Median of two Sorted Arrays of Different Sizes using Binary Search
Last Updated :
12 Jun, 2023
Given two sorted arrays, a[] and b[] os size n and m, the task is to find the median of these sorted arrays, in O(log(min(n, m)), when n is the number of elements in the first array, and m is the number of elements in the second array.
Note: In case of even numbers in total and if we want to return a median that exists in the merged array we can return the element in the (n+m)/2 or ((n+m)/2 – 1)th position.
Examples:
Input: a[] = {-5, 3, 6, 12, 15}, b[] = {-12, -10, -6, -3, 4, 10}
Output : The median is 3.
Explanation: The merged array is {-12, -10, -6, -5 , -3, 3, 4, 6, 10, 12, 15}, with median 3
Input : a[] = {2, 3, 5, 8}, b[] = {10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20}
Output : The median is 11.
Explanation: The merged array is {2, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20}
Median = average of two middle elements (as number of the elements are even) = (10 + 12) / 2 = 11.
Binary Search Approach to find Median of Two Sorted Arrays of Different Sizes:
Let us consider the case for a total of odd number of elements. Also consider, that i elements from the first array and j elements from the 2nd array are on the left half of the median (including median itself). Then the maximum of a[i] and b[j] is the median, The important task is to efficiently find out such i and j.
How to efficiently find i and j?
Let us consider there are i elements from the first array that are on the left of the median and the other elements on the left are from the second array. So the number of other elements are j = (n + m + 1)/2 – i. Now we need to validate if our assumption is correct. For that we have take the following actions:
- If a[i+1] > b[j] and b[j+1] > a[i] then we can definitely say that these are the elements on the left of the median.
- Otherwise, we have to reduce the number of elements taken from any one array. That can be decided based on the following fact:
- If a[i+1] is less than b[j], then we need to consider more elements from the first array.
- Otherwise, if b[j+1] is less than a[i], we need to consider more elements from the second array.
Instead of linear incrementation for considering more elements from any of the array, we can use Binary Search here.
Consider, in a previous search we have found x1 elements must be considered from the first array, and we consider not more than x2 elements can be chose from the first array. Now we are checking for i = (x1 + x2)/2 elements from the first array.
- If a[i+1] < b[j], we will change x1 = i+1.
- If the reverse is true, i.e., b[j+1] < a[i] make x2 = i-1.
So the solution comes down to the following:
Initially take x1 = 0 and x2 = N and repeatedly follow the above binary search concept repeatedly, till we find out such i and j. After that the maximum between a[i] and b[j] will be the median when there are total odd number of elements.
Note that in case the total number of elements is even, the median will be the average of max(a[i], b[j]) and min(a[i+1], b[j+1]).
Note: The partition didn’t work if any one array is empty from the given arrays:
For example: if arr1=[2], arr2=[] by this “(n + m + 1) / 2” formula the value of i=0 and value of j=1 and this give you out of index error because arr2 is empty and arr2[j] give you out of index error. You have to handle this case by checking if one array is empty you can simply return the medium of another array.
What to be careful about during calculation?
There is one scope of error while calculating j = (n + m + 1)/2 – i. This may result in a negative value of j for some cases. So to avoid accessing a negative index, check the value of j, and if it is negative, the median is on the first array itself. Find the element at the position (n + m + 1)/2 [the average of (n+m)/2 and the next element if total even number of elements] and return this as the median.
Illustration of finding Median of two sorted arrays of different size using Binary Search
See the below examples for a better understanding:
Example 1: When the total number of elements is odd:
Step 1: Initially, consider that 3 elements from the first array are to the left of the median. But this does not fit the condition as 20 > 11. So, for the next iteration, a minimum of 4 elements from the first array should be considered.
