Practice Questions for Recursion | Set 2
Last Updated :
25 Apr, 2023
Explain the functionality of the following functions.
Question 1
C++
int fun1(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
return 0;
else
return 1 + fun1(n / 2);
}
|
Java
static int fun1(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
return 0;
else
return 1 + fun1(n / 2);
}
|
Python3
def fun1(n):
if(n == 1):
return 0
else:
return 1 + fun1(n//2)
|
C#
static int fun1(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
return 0;
else
return 1 + fun1(n / 2);
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function fun1(n)
{
if (n == 1)
return 0
else
return 1 + fun1(Math.floor(n / 2))
}
</script>
|
Answer: The function calculates and returns 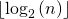
For example, if n is between 8 and 15 then fun1() returns 3. If n is between 16 to 31 then fun1() returns 4.
Question 2
C++
void fun2(int n)
{
if(n == 0)
return;
fun2(n/2);
cout << n%2 << endl;
}
|
C
void fun2(int n)
{
if(n == 0)
return;
fun2(n/2);
printf("%d", n%2);
}
|
Java
static void fun2(int n)
{
if(n == 0)
return;
fun2(n/2);
System.out.println(n%2);
}
|
Python3
def fun2(n):
if(n == 0):
return
fun2(n // 2)
print(n % 2, end="")
|
C#
void fun2(int n)
{
if(n == 0)
return;
fun2(n/2);
Console.Write(n%2);
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function fun2(n)
{
if (n == 0)
return;
fun2(Math.floor(n / 2));
document.write(n % 2 + " ")
}
</script>
|
Auxiliary Space: O(log2N), due to recursion call stack
Time Complexity: O(log N)
Answer: The function fun2() prints the binary equivalent of n. For example, if n is 21 then fun2() prints 10101.
Note: Above functions are just for practicing recursion, they are not the ideal implementation of the functionality they provide.
Please write comments if you find any of the answers/codes incorrect.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...