Kotlin Nested class and Inner class
Last Updated :
08 Feb, 2023
Nested Class
In Kotlin, you can define a class inside another class, which is known as a nested class. Nested classes have access to the members (fields and methods) of the outer class.
Here is an example of a nested class in Kotlin:
Kotlin
class Car {
var make: String
var model: String
var year: Int
inner class Engine {
var horsepower: Int = 0
var cylinders: Int = 0
fun getEngineInfo(): String {
return "$horsepower horsepower, $cylinders cylinders, in a $make $model"
}
}
fun getInfo(): String {
return "$make $model, year $year"
}
}
fun main() {
val myCar = Car()
myCar.make = "Toyota"
myCar.model = "Camry"
myCar.year = 2020
val engine = myCar.Engine()
engine.horsepower = 250
engine.cylinders = 6
println(engine.getEngineInfo())
}
|
Output:
250 horsepower, 6 cylinders, in a Toyota Camry
A class is declared within another class then it is called a nested class. By default nested class is static so we can access the nested class property or variables using dot(.) notation without creating an object of the class.
Syntax of declaration:
class outerClass {
............
// outer class properties or member function
class nestedClass {
..........
// inner class properties or member function
}
}
Note: Nested class can’t access the members of the outer class, but we can access the property of nested class from the outer class without creating an object for nested class.
Kotlin program of accessing nested class properties:
Kotlin
class outerClass {
var str = "Outer class"
class nestedClass {
val firstName = "Praveen"
val lastName = "Ruhil"
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
print(outerClass.nestedClass().firstName)
print(" ")
println(outerClass.nestedClass().lastName)
}
|
Output:
Praveen Ruhil
In Kotlin, to access the member function of nested class, we need to create the object for nested class and call the member function using it.
Kotlin program of accessing nested class member function:
Kotlin
class outerClass {
var str = "Outer class"
class nestedClass {
var s1 = "Nested class"
fun nestfunc(str2: String): String {
var s2 = s1.plus(str2)
return s2
}
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val nested = outerClass.nestedClass()
var result = nested.nestfunc(" member function call successful")
println(result)
}
|
Output:
Nested class member function call successful
Comparison with Java
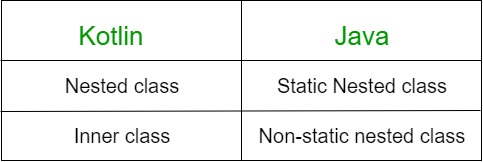
Kotlin classes are much similar to Java classes when we think about the capabilities and use cases, but not identical. Nested in Kotlin is similar to a static nested class in Java and the Inner class is similar to a non-static nested class in Java.
Kotlin Inner Class
When we can declare a class inside another class using the keyword inner then it is called inner class. With the help of the inner class, we can access the outer class property inside the inner class.
class outerClass {
............
// outer class properties or member function
inner class innerClass {
..........
// inner class properties or member function
}
}
In the below program we are trying to access str from the inner class member function. But it does not work and gives a compile-time error.
Kotlin program of inner class:
Kotlin
class outerClass {
var str = "Outer class"
class innerClass {
var s1 = "Inner class"
fun nestfunc(): String {
var s2 = str
return s2
}
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val inner= outerClass().innerClass()
println(inner.nestfunc())
}
|
Output:
Error:(9, 22) Kotlin: Unresolved reference: str
First, use the inner keyword in front of the inner class. Then, create an instance of the outer class else we can’t use inner classes.
Kotlin
class outerClass {
var str = "Outer class"
inner class innerClass {
var s1 = "Inner class"
fun nestfunc(): String {
var s2 = str
return s2
}
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val inner= outerClass().innerClass()
println(inner.nestfunc()+" property accessed successfully from inner class ")
}
|
Output:
Outer class property accessed successfully from inner class
Advantages or Disadvantages:
Advantages of using nested and inner classes in Kotlin:
- Encapsulation: Nested and inner classes allow you to group related functionality together and keep it separate from the rest of the code, improving code organization and readability.
- Reusability: Nested and inner classes can be reused within the same class or across multiple classes, making it easier to write more maintainable code.
- Accessibility: Inner classes have access to the members of the outer class, making it easier to share data between them and reducing code duplication.
Disadvantages of using nested and inner classes in Kotlin:
- Complexity: Adding nested and inner classes can make the code more complex and harder to understand, especially if there are multiple levels of nesting or if inner classes are used excessively.
- Performance: Using nested and inner classes can slow down the performance of your code, especially if they are heavily used or if they are nested to many levels deep.
- Debugging: Debugging nested and inner classes can be challenging, especially if there are multiple levels of nesting or if inner classes are used excessively.
- Overall, it’s important to use nested and inner classes in a balanced and appropriate way to take advantage of their benefits while avoiding their disadvantages.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...