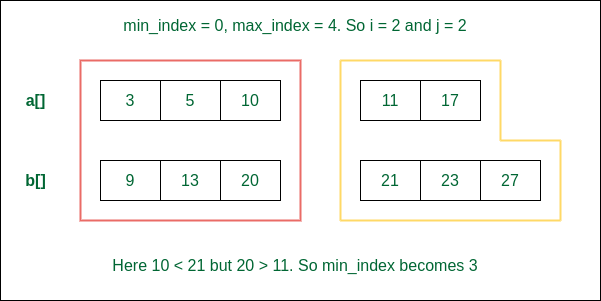
Consider 3 elements from 1st array on the left of the median
Step 2: A minimum of 4 and not more than 5 from the first array can be considered. So we consider 4 elements from the first array. This satisfies the condition and both 11 and 13 are less than 20 and 17 respectively. So the median is max(11, 13) = 13.
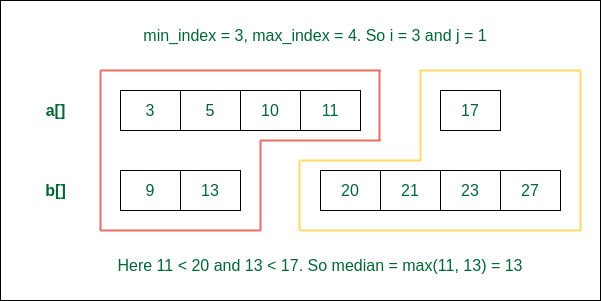
Consider 4 elements from 1st array on the left of the median
Example 2: When the total number of elements is even.
Step 1: Consider 2 elements from the first array to be on the left of the median. But 14 > 5. So more elements from the first array should be considered.
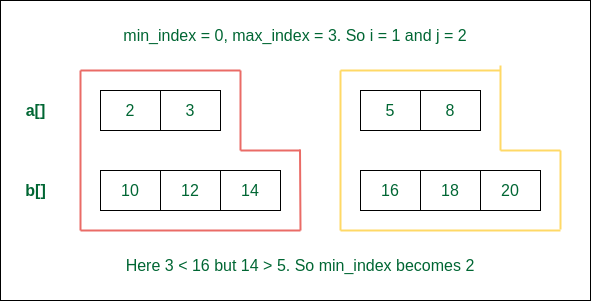
Consider 2 elements from the first on the left of the median
Step 2: At least 3 and not more than 4 elements from the first array can be considered. So, we consider 3 elements. But again 12 > 8. So we need to take more from the first array.
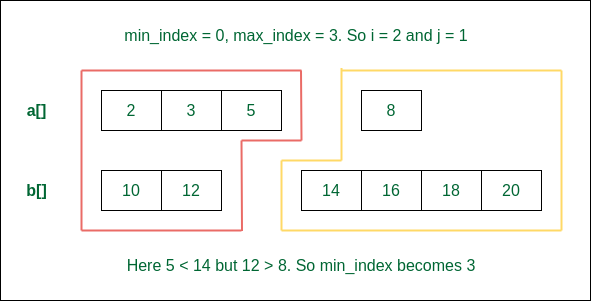
Consider 3 elements from the first on the left of the median
Step 3: We need to consider more than 3 from the first array. So we consider all the elements from the first array and this satisfies the condition that 8 < 12. So now the median becomes the average of max(8, 10) and 12 i.e., (10 + 12)/2 = 11.
