JavaScript Throttling
Last Updated :
08 Dec, 2023
Throttling sometimes also called throttle function is a practice used in websites. Throttling is used to call a function after every millisecond or a particular interval of time only the first click is executed immediately.
Without throttling Function:
Without throttling, a function may be invoked rapidly, leading to performance issues, unnecessary resource consumption, and a potentially poor user experience.
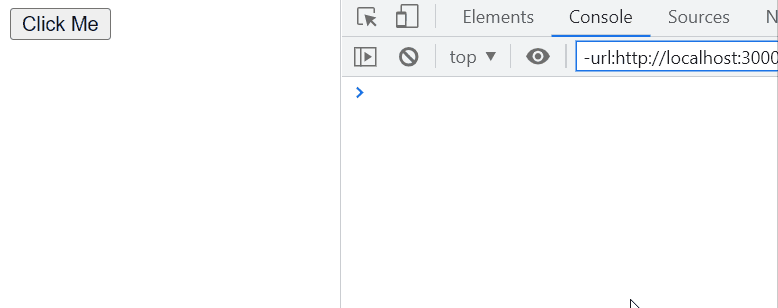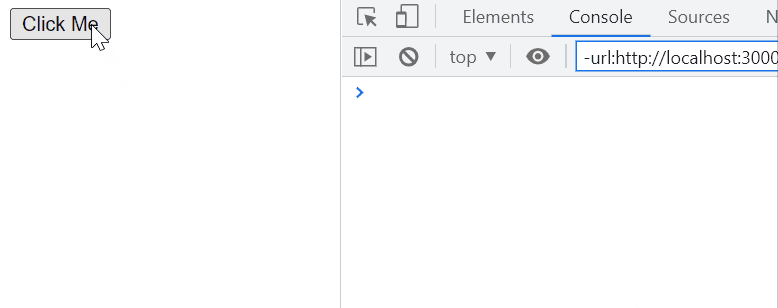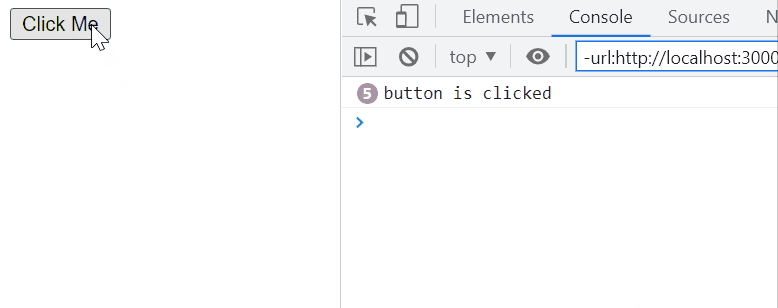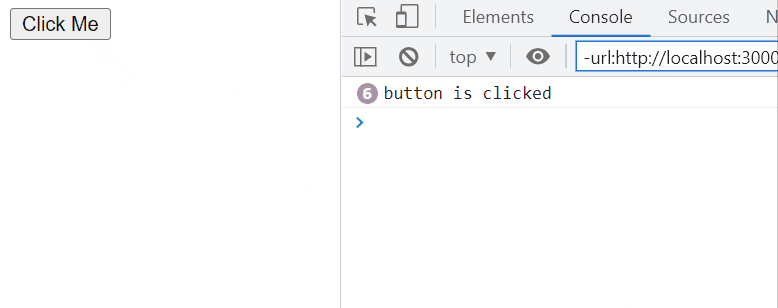
Example: In this example, the code demonstrates an event listener attached to a button without any throttling mechanism. When the button with the id ‘nothrottle’ is clicked, the associated callback function executes immediately, logging the message ‘button is clicked’ to the console.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width,
initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="nothrottle">Click Me</button>
<script>
// Selected button with the given id
const btn = document.
querySelector("#nothrottle");
// Add event listener to the button
// to listen the click event
btn.addEventListener("click", () => {
console.log("button is clicked");
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:
With Throttling function:
With throttling, you limit the frequency of function invocations. For example, you might decide to execute a function at most once every 1500 milliseconds. This prevents the function from being called too frequently and helps maintain a smoother performance.
