Minimum number of cuts required to pay salary from N length Gold Bar
Last Updated :
30 Jan, 2022
Given a gold bar of length N with N equal markings, the task is to find the minimum number of cuts required to pay the salary in N days such that on any ith day the worker has i parts of the gold bar.
Examples:
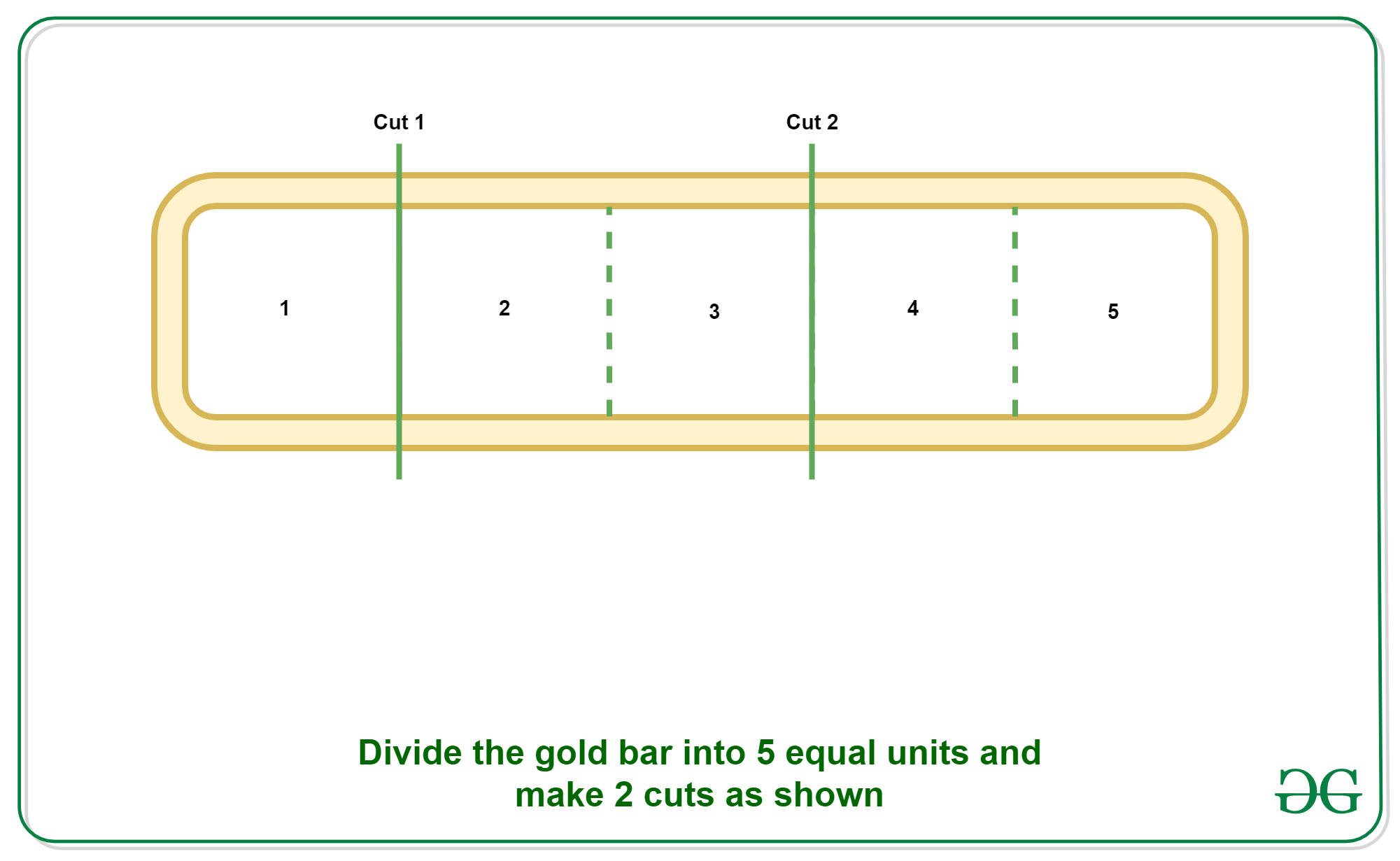
Input: N = 5
Output: 2
Explanation:
Divide the 5 length Gold bar into 3 part of length 1, 2, 2 by making 2 cuts. Then salary for each day will be as:
For Day 1 = 1 (Give 1 length bar)
For Day 2 = 2 – 1 = 1 (Give 2 length bar and take back 1 length bar)
For Day 3 = 1 (Give 1 length bar)
For Day 4 = 2 – 1 = 1 (Give 2 length bar and take back 1 length bar)
For Day 5 = 1 (Give 1 length bar)
Input: N = 15
Output: 3
Explanation:
Divide the 15 length Gold bar into 4 part of length 1, 2, 4, 8 by making 3 cuts. Then salary for each day will be as:
For Day 1 = 1 (Give 1 length bar)
For Day 2 = 2 – 1 = 1 (Give 2 length bar and take back 1 length bar)
For Day 3 = 1 (Give 1 length bar)
For Day 4 = 4 – 2 – 1 = 1 (Give 4 length bar and take back 1 and 2 length bar)
For Day 5 = 1 (Give 1 length bar)
For Day 6 = 2 – 1 = 1 (Give 2 length bar and take back 1 length bar)
For Day 7 = 1 (Give 1 length bar)
For Day 8 = 8 – 4 – 2 – 1 = 1 (Give 8 length bar and take back 1, 2 and 4 length bar)
For Day 9 = 1 (Give 1 length bar)
For Day 10 = 2 – 1 = 1 (Give 2 length bar and take back 1 length bar)
For Day 11 = 1 (Give 1 length bar)
For Day 12 = 4 – 2 – 1 = 1 (Give 4 length bar and take back 1 and 2 length bar)
For Day 13 = 1 (Give 1 length bar)
For Day 14 = 2 – 1 = 1 (Give 2 length bar and take back 1 length bar)
For Day 15 = 1 (Give 1 length bar)
Approach:
