Plateaus in India: Plateaus are elevated flat areas of land. They’re the high tables on Earth’s surface. People often live on plateaus, and they affect the weather and nature around them. This article explains plateaus—flat, elevated lands. It describes types, causes, and examples worldwide, focusing on the significance and characteristics of Indian plateaus.
The exploration of Plateaus in India falls within the purview of the Geography segment in the UPSC Syllabus. Plateaus constitute one of the four primary landforms, alongside mountains, plains, and hills. This article delves into the discussion of Plateaus in India, covering their types, formation, and more.
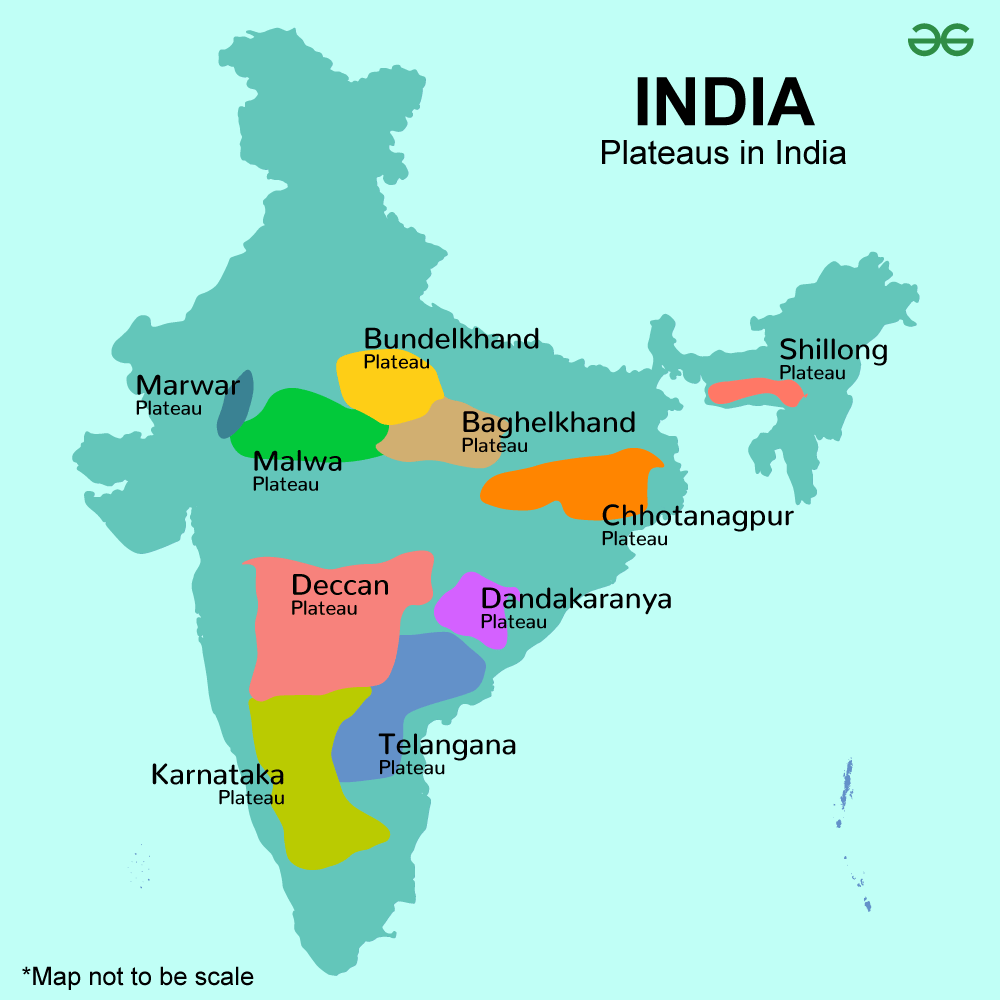
Plateaus in India
Plateaus
Plateaus are elevated flat or gently sloping areas of land that are characterized by their relatively high elevation compared to the surrounding terrain. These geographical features can be found all around the world and come in various types, each with distinct characteristics.
