Find the Maximum Depth or Height of given Binary Tree
Last Updated :
03 Oct, 2023
Given a binary tree, the task is to find the height of the tree. The height of the tree is the number of vertices in the tree from the root to the deepest node.
Note: The height of an empty tree is 0 and the height of a tree with single node is 1.
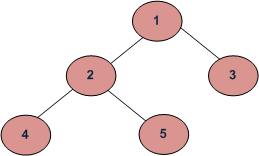
Example of Binary Tree
Recursively calculate the height of the left and the right subtrees of a node and assign height to the node as max of the heights of two children plus 1. See below the pseudo code and program for details.
Illustration:
Consider the following tree:

Example of Tree
maxDepth(‘1’) = max(maxDepth(‘2’), maxDepth(‘3’)) + 1 = 2 + 1
because recursively
maxDepth(‘2’) = max (maxDepth(‘4’), maxDepth(‘5’)) + 1 = 1 + 1 and (as height of both ‘4’ and ‘5’ are 1)
maxDepth(‘3’) = 1
Follow the below steps to Implement the idea:
- Recursively do a Depth-first search.
- If the tree is empty then return 0
- Otherwise, do the following
- Get the max depth of the left subtree recursively i.e. call maxDepth( tree->left-subtree)
- Get the max depth of the right subtree recursively i.e. call maxDepth( tree->right-subtree)
- Get the max of max depths of left and right subtrees and add 1 to it for the current node.
- Return max_depth.
Below is the Implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class node {
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
int maxDepth(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
else {
int lDepth = maxDepth(node->left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node->right);
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return (Node);
}
int main()
{
node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Height of tree is " << maxDepth(root);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
int maxDepth(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
else {
int lDepth = maxDepth(node->left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node->right);
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("Height of tree is %d", maxDepth(root));
getchar();
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
int maxDepth(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
else {
int lDepth = maxDepth(node.left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node.right);
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Height of tree is "
+ tree.maxDepth(tree.root));
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def maxDepth(node):
if node is None:
return 0
else:
lDepth = maxDepth(node.left)
rDepth = maxDepth(node.right)
if (lDepth > rDepth):
return lDepth+1
else:
return rDepth+1
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print("Height of tree is %d" % (maxDepth(root)))
|
C#
using System;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree {
Node root;
int maxDepth(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
else {
int lDepth = maxDepth(node.left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node.right);
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Height of tree is "
+ tree.maxDepth(tree.root));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node
{
constructor(item)
{
this.data=item;
this.left=this.right=null;
}
}
let root;
function maxDepth(node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
else
{
let lDepth = maxDepth(node.left);
let rDepth = maxDepth(node.right);
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
document.write("Height of tree is : " +
maxDepth(root));
</script>
|
OutputHeight of tree is 3
Time Complexity: O(N) (Please see the post on Tree Traversal for details)
Auxiliary Space: O(N) due to recursive stack.
Find the Maximum Depth or Height of a Tree using Level Order Traversal:
Do Level Order Traversal, while adding Nodes at each level to Queue, we have to add NULL Node so that whenever it is encountered, we can increment the value of variable and that level get counted.
Follow the below steps to Implement the idea:
- Traverse the tree in level order traversal starting from root.
- Initialize an empty queue Q, a variable depth and push root, then push null into the Q.
- Run a while loop till Q is not empty.
- Store the front element of Q and Pop out the front element.
- If the front of Q is NULL then increment depth by one and if queue is not empty then push NULL into the Q.
- Else if the element is not NULL then check for its left and right children and if they are not NULL push them into Q.
- Return depth.
