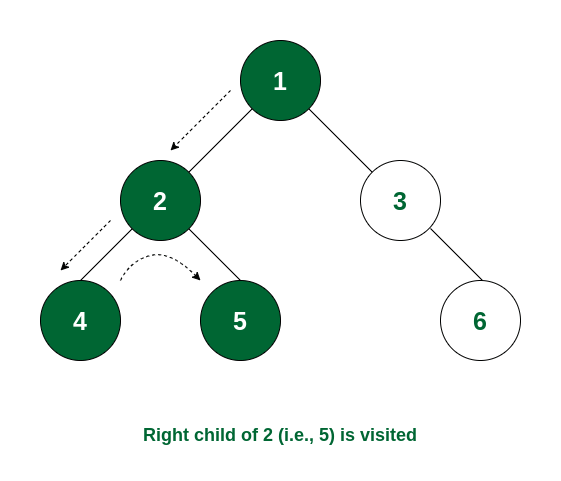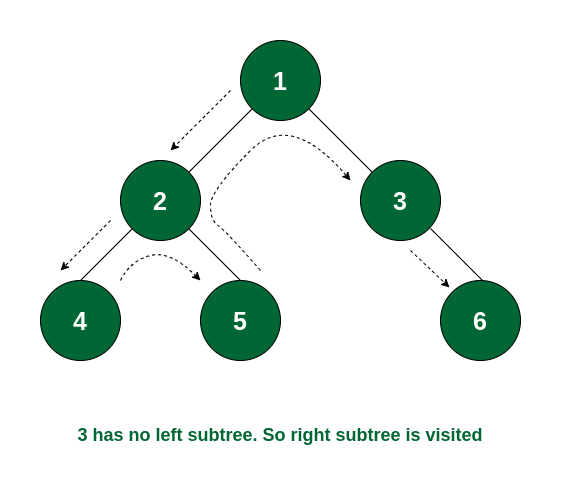
Step 1: At first the root will be visited, i.e. node 1.
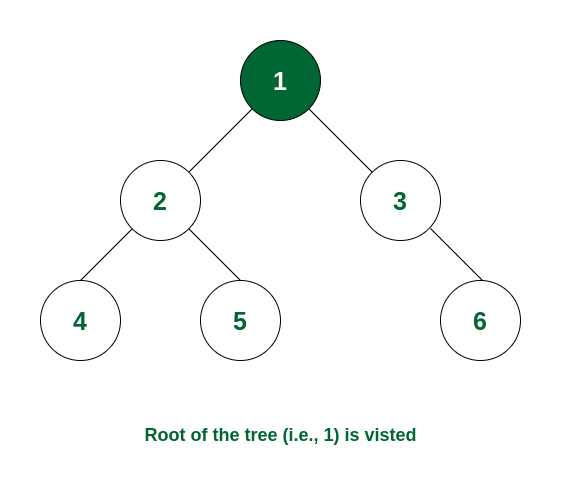
Node 1 is visited
Step 2: After this, traverse in the left subtree. Now the root of the left subtree is visited i.e., node 2 is visited.
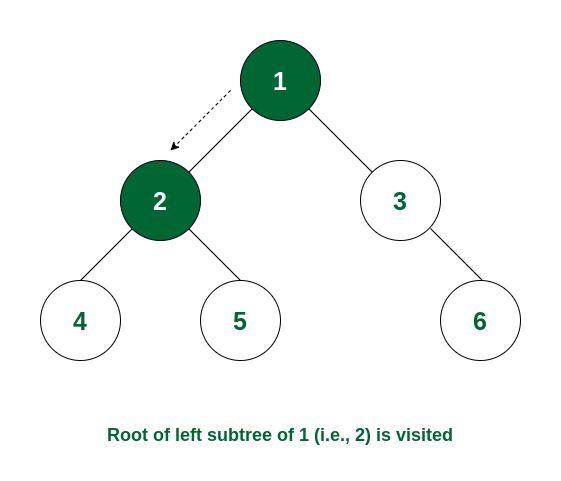
Node 2 is visited
Step 3: Again the left subtree of node 2 is traversed and the root of that subtree i.e., node 4 is visited.
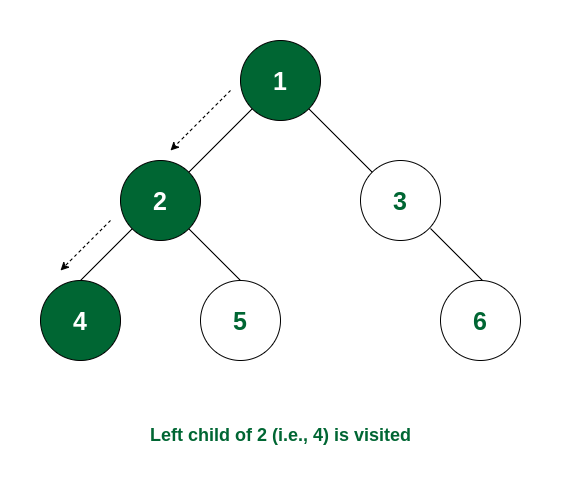
Node 4 is visited
Step 4: There is no subtree of 4 and the left subtree of node 2 is visited. So now the right subtree of node 2 will be traversed and the root of that subtree i.e., node 5 will be visited.
