Minimum increments or decrements required to convert a sorted array into a power sequence
Last Updated :
07 Apr, 2021
Given a sorted array arr[] consisting of N positive integers, the task is to minimize the total number of increments or decrements of each array element required to convert the given array into a power sequence of any arbitrary integer X.
A sequence is called a power sequence of any integer X, if and only if for every ith element (0 ? i < N), arr[i] = Xi, where N is length of the given array.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {1, 3, 4}
Output: 1
Explanation: Decreasing arr[1] by 1 modifies array to {1, 2, 4}, which is a power sequence of 2. Therefore, the total number of increments or decrements required is 1.
Input: arr[] = {1, 5, 7}
Output: 6
Explanation:
Operation 1: Decreasing arr[1] by 1 modifies array to {1, 4, 7}
Operation 2: Decreasing arr[1] by 1 modifies array to {1, 3, 7}
Operation 3: Increasing arr[2] by 1 modifies array to {1, 3, 8}
Operation 4: Increasing arr[2] by 1 modifies array to {1, 3, 9}, which is the power sequence of 3. Therefore, the total number of increments or decrements required is 4.
Approach: The given problem can be solved based on the following observations:
- As the given array needs to be converted into a power sequence for any arbitrary integer X, then the mathematical relations can be written as:
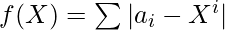
where, 0 <= i < N, N is the number of elements in the array.
- The minimum value of f(X) is the minimum number of operations required to convert it into a power sequence of X and the maximum value of X can be calculated as follows:
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com X^{N - 1} - a[N - 1] \le f(c) \le f(1)](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9832cbbfb4af5f59da3988a78a3e8f8b_l3.png)
=>![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com X^{N - 1} \le f(1) + a{[N - 1]}](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-84b7af3feedff3d5859c95abadd0c130_l3.png)
- Therefore, the idea is to iterate for all possible values of X starting from 1, and check if the following equation satisfies or not:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com X^{N - 1} \le f(1) + a{[N - 1]}](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f6b50d71e9a3be4f5424e2ef0d8c710a_l3.png)
If found to be true, then find all possible values of 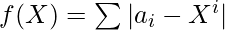 and return the minimum among all the values obtained.
and return the minimum among all the values obtained.
Follow the steps below to solve the given problem:
- Initialize a variable, say ans as (the sum of array elements – N), that stores the minimum number of increments or decrements required to make the array a power sequence.
- Iterate a loop, starting from 1, using the variable X and perform the following steps:
- Initialize two variables, say currCost as 0 and currPower as 1, that stores the sum of the expression
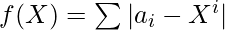 and power of the integer X.
and power of the integer X. - Iterate over the range [0, N – 1] and update the value of currCost as currCost + abs(arr[i] – currPower) and the value of currPower as X * currPower.
- If the expression
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com X^{N - 1} \le ans + a{[N - 1]}](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b42e7158da45cf19f6e455b4855cd7d1_l3.png) is not satisfied, then break out of the loop. Otherwise, update the value of ans to the minimum of ans and currCost.
is not satisfied, then break out of the loop. Otherwise, update the value of ans to the minimum of ans and currCost.
- After completing the above steps, print the value of ans as the required minimum number of operations.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int minOperations(int a[], int n)
{
int ans = accumulate(a, a + n, 0) - n;
for (int x = 1;; x++) {
int curPow = 1, curCost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
curCost += abs(a[i] - curPow);
curPow *= x;
}
if (curPow / x > ans + a[n - 1])
break;
ans = min(ans, curCost);
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 5, 7 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << minOperations(arr, N);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG{
static int minOperations(int a[], int n)
{
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ans += a[i];
}
ans -= n;
for(int x = 1;; x++)
{
int curPow = 1, curCost = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
curCost += Math.abs(a[i] - curPow);
curPow *= x;
}
if (curPow / x > ans + a[n - 1])
break;
ans = Math.min(ans, curCost);
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 5, 7 };
int N = arr.length;
System.out.print(minOperations(arr, N));
}
}
|
Python3
def minOperations(a, n):
ans = 0
for i in range(n):
ans += a[i]
ans -= n
x = 1
while(1):
curPow = 1
curCost = 0
for i in range(n):
curCost += abs(a[i] - curPow)
curPow *= x
if (curPow / x > ans + a[n - 1]):
break
ans = min(ans, curCost)
x += 1
return ans
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [1, 5, 7]
N = len(arr)
print(minOperations(arr, N))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static int minOperations(int []a, int n)
{
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ans += a[i];
}
ans -= n;
for(int x = 1;; x++)
{
int curPow = 1, curCost = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
curCost += Math.Abs(a[i] - curPow);
curPow *= x;
}
if (curPow / x > ans + a[n - 1])
break;
ans = Math.Min(ans, curCost);
}
return ans;
}
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = { 1, 5, 7 };
int N = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(minOperations(arr, N));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function minOperations(a , n) {
var ans = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ans += a[i];
}
ans -= n;
for (x = 1;; x++) {
var curPow = 1, curCost = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
curCost += Math.abs(a[i] - curPow);
curPow *= x;
}
if (curPow / x > ans + a[n - 1])
break;
ans = Math.min(ans, curCost);
}
return ans;
}
var arr = [ 1, 5, 7 ];
var N = arr.length;
document.write(minOperations(arr, N));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N*(S)(1/(N – 1)))
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...