As we know any number can be represented with the help of the numbers in the form of powers of 2. So If we cut the length of Gold Bar into the nearest integer to log2 (N) then we can represent any number up to N.
For example: When N = 15, we can divide the number into the parts 1, 2, 4, 8 and using these numbers we can represent any number from 1 to 15, as shown below:
For 1 - 1
For 2 - 2
For 3 - 2 + 1
For 4 - 4
For 5 - 4 + 1
For 6 - 4 + 2
For 7 - 4 + 2 + 1
For 8 - 8
For 9 - 8 + 1
For 10 - 8 + 2
For 11 - 8 + 2 + 1
For 12 - 8 + 4
For 13 - 8 + 4 + 1
For 14 - 8 + 4 + 2
For 15 - 8 + 4 + 2 + 1
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int pay(int n)
{
int cuts = int(log(n)/log(2));
return cuts;
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
int cuts = pay(n);
cout << cuts << endl;
n = 15;
cuts = pay(n);
cout<<(cuts);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static int pay(int n)
{
int cuts = (int) (Math.log(n)/Math.log(2));
return cuts;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
int cuts = pay(n);
System.out.print(cuts +"\n");
n = 15;
cuts = pay(n);
System.out.print(cuts);
}
}
|
Python
import math
def pay(n):
cuts = int(math.log(n, 2))
return cuts
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 5
cuts = pay(n)
print(cuts)
n = 15
cuts = pay(n)
print(cuts)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int pay(int n)
{
int cuts = (int) (Math.Log(n)/Math.Log(2));
return cuts;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
int cuts = pay(n);
Console.Write(cuts +"\n");
n = 15;
cuts = pay(n);
Console.Write(cuts);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function pay(n)
{
let cuts = parseInt(Math.log(n)/Math.log(2));
return cuts;
}
let n = 5;
let cuts = pay(n);
document.write(cuts + "<br>");
n = 15;
cuts = pay(n);
document.write(cuts + "<br>");
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...