Features of Plateaus: The process of lithosphere thermal expansion, which is relatively straightforward, involves the lithosphere expanding due to heat. Additionally, there is the replacement of the cold mantle lithosphere by the asthenosphere.
What Are Plateaus?
Plateaus are flat, elevated areas of land that stand higher than the surrounding areas. Plateaus have relatively level surfaces, making them distinct geographical features, unlike mountains. They result from geological processes such as uplift, volcanic activity, or erosion. Plateaus can vary in size and are found all around the world. They play crucial roles in shaping landscapes and influencing climate patterns. Due to their elevated nature, plateaus often offer breathtaking panoramic views. Some plateaus are characterized by fertile soil supporting agriculture, while others may feature unique ecosystems.
Check-out: What are the Relief Features of India?
Plateaus In India
India is home to several significant plateaus that contribute to the country’s diverse topography. These plateaus have played crucial roles in shaping the landscape, influencing agriculture, and contributing to historical and cultural developments.
Types Of Plateaus
Plateaus are elevated flat or gently sloping areas that are distinct from the surrounding terrain. They can be classified into various types based on their geological origin, location, and formation. Here are some common kinds of plateaus:
Volcanic Plateaus
- Formation: These plateaus are formed due to volcanic activity where lava accumulates and solidifies over time.
- Example: The Deccan Plateau in India is a volcanic plateau formed by the accumulation of basaltic lava flows.
Dissected Plateaus
- Formation: These plateaus undergo erosion by rivers and other natural forces, leading to the formation of deep valleys and gorges.
- Example: The Colorado Plateau in the United States, characterized by canyons like the Grand Canyon, is a dissected plateau.
Intermontane Plateaus
- Formation: Found between mountain ranges, these plateaus are formed due to tectonic activity and the uplifting of the Earth’s crust.
- Example: The Tibetan Plateau, often referred to as the “Roof of the World,” is an intermontane plateau situated between the Himalayas and other mountain ranges.
Piedmont Plateaus
- Formation: These plateaus are located at the base of mountains and are formed by the accumulation of sediments washed down from the mountains.
- Example: The Appalachian Piedmont in the eastern United States is a piedmont plateau.
Lava Plateaus
- Formation: Similar to volcanic plateaus, these plateaus are formed by the accumulation and solidification of lava, but they are typically flatter.
- Example: The Columbia Plateau in the northwestern United States is a lava plateau formed by extensive basaltic lava flows.
Dome Plateaus
- Formation: Dome-shaped plateaus are formed by the uplifting of large, geologically stable areas, often composed of resistant rocks.
- Example: The Colorado Plateau in the United States exhibits dome-like structures.
Submarine Plateaus
- Formation: These plateaus are located beneath the sea and are often remnants of ancient continental shelves.
- Example: The Sargasso Sea, a region in the North Atlantic Ocean, has an underwater plateau.
Polar Plateaus
- Location: Found near the Earth’s poles, these plateaus are covered with ice and snow.
- Example: The Antarctic Plateau, which contains the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, is a polar plateau.
Check-out: Why Chota Nagpur plateau has huge concentration of steel?
Indian Peninsular Plateau
The Indian Peninsular Plateau is a vast elevated region in South India, characterized by its flat-topped hills and tablelands. It spans major states like Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh. This plateau, also known as the Deccan Plateau, holds historical and geographical significance. Its landscape is shaped by volcanic activity, resulting in black soil conducive to agriculture. Rivers like the Godavari and Krishna originate here, enriching the fertile plains. The plateau hosts diverse flora and fauna, contributing to India’s biodiversity. Its central location has made it a crossroads of cultural and trade routes throughout history, playing a vital role in the subcontinent’s development.
Importance Of Plateaus in India
Plateaus in India are important for the various reasons listed below:
- Plateaus, like the Deccan Plateau, boast fertile soils supporting crucial crops due to their volcanic origins.
- Many major rivers, such as the Godavari and Krishna, originate from plateaus, providing water for irrigation and daily use.
- Plateaus house diverse ecosystems, contributing significantly to India’s rich biodiversity.
- Plateaus act as natural pathways, connecting different regions and facilitating transportation and trade.