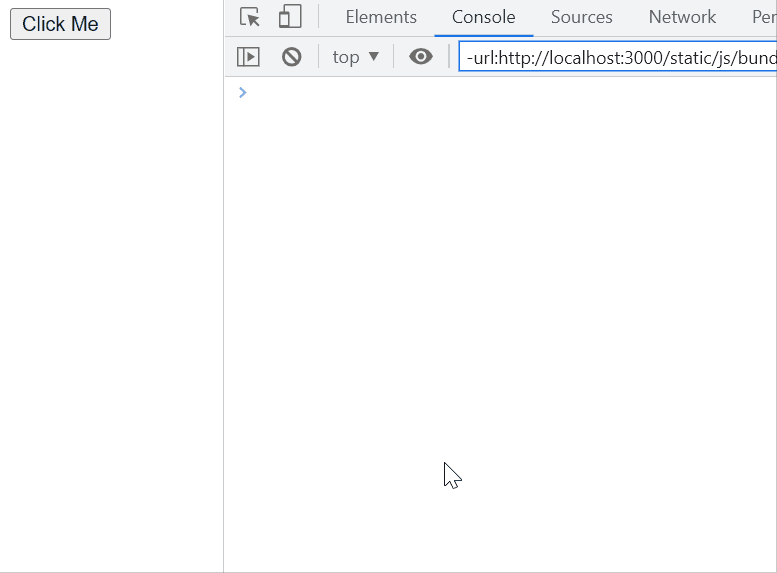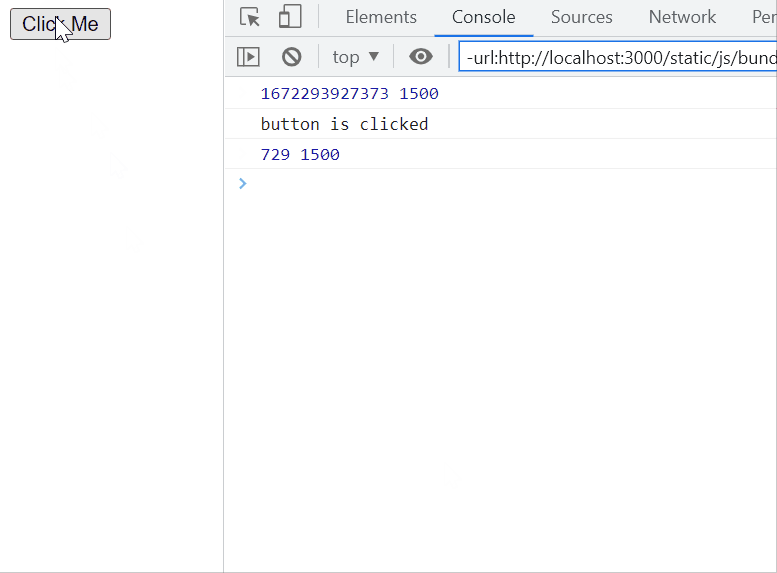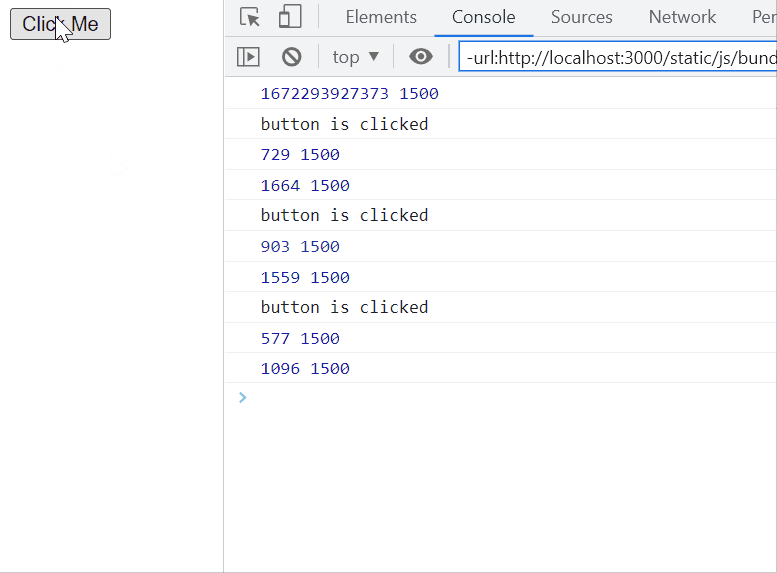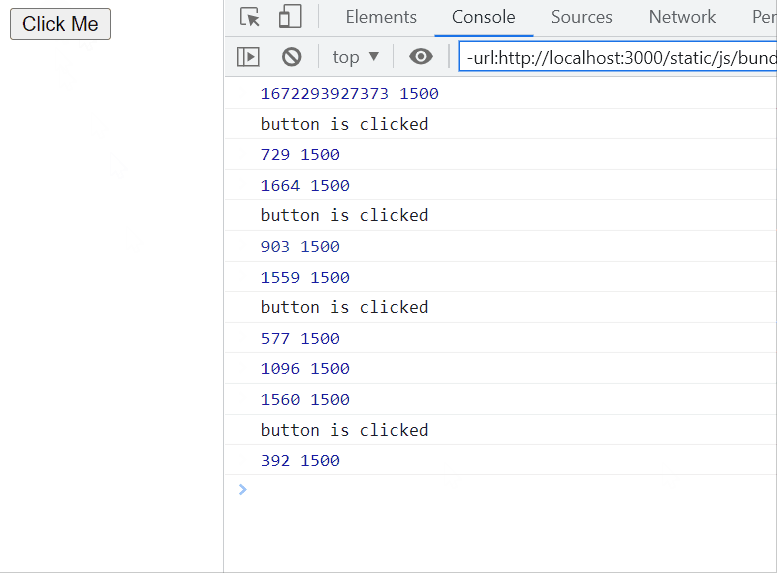
Example: In this example, a button with the id ‘throttle’ is equipped with a throttling mechanism using a custom throttle function. When clicked, the associated callback function, logging ‘button is clicked’ to the console, is throttled to execute at most once every 1500 milliseconds.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width,
initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="throttle">Click Me</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector("#throttle");
// Throttling Function
const throttleFunction = (func, delay) => {
// Previously called time of the function
let prev = 0;
return (...args) => {
// Current called time of the function
let now = new Date().getTime();
// Logging the difference
// between previously
// called and current called timings
console.log(now - prev, delay);
// If difference is greater
// than delay call
// the function again.
if (now - prev > delay) {
prev = now;
// "..." is the spread
// operator here
// returning the function with the
// array of arguments
return func(...args);
}
}
}
btn.addEventListener("click",
throttleFunction(() => {
console.log("button is clicked")
}, 1500));
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:
Advantages of throttling function:
- It prevents frequent calling of the function.
- It makes the website faster and controls the rate at which a particular function is called.
- Performance Optimization.
- Improved Responsiveness.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...