Nodes at Kth level without duplicates in a Binary Tree
Last Updated :
03 Dec, 2021
Given a binary tree with N nodes and an integer K, the task is to print nodes of the Kth level of a binary tree without duplicates.
Examples:
Input:
60 --- Level 0
/ \
50 30 --- Level 1
/ \ /
80 10 40 --- Level 2
K = 1
Output: 30 50
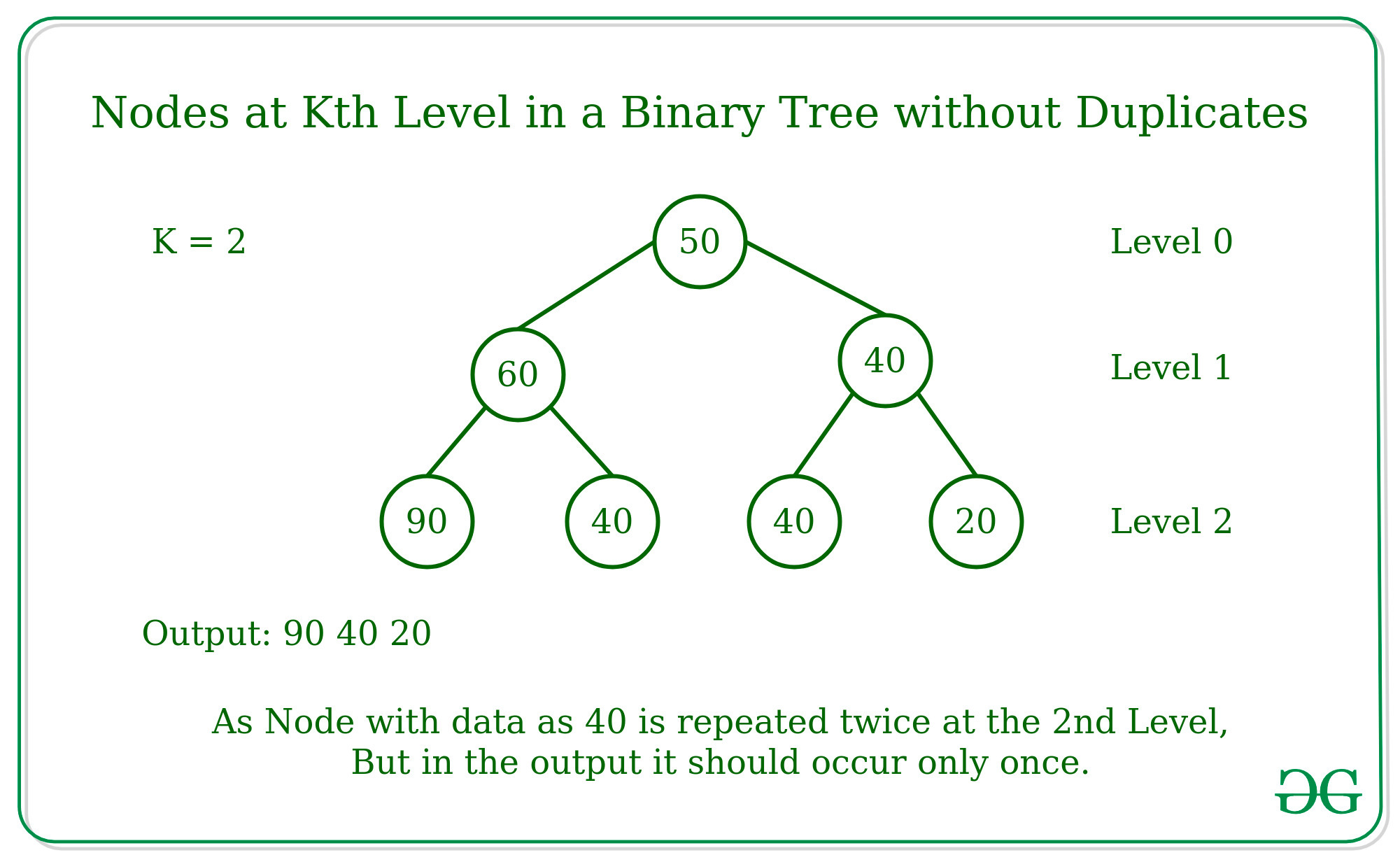
Input:
50 --- Level 0
/ \
60 70 --- Level 1
/ \ / \
90 40 40 20 --- Level 2
K = 2
Output: 20 40 90
Approach: The idea is to traverse the Binary Tree using the Level Order Traversal with the help of queue and if the Level of the Traversal is K then store all the Nodes of that Level in a Set such that there are no duplicate nodes at that level.
Algorithm:
- Initialize an Empty Queue to store the nodes at a level.
- Enqueue the Root node of the Binary Tree in the queue.
- Initialize the Level as 0, as the first level of the tree is supposed to be 0 here.
- Initialize the flag as 0 to check Kth level is reached or not.
- Iterate using a while loop until the queue is not empty.
- Find the size of the queue and store in a variable size to visit only the nodes of a current level.
- Iterate with another while loop until the size variable is not 0
- Deque a node from the queue and Enqueue its Left and right childs in the Queue.
- If the current level is equal to the K, then add the data of the node into the set and also set the flag.
- If flag is set then break the loop to not visit further levels, otherwise increment the current level by 1.
- Print the elements of the set with the help of iterator.