- They have been historical crossroads, influencing the cultural exchange and development of civilizations in the subcontinent.
- Plateaus often feature scenic landscapes and historical sites, attracting tourists and contributing to the economy.
- Plateaus are sources of valuable minerals, playing a role in India’s mineral wealth and economic development.
- The plateau’s elevated terrain aids in preventing rapid soil erosion, maintaining ecological balance.
- Plateaus influence regional climates, affecting rainfall patterns and temperatures in surrounding areas.
- Some plateaus provide natural defense advantages due to their topography, influencing military considerations.
Check-out: Geographical Location of India
A plateau is caused by different natural processes that shape the Earth’s surface. Here are some simple explanations:
1. Volcanic Activity: Formed when hot lava from a volcano spreads out and cools, creating a flat surface.
2. Erosion: Gradual wearing away of land by wind, water, or ice shapes the ground into a flat and elevated area.
3. Tectonic Movements: Earth’s crust movements uplift land, resulting in a high, flat region called a plateau.
4. Dissected by Rivers: Rivers and streams carve deep valleys into elevated land, forming a dissected plateau.
5. Lava Flow: Outpouring of lava, cooling, and solidifying lead to the creation of a flat and elevated landscape.
6. Glacial Activity: During ice ages, glaciers cover large areas; as they retreat, they leave behind flat terrain, forming an interglacial plateau.
List Of Plateaus In India
Below is the table for the List of Plateaus in India:
| Plateau |
Location (States) |
Formation |
Key Features |
Significance |
| Deccan Plateau |
Telangana, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Odisha (part), Madhya Pradesh (part) |
Volcanic activity (Deccan Traps) |
Largest plateau in India, diverse landscapes (hills, plateaus, mountains), fertile black soil, rich mineral resources, wildlife sanctuaries |
Agriculture, mining, tourism, cultural heritage |
| Central Highlands |
Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Rajasthan |
Ancient tectonic movements |
Two mountain ranges (Vindhyas & Satpuras), diverse ecosystems (forests, grasslands), historical sites, tribal communities |
Mineral resources, wildlife tourism, cultural heritage |
| Chota Nagpur Plateau |
Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh |
Upliftment and erosion of ancient rocks |
Rich in mineral resources (coal, iron ore), rolling hills and valleys, tribal communities |
Mining, agriculture, wildlife sanctuaries |
| Meghalaya Plateau |
Northeast India (7 states) |
Upliftment of ancient rocks |
Rolling hills, lush greenery, unique rock formations, diverse ecosystems, tribal communities |
Tourism, wildlife conservation, cultural heritage |
| Marwar Plateau |
Western Rajasthan |
Erosion of ancient rocks |
Arid landscape, desert features, historical forts and palaces |
Tourism, cultural heritage, traditional crafts |
| Bundelkhand Upland |
Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh |
Upliftment and erosion of ancient rocks |
Rich in mineral resources (sandstone, limestone), hills and valleys, historical sites |
Mining, agriculture, cultural heritage |
| Malwa Plateau |
Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan (part) |
Upliftment and erosion of ancient rocks |
Fertile black soil, rolling hills and valleys, historical sites |
Agriculture, cultural heritage |
| Baghelkhand |
Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh |
Upliftment and erosion of ancient rocks |
Dense forests, hills and valleys, waterfalls, rich biodiversity |
Wildlife conservation, agriculture, tribal communities |
| Aravalli Range (Plateau Section) |
Rajasthan, Gujarat (part) |
Upliftment and erosion of ancient rocks |
Rocky terrain, hills and valleys, desert features, historical sites |
Wildlife conservation, cultural heritage, tourism |
| Chotanagpur Plateau Extension |
West Bengal, Bihar |
Upliftment and erosion of ancient rocks |
Rich in mineral resources (coal, mica), rolling hills and valleys, tribal communities |
Mining, agriculture, wildlife sanctuaries |
| Shillong Plateau (Meghalaya) Sub-plateaus |
Meghalaya |
Upliftment and erosion of ancient rocks |
Garo Hills, Khasi Hills, Jaintia Hills (diverse landscapes, waterfalls, unique rock formations) |
Tourism, wildlife conservation, cultural heritage |
| Deccan Plateau Sub-plateaus |
Maharashtra, Kerala |
Volcanic activity (Deccan Traps) |
Mahabaleshwar Plateau, Panchmarhi Hills (scenic beauty, unique geological features) |
Tourism, wildlife conservation, historical sites |
Check-out: What are the features of east and west flowing rivers?