Below is the Implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
int height(struct Node* root)
{
int depth = 0;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if (temp == NULL) {
depth++;
}
if (temp != NULL) {
if (temp->left) {
q.push(temp->left);
}
if (temp->right) {
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
else if (!q.empty()) {
q.push(NULL);
}
}
return depth;
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Height(Depth) of tree is: " << height(root);
}
|
Java
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class GFG {
static class Node {
int key;
Node left;
Node right;
}
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
public static int height(Node root)
{
int depth = 0;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
q.add(null);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node temp = q.peek();
q.remove();
if (temp == null) {
depth++;
}
if (temp != null) {
if (temp.left != null) {
q.add(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null) {
q.add(temp.right);
}
}
else if (!q.isEmpty()) {
q.add(null);
}
}
return depth;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
System.out.println("Height(Depth) of tree is: "
+ height(root));
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.key = 0
self.left, self.right = None, None
def newNode(key):
temp = Node()
temp.key = key
temp.left, temp.right = None, None
return temp
def height(root):
depth = 0
q = []
q.append(root)
q.append(None)
while(len(q) > 0):
temp = q[0]
q = q[1:]
if(temp == None):
depth += 1
if(temp != None):
if(temp.left):
q.append(temp.left)
if(temp.right):
q.append(temp.right)
elif(len(q) > 0):
q.append(None)
return depth
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
print(f"Height(Depth) of tree is: {height(root)}")
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree {
Node root;
int height()
{
int depth = 0;
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
q.Enqueue(root);
q.Enqueue(null);
while (q.Count != 0) {
Node temp = q.Dequeue();
if (temp == null)
depth++;
if (temp != null) {
if (temp.left != null) {
q.Enqueue(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null) {
q.Enqueue(temp.right);
}
}
else if (q.Count != 0) {
q.Enqueue(null);
}
}
return depth;
}
public static void Main()
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Height(Depth) of tree is: "
+ tree.height());
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node{
constructor(){
this.key = 0
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
}
function newNode(key){
let temp = new Node()
temp.key = key
temp.left = null
temp.right = null
return temp
}
function height(root){
let depth = 0
let q = []
q.push(root)
q.push(null)
while(q.length>0){
let temp = q.shift()
if(temp == null)
depth += 1
if(temp != null){
if(temp.left)
q.push(temp.left)
if(temp.right)
q.push(temp.right)
}
else if(q.length>0)
q.push(null)
}
return depth
}
let root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
document.write(`Height(Depth) of tree is: ${height(root)}`,"</br>")
</script>
|
OutputHeight(Depth) of tree is: 3
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
This method also uses the concept of Level Order Traversal but we wont be adding null in the Queue. Simply increase the counter when the level increases and push the children of current node into the queue, then remove all the nodes from the queue of the current Level.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
int height(Node* root)
{
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
int height = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if (temp->left != NULL) {
q.push(temp->left);
}
if (temp->right != NULL) {
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
height++;
}
return height;
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Height(Depth) of tree is: " << height(root);
}
|
Java
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class GFG {
static class Node {
int key;
Node left;
Node right;
}
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
public static int height(Node root)
{
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<Node>();
q.add(root);
int height = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node temp = q.poll();
if (temp.left != null) {
q.add(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null) {
q.add(temp.right);
}
}
height++;
}
return height;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
System.out.println("Height(Depth) of tree is: "
+ height(root));
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.key = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def height(root):
if root is None:
return 0
q = []
q.append(root)
height = 0
while q:
nodeCount = len(q)
while nodeCount > 0:
node = q.pop(0)
if node.left is not None:
q.append(node.left)
if node.right is not None:
q.append(node.right)
nodeCount -= 1
height += 1
return height
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print("Height(Depth) of tree is", height(root))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
class Node {
public int key;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int key)
{
this.key=key;
this.left=this.right=null;
}
}
static int height(Node root)
{
Queue<Node> q=new Queue<Node>();
q.Enqueue(root);
int height = 0;
while (q.Count>0) {
int size = q.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node temp = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
if (temp.left != null) {
q.Enqueue(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null) {
q.Enqueue(temp.right);
}
}
height++;
}
return height;
}
public static void Main()
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.Write("Height(Depth) of tree is: " + height(root));
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node{
constructor(key){
this.key = key;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
function newNode(key){
return new Node(key);
}
function height(root){
let q = [];
q.push(root);
let height = 0;
while(q.length > 0){
let size = q.length;
for(let i = 0; i<size; i++){
let temp = q.shift();
if(temp.left != null){
q.push(temp.left);
}
if(temp.right != null){
q.push(temp.right);
}
}
height++;
}
return height;
}
let root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
document.write("Height(Depth) of tree is: " + height(root));
|
OutputHeight(Depth) of tree is: 3
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...