Explanation with Example:
Binary Tree -
50 --- Level 0
/ \
60 70 --- Level 1
/ \ / \
90 40 40 20 --- Level 2
K = 2
Initialize Queue and Set and append Root in queue
Step 1:
Queue = [50], Set = {}, Level = 0
As current Level is not equal to K,
Deque nodes from the queue and enqueue its child
Step 2:
Queue = [60, 70], Set = {}, Level = 1
As current level is not equal to K
Deque nodes one by one from the queue and enqueue its child
Step 3:
Queue = [90, 40, 40, 20], Set = {}, Level = 2
As the current level is equal to K
Deque all the nodes from the queue and add to the set
Set = {90, 40, 20}
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* temp = new struct node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = nullptr;
temp->right = nullptr;
return temp;
};
void nodesAtKthLevel(struct node* root,
int k){
if (root == nullptr)
return;
queue<struct node*> que;
que.push(root);
set<int> s;
int level = 0;
int flag = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
while (size--) {
struct node* ptr = que.front();
que.pop();
if (level == k) {
flag = 1;
s.insert(ptr->data);
}
else {
if (ptr->left)
que.push(ptr->left);
if (ptr->right)
que.push(ptr->right);
}
}
level++;
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
set<int>::iterator it;
for (it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
struct node* root = new struct node;
root = newNode(60);
root->left = newNode(20);
root->right = newNode(30);
root->left->left = newNode(80);
root->left->right = newNode(10);
root->right->left = newNode(40);
int level = 1;
nodesAtKthLevel(root, level);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class node {
int data;
node left;
node right;
};
static node newNode(int data)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
};
static void nodesAtKthLevel(node root,
int k){
if (root == null)
return;
Queue<node> que = new LinkedList<node>();
que.add(root);
HashSet<Integer> s = new HashSet<Integer>();
int level = 0;
int flag = 0;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int size = que.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
node ptr = que.peek();
que.remove();
if (level == k) {
flag = 1;
s.add(ptr.data);
}
else {
if (ptr.left!=null)
que.add(ptr.left);
if (ptr.right!=null)
que.add(ptr.right);
}
}
level++;
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
for (int it : s) {
System.out.print(it+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
node root = new node();
root = newNode(60);
root.left = newNode(20);
root.right = newNode(30);
root.left.left = newNode(80);
root.left.right = newNode(10);
root.right.left = newNode(40);
int level = 1;
nodesAtKthLevel(root, level);
}
}
|
Python3
from collections import deque
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
def nodesAtKthLevel(root: Node, k: int):
if root is None:
return
que = deque()
que.append(root)
s = set()
level = 0
flag = 0
while que:
size = len(que)
while size:
ptr = que[0]
que.popleft()
if level == k:
flag = 1
s.add(ptr.data)
else:
if ptr.left:
que.append(ptr.left)
if ptr.right:
que.append(ptr.right)
size -= 1
level += 1
if flag == 1:
break
for it in s:
print(it, end = " ")
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(60)
root.left = Node(20)
root.right = Node(30)
root.left.left = Node(80)
root.left.right = Node(10)
root.right.left = Node(40)
level = 1
nodesAtKthLevel(root, level)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
class node {
public int data;
public node left;
public node right;
};
static node newNode(int data)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
static void nodesAtKthLevel(node root,
int k){
if (root == null)
return;
List<node> que = new List<node>();
que.Add(root);
HashSet<int> s = new HashSet<int>();
int level = 0;
int flag = 0;
while (que.Count != 0) {
int size = que.Count;
while (size-- > 0) {
node ptr = que[0];
que.RemoveAt(0);
if (level == k) {
flag = 1;
s.Add(ptr.data);
}
else {
if (ptr.left != null)
que.Add(ptr.left);
if (ptr.right != null)
que.Add(ptr.right);
}
}
level++;
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
foreach (int it in s) {
Console.Write(it+ " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
node root = new node();
root = newNode(60);
root.left = newNode(20);
root.right = newNode(30);
root.left.left = newNode(80);
root.left.right = newNode(10);
root.right.left = newNode(40);
int level = 1;
nodesAtKthLevel(root, level);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class node {
constructor()
{
this.data = 0;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
};
function newNode(data)
{
var temp = new node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
function nodesAtKthLevel(root, k){
if (root == null)
return;
var que = [];
que.push(root);
var s = new Set();
var level = 0;
var flag = 0;
while (que.length != 0) {
var size = que.length;
while (size-- > 0) {
var ptr = que[0];
que.shift();
if (level == k) {
flag = 1;
s.add(ptr.data);
}
else {
if (ptr.left != null)
que.push(ptr.left);
if (ptr.right != null)
que.push(ptr.right);
}
}
level++;
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
for(var it of s) {
document.write(it+ " ");
}
document.write("<br>");
}
var root = new node();
root = newNode(60);
root.left = newNode(20);
root.right = newNode(30);
root.left.left = newNode(80);
root.left.right = newNode(10);
root.right.left = newNode(40);
var level = 1;
nodesAtKthLevel(root, level);
</script>
|
Performance Analysis:
- Time Complexity: As in the above approach in the worst case all the N nodes of the Tree are visited, So the Time complexity will be O(N)
- Space Complexity: As in the worst case at the bottom most level of the Tree it can have the maximum number of the nodes which is 2H-1 where H is the height of the Binary Tree, then Space complexity of the Binary Tree will be O(2H-1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...