Types of Plateaus in India
India features seven Plateaus in India. These include the Marwar Plateau, Central Highland, Bundelkhand Upland, Malwa Plateau, Baghelkhand, Chota Nagpur Plateau, Meghalaya Plateau, Deccan Plateau, and Maharashtra Plateau.
Deccan Plateau
The Deccan Plateau, found in central and southern India, is a large elevated area formed by ancient volcanic activity. It has a mix of fertile plains, rocky hills, and unique basaltic formations. Surrounded by the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats, this plateau has a rich history, playing a key role in ancient civilizations and contributing to India’s overall development.
- Location: Central and southern India.
- Characteristics: Formed by volcanic activity, the Deccan Plateau is a vast elevated region with diverse landscapes. It encompasses fertile plains, rocky hills, and basaltic rock formations. It is flanked by the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats.
Central Highlands
The Central Highlands, spanning from Gujarat to Chhattisgarh, is a region of hills and plateaus in central India. It includes the Vindhya and Satpura ranges, influencing the flow of major rivers. This area has diverse landscapes and holds historical importance as the heart of India.
- Location: Central India, extending from Gujarat in the west to Chhattisgarh in the east.
- Characteristics: Comprising plateaus and hills, the Central Highlands are known for the Malwa Plateau and the Vindhya and Satpura ranges. This region influences the drainage patterns of major rivers.
Chota Nagpur Plateau
The Chota Nagpur Plateau, in eastern India (Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha), is known for its hills, valleys, and dense forests. Valuable for its coal and iron ore deposits, it’s a significant industrial area contributing to India’s mineral wealth.
- Location: Eastern India, covering parts of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
- Characteristics: Rich in mineral resources, the Chota Nagpur Plateau features hills, valleys, and dense forests. It is a crucial industrial region with significant coal and iron ore deposits.
Check-out: Which are the major physiographic divisions of India?
Meghalaya Plateau
The Meghalaya Plateau in northeastern India, particularly Meghalaya state, is marked by heavy rainfall and lush greenery. Home to the Shillong Plateau, it’s a biodiversity hotspot with unique flora and fauna, as well as diverse indigenous communities.
- Location: Northeastern India, covering the state of Meghalaya.
- Characteristics: Known for heavy rainfall and lush green landscapes, the Meghalaya Plateau includes the Shillong Plateau. It is home to diverse flora and fauna and is an important biodiversity hotspot.
Marwar Plateau
The Marwar Plateau in western Rajasthan has a semi-arid landscape with rocky terrain and sparse vegetation. Part of the Thar Desert, it greatly influences the region’s climate and showcases adaptations to arid environments.
- Location: Western Rajasthan.
- Characteristics: A semi-arid region, the Marwar Plateau is characterized by rocky terrain and sparse vegetation. It is part of the larger Thar Desert and has a significant impact on the region’s climate.
Bundelkhand Upland
The Bundelkhand Upland, extending across parts of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, has a rocky terrain and historical significance. It has witnessed the rise and fall of ancient civilizations and supports agriculture in certain areas.
- Location: Parts of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- Characteristics: Known for its rocky landscape, the Bundelkhand Upland has historical significance and has witnessed the rise and fall of several ancient civilizations. Agriculture is practiced in the fertile pockets.
Malwa Plateau
The Malwa Plateau in northwestern Madhya Pradesh is known for its fertile soil, making it suitable for agriculture. Bounded by the Aravalli Range, it’s a crucial region for food production and holds historical and cultural importance.
- Location: Northwestern part of Madhya Pradesh.
- Characteristics: Characterized by fertile soil, the Malwa Plateau is suitable for agriculture. It is bounded by the Aravalli Range and is an important region for food production.
