Merge and Append Queries in Power BI
Last Updated :
13 Dec, 2023
Power BI is a popular data visualization tool that can be used to create interactive reports and dashboards. It can work on different types of data. A key feature to be noted is its ability to combine multiple data. The merging and appending functions in Power BI let you combine data from several tables.
Depending on the kind of concatenation you need to perform for your needs, you can choose between merge and append queries.
- Merge queries are mostly used when you have two tables that have one column in common. Thus, it can help us create a new table or make changes to an existing table based on the common column.
- On the other hand, append queries will help you join two or more queries by stacking them on top of each other. Therefore, it adds more rows to an existing query or creates a new query by appending multiple queries.
In this article, we will discuss about merging and appending queries in Power BI. We will discover the variations between append and merge queries, various joint kinds, and applications for fuzzy matching.
Merge Queries
Based on common criteria (a common column) between the tables, merge operations unite various datasets or tables horizontally. This means that data is added to the matching rows in the base or first table from the second and subsequent tables.
The primary table will consist of the same number of rows after the procedure as it did at the beginning if you use the default merge operation, but each row will have one or more new columns. However, if you choose for an other type of merge, this will not be applicable. The default merge functions in the same manner as an SQL left outer join.
How to Merge Queries?
Consider that we have two tables. The Sales Data is the first, and the next is Product data.
Sales Data:

Sales Data
Product Data:

Product Data
The following are the steps to merge the queries:
Step 1. Choose the query (table) that you want to combine the other query (or table) into from the Power Query Editor’s left pane. It’s Sales Data in this instance.
Step2. Select Sales Data Table. To access the Ribbon Menu, click the Home Tab.
Step 3. In the Combine section, click Merge.
Step 4. We will see two options under “Merge Queries”: “Merge Queries” and “Merge Queries as New.”
Step 5. After selecting Merge Queries option, choose Sales Data from the first drop-down option, then click Product Key (the shared column that separates the Sales and Product tables).
Step 6. Choose Product Data from the second drop-down option, then click Product_Key.
Step 7. Click on OK.
- Merge Queries option doesn’t generate a new table; instead, it merges two tables. Whereas, to build a new table by merging two or more, you must select Merge Queries as New option.
- We may choose the two tables from the drop-down list on the merge page, and then we can choose which column or columns (we can even choose several columns to join upon) will be combined together.
- We are utilizing Product_Key from the Sales Data table and Product_Key from the Product Data dataset below.

Merge Query
Join Types
There are six different kinds of joins:
- Left Outer Join: It includes all rows from first selected data and only the matching rows from second query.
- Left Outer Join: It includes all rows from second selected data and only the matching rows from first query.
- Full Outer Join: It includes all rows from both, first and second selected query.
- Inner Join: It selects only the matching rows from both query.
- Left Anti Join: It includes only the rows from the first query.
- Right Anti Join: It includes only the rows from the second query.

Types Of Join

Join Kind
Fuzzy Match
By selecting the fuzzy match option, we can increase the Merge function’s reach.
When the fuzzy matching option is used, the number of matches will grow. The range of the similarity threshold is 0 to 1. In general, a default value of 0 would indicate a full outer join in SQL—match on precise matches—while a value of 1.00 would indicate an inner join.
In order to discover the matching join, the match by combining text portions option will combine two text values.

Fuzzy Match in Merge Queries
Append Queries
Append Operation is used to combine queries by stacking them on top of each other. When the column values in two tables match, the data rows from a given table will be added (or inserted) at the bottom of the other table’s data rows.
The base table will therefore have same number of columns at the conclusion of the procedures as it did at the beginning, but each column will have extra rows in an append operation.
Append refers to the process of combining the output of two or more queries—which are tables themselves—into a single query.
- One row at a time will be inserted. (For instance, adding a 250-row query to a 150-row query will result in a 400-row result set.)
- Each query* will have the same number of columns. (Column1, Column2,…, Column7 in the first query, for instance, will result in one table with a single set of column1, Column2…, Column7 once the same columns are appended in the second query.)
How to Append Queries?
The following are the steps to append the queries:
Step 1. Choose the query (table) that you wish the other query to append from the Power Query Editor’s left pane. It’s Sales Data in this instance.
Step 2. After selecting Sales Data Table click the Home Tab to access the Ribbon Menu.
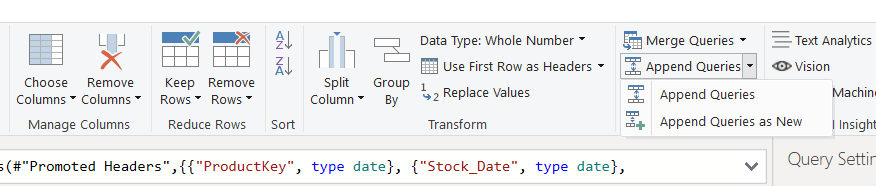
Append Queries
Step 3. Select Append Queries from the Combine menu.
Step 4. Select Add Queries as New. A pop-up menu will appear.

Append Query popup
Step 5. Pick first query from the first drop-down selection.
Step 6. Choose second query from the second drop-down selection.
Step 7. Select OK.

After Appending Queries
- Select Append Queries as New if you want to preserve the current query result and generate a new query with the appended result. If not, simply choose Append Queries. Additionally, you have the option to add three or more tables to the list at a time.
- Duplicate rows cannot be eliminated by appending queries; instead, we must use Group by or remove duplicate records.
What if the columns are different in the queries?
Append still functions even if the columns in the source queries are different; however, it will add one column to the output for every new column. The cell value of that column for those rows will be null if that column is absent from one of the sources. Append is equivalent to SQL’s UNION ALL.
Why should we combine Queries?
Before we dive deep into the concept of Merge and Append Queries, we must understand why combining queries is useful.
- Combination Of Data From Multiple Sources: It helps to combine the data that may have been stored in multiple different locations such as a CRM system, an ERP system, and a database. You can combine it into a single table to create reports.
- Create New Relationships: Two more columns can be related using a single common column. Therefore, you study this relationship further and draw insights by combining queries.
- Clean and Transform Data: Merge and Append Queries are also used to clean and transform the data before creating a report or dashboard. For example, we can remove duplicate rows or rename columns easily.
- Improve performance Of Reports And Dashboard: It allows us to create an efficient data model that can load faster and have improved performance.
Difference Between Merge And Append Query
|
merges two tables according to a shared column
|
stacks two tables on top of one another to combine them.
|
|
In each table, at least one matching column must exist.
|
It may require all columns to match in each table
|
|
Number of columns may differ in the queries
|
Queries to be appended should have same number of column
|
|
Additions of columns to the query
|
Addition of more rows to the query
|
|
When you need to combine two tables into one by adding more columns, or when you need to create new relationships between tables
|
When a table already exists and you need to add more rows of data
|
Conclusion
Thus, it is easy to work with the data using PowerBI due to features like Merge and Append. Power BI merge and append queries are highly useful when getting ready to visualize your data because they allow you to combine data from several tables. When merge queries contain the fuzzy matching feature, which joins two tables based on partial matches, they become far more powerful.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...