Binary Search – Data Structure and Algorithm Tutorials
Last Updated :
16 Apr, 2024
Binary Search is defined as a searching algorithm used in a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half. The idea of binary search is to use the information that the array is sorted and reduce the time complexity to O(log N).
Example of Binary Search Algorithm
Conditions for when to apply Binary Search in a Data Structure:
To apply Binary Search algorithm:
- The data structure must be sorted.
- Access to any element of the data structure takes constant time.
Binary Search Algorithm:
In this algorithm,

Finding the middle index “mid” in Binary Search Algorithm
- Compare the middle element of the search space with the key.
- If the key is found at middle element, the process is terminated.
- If the key is not found at middle element, choose which half will be used as the next search space.
- If the key is smaller than the middle element, then the left side is used for next search.
- If the key is larger than the middle element, then the right side is used for next search.
- This process is continued until the key is found or the total search space is exhausted.
How does Binary Search work?
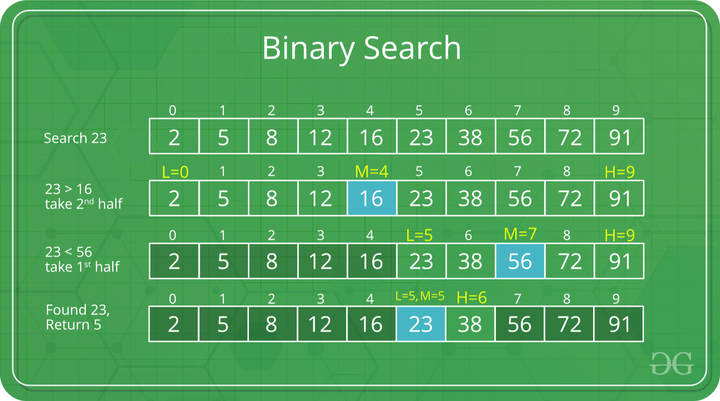
To understand the working of binary search, consider the following illustration:
Consider an array arr[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 23, 38, 56, 72, 91}, and the target = 23.
First Step: Calculate the mid and compare the mid element with the key. If the key is less than mid element, move to left and if it is greater than the mid then move search space to the right.
- Key (i.e., 23) is greater than current mid element (i.e., 16). The search space moves to the right.

Binary Search Algorithm : Compare key with 16
- Key is less than the current mid 56. The search space moves to the left.

Binary Search Algorithm : Compare key with 56
Second Step: If the key matches the value of the mid element, the element is found and stop search.