Check-out: Write a short note on the Central Highlands
Baghelkhand
Baghelkhand, covering eastern Madhya Pradesh and parts of Chhattisgarh, features hills and plateaus. It’s known for its forests and is used for agricultural activities, showcasing a mix of natural landscapes and human settlements.
- Location: Eastern Madhya Pradesh and parts of Chhattisgarh.
- Characteristics: Comprising hills and plateaus, Baghelkhand has a mixed topography. It is known for its forests and agricultural activities.
Aravalli Range
The Aravalli Range, primarily a mountain range, includes sections with elevated plateaus. Stretching through Rajasthan, Haryana, and Gujarat, it influences the climate and ecology of the surrounding regions, playing a vital role in western India’s geography.
- Location: Western India, extending through Rajasthan and into Haryana and Gujarat.
- Characteristics: While the Aravalli Range is primarily a mountain range, it has sections with elevated plateaus. It plays a crucial role in influencing the climate and ecology of the surrounding regions.
Chotanagpur Plateau Extension
An extension of the Chota Nagpur Plateau, this area in Bihar, Jharkhand, and Chhattisgarh shares characteristics with the main plateau. It contributes to the region’s industrial and economic significance.
- Location: Extension of the Chota Nagpur Plateau.
- Characteristics: Similar to the Chota Nagpur Plateau, it is rich in minerals and supports industrial activities. It includes parts of Bihar, Jharkhand, and Chhattisgarh.
Shillong Plateau Sub-Plateaus
The Shillong Plateau in Meghalaya has undulating terrain and high rainfall. Comprising sub-plateaus, it’s known for cultural diversity and unique biodiversity, with various indigenous communities residing there.
- Location: Northeastern India, in the state of Meghalaya.
- Characteristics: Distinguished by its undulating terrain and high rainfall, the Shillong Plateau supports agriculture and is known for its unique cultural diversity.
Check-out: Northern Plains of India
Deccan Plateaus Sub Plateaus
The Deccan Plateaus has sub plateaus, like the Malwa Plateau and Telangana Plateau, each with its own characteristics. These sub-plateaus within the broader Deccan Plateau influence agriculture, biodiversity, and human settlements.
- Location: Various subregions within the Deccan Plateau.
- Characteristics: The Deccan Plateau consists of sub-plateaus with varying landscapes, including the Malwa Plateau, Telangana Plateau, and others. Each sub-plateau contributes to the overall diversity of the Deccan region.
Features Of Peninsular Plateau
Here are the features of the Peninsular Plateau (Deccan Plateau):
- Volcanic Origins: Formed by massive volcanic eruptions around 66 million years ago, creating thick layers of basalt rock and shaping its unique landscape.
- Vast and Diverse: Encompassing eight states in southern India, it’s the largest plateau in the country, boasting varied features like rolling hills, plateaus, and mountain ranges.
- Rich Resource Base: Abundant in minerals like coal, iron ore, and bauxite, supporting mining and industries, while fertile black soil in some areas promotes agriculture.
- Ecological Treasure Trove: Supports diverse ecosystems from dry deciduous forests and scrublands to lush wetlands, providing habitat for a wide range of plant and animal species, including endangered ones.
- Cultural Mosaic: Home to a vibrant tapestry of ethnic groups, languages, and traditions, from Telugu and Kannada to tribal communities, with historical sites and ancient cave paintings offering glimpses into its rich past.