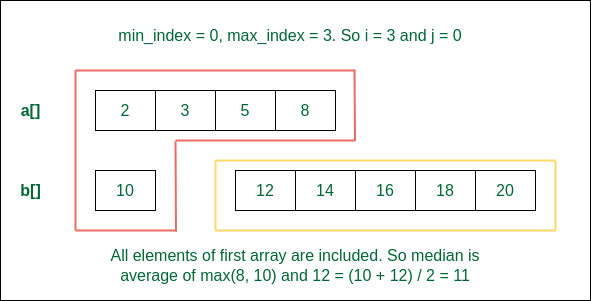
Consider all elements from the first on the left of the median
Code implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using std::cout;
int maximum(int a, int b);
int minimum(int a, int b);
double findMedianSortedArrays(int* a, int n, int* b, int m)
{
int min_index = 0, max_index = n, i, j, median;
while (min_index <= max_index) {
i = (min_index + max_index) / 2;
j = ((n + m + 1) / 2) - i;
if (j < 0) {
max_index = i - 1;
continue;
}
if (i < n && j > 0 && b[j - 1] > a[i])
min_index = i + 1;
else if (i > 0 && j < m && b[j] < a[i - 1])
max_index = i - 1;
else {
if (i == 0)
median = b[j - 1];
else if (j == 0)
median = a[i - 1];
else
median = maximum(a[i - 1], b[j - 1]);
break;
}
}
if ((n + m) % 2 == 1)
return (double)median;
if (i == n)
return (median + b[j]) / 2.0;
if (j == m)
return (median + a[i]) / 2.0;
return (median + minimum(a[i], b[j])) / 2.0;
}
int maximum(int a, int b) { return a > b ? a : b; }
int minimum(int a, int b) { return a < b ? a : b; }
int main()
{
int a[] = { 900 };
int b[] = { 10, 13, 14 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(int);
int m = sizeof(b) / sizeof(int);
if (n < m)
cout << "The median is : "
<< findMedianSortedArrays(a, n, b, m);
else
cout << "The median is : "
<< findMedianSortedArrays(b, m, a, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int[] a = new int[] { 900 };
static int[] b = new int[] { 10, 13, 14 };
static int maximum(int a, int b)
{
return a > b ? a : b;
}
static int minimum(int a, int b)
{
return a < b ? a : b;
}
static double findMedianSortedArrays(int n, int m)
{
int min_index = 0, max_index = n, i = 0, j = 0,
median = 0;
while (min_index <= max_index) {
i = (min_index + max_index) / 2;
j = ((n + m + 1) / 2) - i;
if (i < n && j > 0 && b[j - 1] > a[i])
min_index = i + 1;
else if (i > 0 && j < m && b[j] < a[i - 1])
max_index = i - 1;
else {
if (i == 0)
median = b[j - 1];
else if (j == 0)
median = a[i - 1];
else
median = maximum(a[i - 1], b[j - 1]);
break;
}
}
if ((n + m) % 2 == 1)
return (double)median;
if (i == n)
return (median + b[j]) / 2.0;
if (j == m)
return (median + a[i]) / 2.0;
return (median + minimum(a[i], b[j])) / 2.0;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n = a.length;
int m = b.length;
if (n < m)
System.out.print(
"The median is : "
+ findMedianSortedArrays(n, m));
else
System.out.print(
"The median is : "
+ findMedianSortedArrays(m, n));
}
}
|
Python3
median = 0
i = 0
j = 0
def maximum(a, b):
return a if a > b else b
def minimum(a, b):
return a if a < b else b
def findMedianSortedArrays(a, n, b, m):
if n == 0:
if m % 2 == 0:
return (b[m/2]+b[(m/2)+1])/2
else:
return b[int(m/2)]
elif m == 0:
if n % 2 == 0:
return (a[n/2]+a[(n/2)+1])/2
else:
return a[int(n/2)]
global median, i, j
min_index = 0
max_index = n
while (min_index <= max_index):
i = int((min_index + max_index) / 2)
j = int(((n + m + 1) / 2) - i)
if (i < n and j > 0 and b[j - 1] > a[i]):
min_index = i + 1
elif (i > 0 and j < m and b[j] < a[i - 1]):
max_index = i - 1
else:
if (i == 0):
median = b[j - 1]
elif (j == 0):
median = a[i - 1]
else:
median = maximum(a[i - 1], b[j - 1])
break
if ((n + m) % 2 == 1):
return median
if (i == n):
return ((median + b[j]) / 2.0)
if (j == m):
return ((median + a[i]) / 2.0)
return ((median + minimum(a[i], b[j])) / 2.0)
a = [900]
b = [10, 13, 14]
n = len(a)
m = len(b)
if (n < m):
print("The median is : {}".format(findMedianSortedArrays(a, n, b, m)))
else:
echo("The median is : {}".format(findMedianSortedArrays(b, m, a, n)))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int maximum(int a, int b)
{
return a > b ? a : b;
}
static int minimum(int a, int b)
{
return a < b ? a : b;
}
static double findMedianSortedArrays(ref int[] a, int n,
ref int[] b, int m)
{
int min_index = 0, max_index = n, i = 0, j = 0,
median = 0;
while (min_index <= max_index) {
i = (min_index + max_index) / 2;
j = ((n + m + 1) / 2) - i;
if (i < n && j > 0 && b[j - 1] > a[i])
min_index = i + 1;
else if (i > 0 && j < m && b[j] < a[i - 1])
max_index = i - 1;
else {
if (i == 0)
median = b[j - 1];
else if (j == 0)
median = a[i - 1];
else
median = maximum(a[i - 1], b[j - 1]);
break;
}
}
if ((n + m) % 2 == 1)
return (double)median;
if (i == n)
return (median + b[j]) / 2.0;
if (j == m)
return (median + a[i]) / 2.0;
return (median + minimum(a[i], b[j])) / 2.0;
}
static void Main()
{
int[] a = new int[] { 900 };
int[] b = new int[] { 10, 13, 14 };
int n = a.Length;
int m = b.Length;
if (n < m)
Console.Write("The median is : "
+ findMedianSortedArrays(
ref a, n, ref b, m));
else
Console.Write("The median is : "
+ findMedianSortedArrays(
ref b, m, ref a, n));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
$median = 0;
$i = 0; $j = 0;
function maximum($a, $b)
{
return $a > $b ? $a : $b;
}
function minimum($a, $b)
{
return $a < $b ? $a : $b;
}
function findMedianSortedArrays(&$a, $n,
&$b, $m)
{
global $median, $i, $j;
$min_index = 0;
$max_index = $n;
while ($min_index <= $max_index)
{
$i = intval(($min_index +
$max_index) / 2);
$j = intval((($n + $m + 1) /
2) - $i);
if ($i < $n && $j > 0 &&
$b[$j - 1] > $a[$i])
$min_index = $i + 1;
else if ($i > 0 && $j < $m &&
$b[$j] < $a[$i - 1])
$max_index = $i - 1;
else
{
if ($i == 0)
$median = $b[$j - 1];
else if ($j == 0)
$median = $a[$i - 1];
else
$median = maximum($a[$i - 1],
$b[$j - 1]);
break;
}
}
if (($n + $m) % 2 == 1)
return $median;
if ($i == $n)
return (($median +
$b[$j]) / 2.0);
if ($j == $m)
return (($median +
$a[$i]) / 2.0);
return (($median +
minimum($a[$i],
$b[$j])) / 2.0);
}
$a = array(900);
$b = array(10, 13, 14);
$n = count($a);
$m = count($b);
if ($n < $m)
echo ("The median is : " .
findMedianSortedArrays($a, $n,
$b, $m));
else
echo ("The median is : " .
findMedianSortedArrays($b, $m,
$a, $n));
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
let a=[900];
let b=[10, 13, 14];
function maximum(a,b)
{
return a > b ? a : b;
}
function minimum(a,b)
{
return a < b ? a : b;
}
function findMedianSortedArrays(n,m)
{
let min_index = 0,
max_index = n, i = 0,
j = 0, median = 0;
while (min_index <= max_index)
{
i = Math.floor((min_index + max_index) / 2);
j = Math.floor((n + m + 1) / 2) - i;
if (i < n && j > 0 && b[j - 1] > a[i])
min_index = i + 1;
else if (i > 0 && j < m && b[j] < a[i - 1])
max_index = i - 1;
else
{
if (i == 0)
median = b[j - 1];
else if (j == 0)
median = a[i - 1];
else
median = maximum(a[i - 1],
b[j - 1]);
break;
}
}
if ((n + m) % 2 == 1)
return median;
if (i == n)
return (median + b[j]) / 2.0;
if (j == m)
return (median + a[i]) / 2.0;
return (median + minimum(a[i],
b[j])) / 2.0;
}
let n = a.length;
let m = b.length;
if (n < m)
document.write("The median is : " +
findMedianSortedArrays(n, m));
else
document.write("The median is : " +
findMedianSortedArrays(m, n));
</script>
|
Output
The median is : 13.5
Time Complexity: O(log(min(n, m))
Auxiliary Space: O(1), the space complexity of this algorithm is O(1), as we are not using any extra space.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...