Binary Search Algorithm : Key matches with mid
How to Implement Binary Search?
The Binary Search Algorithm can be implemented in the following two ways
- Iterative Binary Search Algorithm
- Recursive Binary Search Algorithm
Given below are the pseudocodes for the approaches.
1. Iterative Binary Search Algorithm:
Here we use a while loop to continue the process of comparing the key and splitting the search space in two halves.
Implementation of Iterative Binary Search Algorithm:
C++
// C++ program to implement iterative Binary Search
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// An iterative binary search function.
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// If we reach here, then element was not present
return -1;
}
// Driver code
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1)
? cout << "Element is not present in array"
: cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
}
// C program to implement iterative Binary Search
#include <stdio.h>
// An iterative binary search function.
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// If we reach here, then element was not present
return -1;
}
// Driver code
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1) ? printf("Element is not present"
" in array")
: printf("Element is present at "
"index %d",
result);
return 0;
}
// Java implementation of iterative Binary Search
import java.io.*;
class BinarySearch {
// Returns index of x if it is present in arr[].
int binarySearch(int arr[], int x)
{
int l = 0, r = arr.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// If we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinarySearch ob = new BinarySearch();
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.length;
int x = 10;
int result = ob.binarySearch(arr, x);
if (result == -1)
System.out.println(
"Element is not present in array");
else
System.out.println("Element is present at "
+ "index " + result);
}
}
# Python3 code to implement iterative Binary
# Search.
# It returns location of x in given array arr
def binarySearch(arr, l, r, x):
while l <= r:
mid = l + (r - l) // 2
# Check if x is present at mid
if arr[mid] == x:
return mid
# If x is greater, ignore left half
elif arr[mid] < x:
l = mid + 1
# If x is smaller, ignore right half
else:
r = mid - 1
# If we reach here, then the element
# was not present
return -1
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [2, 3, 4, 10, 40]
x = 10
# Function call
result = binarySearch(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, x)
if result != -1:
print("Element is present at index", result)
else:
print("Element is not present in array")
// C# implementation of iterative Binary Search
using System;
class GFG {
// Returns index of x if it is present in arr[]
static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int x)
{
int l = 0, r = arr.Length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// If we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.Length;
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, x);
if (result == -1)
Console.WriteLine(
"Element is not present in array");
else
Console.WriteLine("Element is present at "
+ "index " + result);
}
}
// Program to implement iterative Binary Search
// A iterative binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
function binarySearch(arr, x)
{
let l = 0;
let r = arr.length - 1;
let mid;
while (r >= l) {
mid = l + Math.floor((r - l) / 2);
// If the element is present at the middle
// itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
r = mid - 1;
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
else
l = mid + 1;
}
// We reach here when element is not
// present in array
return -1;
}
arr =new Array(2, 3, 4, 10, 40);
x = 10;
n = arr.length;
result = binarySearch(arr, x);
(result == -1) ? console.log("Element is not present in array")
: console.log ("Element is present at index " + result);
// This code is contributed by simranarora5sos and rshuklabbb
<?php
// PHP program to implement
// iterative Binary Search
// An iterative binary search
// function
function binarySearch($arr, $l,
$r, $x)
{
while ($l <= $r)
{
$m = $l + ($r - $l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if ($arr[$m] == $x)
return floor($m);
// If x greater, ignore
// left half
if ($arr[$m] < $x)
$l = $m + 1;
// If x is smaller,
// ignore right half
else
$r = $m - 1;
}
// If we reach here, then
// element was not present
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(2, 3, 4, 10, 40);
$n = count($arr);
$x = 10;
$result = binarySearch($arr, 0,
$n - 1, $x);
if(($result == -1))
echo "Element is not present in array";
else
echo "Element is present at index ",
$result;
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
?>
OutputElement is present at index 3
Time Complexity: O(log N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
2. Recursive Binary Search Algorithm:
Create a recursive function and compare the mid of the search space with the key. And based on the result either return the index where the key is found or call the recursive function for the next search space.
Implementation of Recursive Binary Search Algorithm:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int leftIndex, int rightIndex, int query)
{
while(leftIndex <= rightIndex) {
// Calculate the middle index
int middleIndex = leftIndex + (rightIndex - leftIndex) / 2;
// Compare middle element with the query
if(arr[middleIndex] == query) {
return middleIndex;
}
// If query greater, ignore left half
if(arr[middleIndex] < query) {
leftIndex = middleIndex + 1;
}
// If query is smaller, ignore right half
else {
rightIndex = middleIndex - 1;
}
}
// Element is not present in array
return -1;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int query = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, query);
(result == -1)
? cout << "Element is not present in array"
: cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
}
// C program to implement recursive Binary Search
#include <stdio.h>
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
if (r >= l) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
// If the element is present at the middle
// itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not
// present in array
return -1;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1)
? printf("Element is not present in array")
: printf("Element is present at index %d", result);
return 0;
}
// Java implementation of recursive Binary Search
class BinarySearch {
// Returns index of x if it is present in arr[l..
// r], else return -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
if (r >= l) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
// If the element is present at the
// middle itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not present
// in array
return -1;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinarySearch ob = new BinarySearch();
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.length;
int x = 10;
int result = ob.binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
if (result == -1)
System.out.println(
"Element is not present in array");
else
System.out.println(
"Element is present at index " + result);
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
# Python3 Program for recursive binary search.
# Returns index of x in arr if present, else -1
def binarySearch(arr, l, r, x):
# Check base case
if r >= l:
mid = l + (r - l) // 2
# If element is present at the middle itself
if arr[mid] == x:
return mid
# If element is smaller than mid, then it
# can only be present in left subarray
elif arr[mid] > x:
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid-1, x)
# Else the element can only be present
# in right subarray
else:
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x)
# Element is not present in the array
else:
return -1
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [2, 3, 4, 10, 40]
x = 10
# Function call
result = binarySearch(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, x)
if result != -1:
print("Element is present at index", result)
else:
print("Element is not present in array")
// C# implementation of recursive Binary Search
using System;
class GFG {
// Returns index of x if it is present in
// arr[l..r], else return -1
static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int l, int r, int x)
{
if (r >= l) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
// If the element is present at the
// middle itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not present
// in array
return -1;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.Length;
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
if (result == -1)
Console.WriteLine(
"Element is not present in arrau");
else
Console.WriteLine("Element is present at index "
+ result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.
// JavaScript program to implement recursive Binary Search
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
function binarySearch(arr, l, r, x){
if (r >= l) {
let mid = l + Math.floor((r - l) / 2);
// If the element is present at the middle
// itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not
// present in array
return -1;
}
let arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ];
let x = 10;
let n = arr.length
let result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1) ? console.log( "Element is not present in array")
: console.log("Element is present at index " +result);
<?php
// PHP program to implement
// recursive Binary Search
// A recursive binary search
// function. It returns location
// of x in given array arr[l..r]
// is present, otherwise -1
function binarySearch($arr, $l, $r, $x)
{
if ($r >= $l)
{
$mid = ceil($l + ($r - $l) / 2);
// If the element is present
// at the middle itself
if ($arr[$mid] == $x)
return floor($mid);
// If element is smaller than
// mid, then it can only be
// present in left subarray
if ($arr[$mid] > $x)
return binarySearch($arr, $l,
$mid - 1, $x);
// Else the element can only
// be present in right subarray
return binarySearch($arr, $mid + 1,
$r, $x);
}
// We reach here when element
// is not present in array
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(2, 3, 4, 10, 40);
$n = count($arr);
$x = 10;
$result = binarySearch($arr, 0, $n - 1, $x);
if(($result == -1))
echo "Element is not present in array";
else
echo "Element is present at index ",
$result;
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
?>
OutputElement is present at index 3
- Time Complexity:
- Best Case: O(1)
- Average Case: O(log N)
- Worst Case: O(log N)
- Auxiliary Space: O(1), If the recursive call stack is considered then the auxiliary space will be O(logN).
Advantages of Binary Search:
- Binary search is faster than linear search, especially for large arrays.
- More efficient than other searching algorithms with a similar time complexity, such as interpolation search or exponential search.
- Binary search is well-suited for searching large datasets that are stored in external memory, such as on a hard drive or in the cloud.
Drawbacks of Binary Search:
- The array should be sorted.
- Binary search requires that the data structure being searched be stored in contiguous memory locations.
- Binary search requires that the elements of the array be comparable, meaning that they must be able to be ordered.
Applications of Binary Search:
- Binary search can be used as a building block for more complex algorithms used in machine learning, such as algorithms for training neural networks or finding the optimal hyperparameters for a model.
- It can be used for searching in computer graphics such as algorithms for ray tracing or texture mapping.
- It can be used for searching a database.
Follow the link to know about Binary Search on Answers
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...