The Central Highlands
The Central Highlands form a vital part of India’s landscape, stretching across several states in the central region. Here’s a detailed look at its key features:
| Feature |
Details |
| Location |
Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Rajasthan |
| Area |
Approximately 4 lakh sq km (154,000 sq mi) |
| Elevation |
300-900 meters (980-2,950 ft) |
| Topography |
Plateaus, hills, valleys, two parallel mountain ranges: Vindhyas and Satpuras, separated by Narmada River valley |
| Geology |
Ancient tectonic movements, exposed igneous and metamorphic rocks, rich in minerals (bauxite, coal, iron ore, limestone) |
| Ecology |
Dry deciduous forests, grasslands, pockets of moist evergreen forests, diverse plant and animal species, endangered species (tiger, sloth bear, chital, gaur) |
| Protected areas |
Kanha National Park, Satpura National Park, Pench National Park, numerous other sanctuaries |
| Culture |
Diverse ethnic groups (Gond, Bhil, Baga, Korku, Malwi), unique traditions and languages, rich tribal art and crafts (Warli paintings, Dhokra metalwork) |
| Historical sites |
Ancient forts, temples, rock-cut caves (Ajanta-Ellora) |
| Challenges |
Deforestation, soil erosion, Naxalite-Maoist insurgency, tribal displacement, development project impacts |
| Significance |
Ancient geological formations, diverse ecosystems, rich cultural heritage, mineral resources, wildlife tourism potential |
Check-out: Which physical feature of India is a flat land?
The Deccan Plateau
The Deccan Plateau is a vast and fascinating region in southern India, boasting a rich geological history, diverse ecosystems, and significant cultural and economic importance. Here’s a breakdown of its key features:
| Feature |
Description |
| Location |
South India, covering parts of Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu |
| Area |
Over 500,000 square kilometers (approximately 27.7% of India’s landmass) |
| Elevation |
Average of 600 meters, sloping eastward with peaks exceeding 2,600 meters in the Western Ghats |
| Formation |
Result of volcanic activity during the Cretaceous period (66 million years ago) |
| Landforms |
Mostly Deccan Traps (basaltic lava flows), hills, valleys, plateaus, and plains |
| Rivers |
Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri (Cauvery) – flow eastward from Western Ghats to Bay of Bengal |
| Climate |
Tropical, with a drier interior and wetter coasts |
| Natural Resources |
Rich in minerals like coal, iron ore, bauxite, and diamonds; fertile black soil in parts |
| Agriculture |
Important crops include cotton, soybeans, pulses, rice, sugarcane, and fruits |
| Wildlife |
Tigers, leopards, sloth bears, Indian elephants, gaur, chital, birds, and reptiles |
| Cultural Significance |
Home to diverse cultures, languages, and historical sites like temples, forts, and caves |
| Economic Importance |
Agriculture, mining, industries, tourism, hydroelectric power |
| Environmental Challenges |
Soil erosion, deforestation, drought, water scarcity |
| Government Initiatives |
Soil conservation programs, irrigation projects, sustainable development initiatives |
The Northeastern Plateau
The Northeastern Plateaus, also known as the Shillong Plateau or the Assam Plateau, is a large plateau region in Northeast India. It consists of several smaller plateaus and hill ranges, including:
| Plateau |
Location |
Features |
| Garo Hills |
Western Meghalaya |
Dense forests, waterfalls, stunning scenery |
| Khasi Hills |
Eastern Meghalaya |
Rolling hills, lush greenery, unique rock formations |
| Jaintia Hills |
Southern Meghalaya |
Coal mines, waterfalls, orange orchards |
| Karbi Anglong Plateau |
Central Assam |
Rich biodiversity, wildlife sanctuaries, tribal culture |
| Patkai Hills |
India-Myanmar border |
Dense forests, bamboo groves, diverse wildlife |
Check-out: India and the World
Plateau In India UPSC
For UPSC aspirants, understanding Plateaus in India is important for exams as they are integral to geography, history, and environmental science topics. Knowing their geographical features, historical importance, and socio-economic roles is essential for success in UPSC examinations.
For Example:
- Types of Plateaus: Identify the major types of plateaus in India, such as volcanic (Deccan Traps), weathered (Central Highlands), and dissected (Chota Nagpur). Understand their formation processes and distinctive features.
- Significance of Plateaus: Analyze the economic, agricultural, environmental, and cultural importance of plateaus. For example, the mineral resources of the Chota Nagpur Plateau or the black soil-based agriculture of the Deccan Plateau.
- Impact on Indian Geography: Examine how plateaus influence drainage patterns, river systems, and climatic variations across India. Understand the role of Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats in shaping monsoon patterns.
- Development Challenges: Discuss the unique challenges faced by plateau regions, such as soil erosion, deforestation, and lack of infrastructure. Analyze government initiatives and policies addressing these issues.