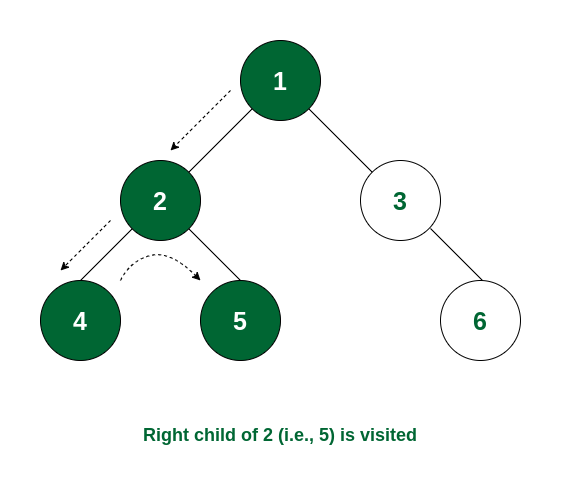
Node 5 is visited
Step 5: The left subtree of node 1 is visited. So now the right subtree of node 1 will be traversed and the root node i.e., node 3 is visited.
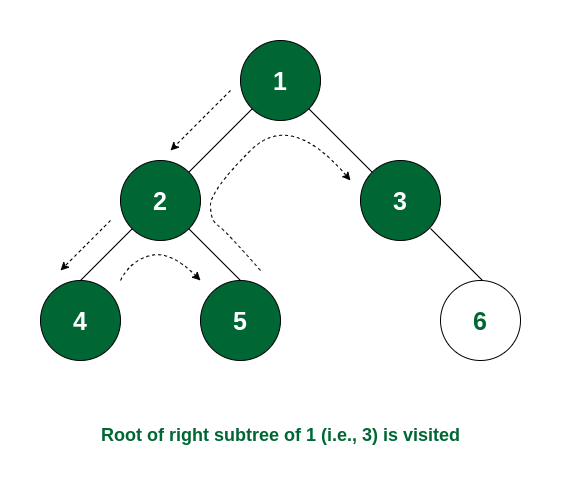
Node 3 is visited
Step 6: Node 3 has no left subtree. So the right subtree will be traversed and the root of the subtree i.e., node 6 will be visited. After that there is no node that is not yet traversed. So the traversal ends.
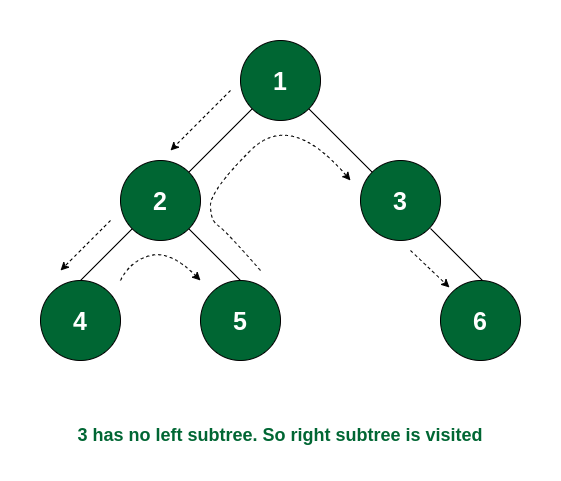
The complete tree is visited
So the order of traversal of nodes is 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> 3 -> 6.
Program to Implement Preorder Traversal of Binary Tree
Below is the code implementation of the preorder traversal:
C++
// C++ program for preorder traversals
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure of a Binary Tree Node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
Node(int v)
{
data = v;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// Function to print preorder traversal
void printPreorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// Deal with the node
cout << node->data << " ";
// Recur on left subtree
printPreorder(node->left);
// Recur on right subtree
printPreorder(node->right);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->right = new Node(6);
// Function call
cout << "Preorder traversal of binary tree is: \n";
printPreorder(root);
return 0;
}
// Java program for preorder traversals
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item) {
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
BinaryTree() {
root = null;
}
// Function to print preorder traversal
void printPreorder(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
// Deal with the node
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
// Recur on left subtree
printPreorder(node.left);
// Recur on right subtree
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
// Constructing the binary tree
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(6);
// Function call
System.out.println("Preorder traversal of binary tree is: ");
tree.printPreorder(tree.root);
}
}
# Python program for preorder traversals
# Structure of a Binary Tree Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, v):
self.data = v
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print preorder traversal
def printPreorder(node):
if node is None:
return
# Deal with the node
print(node.data, end=' ')
# Recur on left subtree
printPreorder(node.left)
# Recur on right subtree
printPreorder(node.right)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.right = Node(6)
# Function call
print("Preorder traversal of binary tree is:")
printPreorder(root)
// C# program for preorder traversals
using System;
// Structure of a Binary Tree Node
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int v)
{
data = v;
left = right = null;
}
}
// Class to print preorder traversal
public class BinaryTree {
// Function to print preorder traversal
public static void printPreorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// Deal with the node
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
// Recur on left subtree
printPreorder(node.left);
// Recur on right subtree
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(6);
// Function call
Console.WriteLine(
"Preorder traversal of binary tree is: ");
printPreorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli
// Structure of a Binary Tree Node
class Node {
constructor(v) {
this.data = v;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// Function to print preorder traversal
function printPreorder(node) {
if (node === null) {
return;
}
// Deal with the node
console.log(node.data);
// Recur on left subtree
printPreorder(node.left);
// Recur on right subtree
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Driver code
function main() {
const root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(6);
// Function call
console.log("Preorder traversal of binary tree is:");
printPreorder(root);
}
main();
OutputPreorder traversal of binary tree is:
1 2 4 5 3 6
Explanation:
How preorder traversal works
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity: O(N) where N is the total number of nodes. Because it traverses all the nodes at least once.
Auxiliary Space:
- O(1) if no recursion stack space is considered.
- Otherwise, O(h) where h is the height of the tree
- In the worst case, h can be the same as N (when the tree is a skewed tree)
- In the best case, h can be the same as logN (when the tree is a complete tree)
Use cases of Preorder Traversal:
Some use cases of preorder traversal are:
- This is often used for creating a copy of a tree.
- It is also useful to get the prefix expression from an expression tree.
Related Articles:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...