- Case Studies: Deep dive into specific plateau regions within India. Choose an example like the tribal communities of the Meghalaya Plateau or the coal mining industry in the Chota Nagpur Plateau. Analyze their socio-economic dynamics and challenges.
Famous Plateaus Of The World
Here are Five World Famous Plateaus that have captivated people’s imaginations for centuries, each for different reasons:
Tibetan Plateau (Asia)
The “Roof of the World”, the Tibetan Plateau is the highest and largest plateau on Earth, covering over 2.5 million square kilometers. Its vast grasslands, snow-capped peaks like Mount Everest, and unique cultural heritage make it a truly awe-inspiring destination.
Colorado Plateau (North America)
This iconic American plateau encompasses breathtaking canyons like the Grand Canyon, Zion National Park, and Monument Valley. Its colorful rock formations, diverse ecosystems, and rich Native American history attract millions of visitors each year.
Check-out: The Peninsular River System
Deccan Plateau (India)
The largest plateau in India, the Deccan is known for its ancient volcanic eruptions, fertile black soil, and diverse wildlife. It’s home to iconic tiger reserves like Kanha National Park and ancient cave temples like Ajanta-Ellora.
Patagonian Plateau (South America)
This vast plateau stretching across Argentina and Chile boasts glaciers, windswept steppes, and stunning fjords. The Torres del Paine National Park and the Perito Moreno Glacier are just a few of its natural wonders.
Ethiopian Highlands (Africa)
Known as the “Roof of Africa”, the Ethiopian Highlands offer stunning scenery with soaring mountains, ancient rock-hewn churches, and the source of the Blue Nile River. The Simien Mountains National Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site renowned for its unique biodiversity.
Plateaus UPSC
The topic of Plateaus, a key part of the Geography section in the UPSC Syllabus, focuses on one of the four major landforms. Specifically, there are seven main types of Plateaus in India. For in-depth knowledge, candidates can consult Geography books for UPSC preparation. Additionally, reviewing the UPSC Prelims Previous Year Questions from the UPSC Prelims is beneficial for grasping the exam pattern.
Conclusion
In Conclusion, India’s plateaus are important geographical features that have shaped the country’s diverse landscape and influenced its development. Plateaus like the Deccan and Chota Nagpur have acted as natural barriers, supported biodiversity, and played a role in historical events. These elevated areas are vital for agriculture, sustaining the livelihoods of many people. Despite challenges like soil erosion, efforts are being made to use sustainable practices. In summary, India’s plateaus tell a story of diversity, history, and agricultural importance. They remain crucial for the country’s sustainable development and the balance between preserving nature and progressing as a society.
Related Resources:
Plateaus In India – FAQs
What Are The 5 Plateaus In India?
There are more than five plateaus in India, but some of the most prominent ones include:
- Deccan Plateau
- Chota Nagpur Plateau
- Meghalaya Plateau
- Central Highlands
- Malwa Plateau
What Is Plateau In Geography?
A plateau is a raised area of land with a relatively flat surface. It stands above the surrounding plains or valleys and often has one or more sides with steep slopes. Plateaus can be formed in various ways, such as through volcanic activity, erosion, or the uplift of tectonic plates.
What Is The Old Plateau In India?
The Deccan Plateau is considered one of the oldest plateaus in India, estimated to be around 66 million years old. It was formed by volcanic activity during the Cretaceous period.
Which is the largest plateau in India?
The Tibetan Plateau in Asia is the biggest plateau in the world, with an area of over 5 million square kilometers.
What Is The Smallest Plateau In The World?
The Kerguelen Plateau, located in the Southern Ocean near Antarctica, is considered the smallest plateau in the world, with an area of around 50,000 square kilometers.
Which Is The Oldest Plateau In The World?
The Canadian Shield is considered the oldest plateau in the world, with parts of it estimated to be over 4 billion years old.
Which Plateau Is Called Roof Of India?
The Chota Nagpur Plateau in eastern India is often referred to as the “Roof of the East” due to its high elevation and cool climate.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...