Java Program To Check For Balanced Brackets In An Expression (Well-Formedness) Using Stack
Last Updated :
14 Dec, 2021
Given an expression string exp, write a program to examine whether the pairs and the orders of “{“, “}”, “(“, “)”, “[“, “]” are correct in exp.
Example:
Input: exp = “[()]{}{[()()]()}”
Output: Balanced
Input: exp = “[(])”
Output: Not Balanced
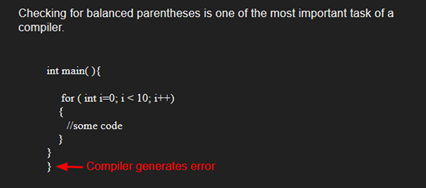
Algorithm:
- Declare a character stack S.
- Now traverse the expression string exp.
- If the current character is a starting bracket (‘(‘ or ‘{‘ or ‘[‘) then push it to stack.
- If the current character is a closing bracket (‘)’ or ‘}’ or ‘]’) then pop from stack and if the popped character is the matching starting bracket then fine else brackets are not balanced.
- After complete traversal, if there is some starting bracket left in stack then “not balanced”
Below image is a dry run of the above approach:
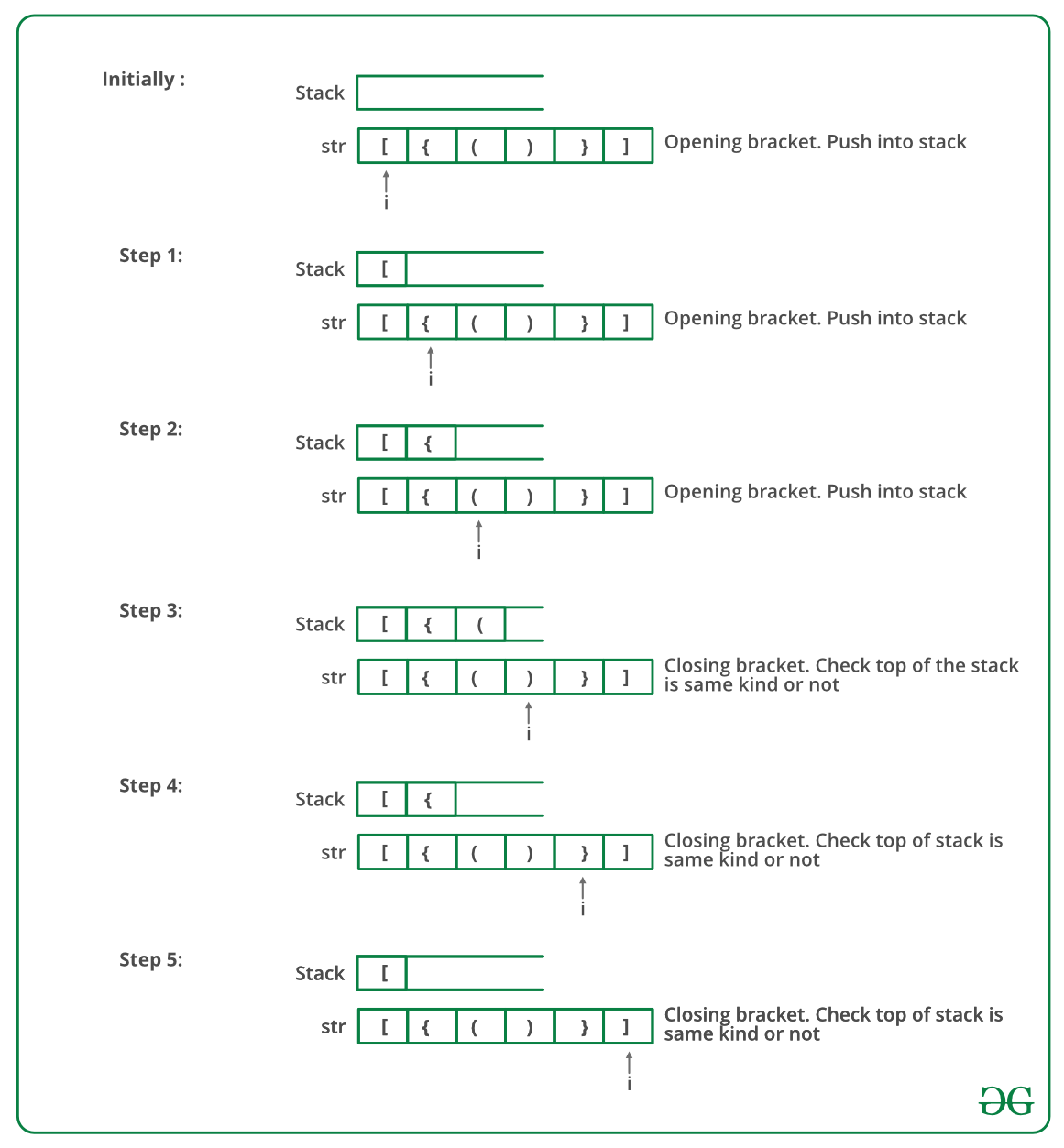
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class BalancedBrackets {
static boolean areBracketsBalanced(String expr)
{
Deque<Character> stack
= new ArrayDeque<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < expr.length(); i++)
{
char x = expr.charAt(i);
if (x == '(' || x == '[' || x == '{')
{
stack.push(x);
continue;
}
if (stack.isEmpty())
return false;
char check;
switch (x) {
case ')':
check = stack.pop();
if (check == '{' || check == '[')
return false;
break;
case '}':
check = stack.pop();
if (check == '(' || check == '[')
return false;
break;
case ']':
check = stack.pop();
if (check == '(' || check == '{')
return false;
break;
}
}
return (stack.isEmpty());
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String expr = "([{}])";
if (areBracketsBalanced(expr))
System.out.println("Balanced ");
else
System.out.println("Not Balanced ");
}
}
|
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(n) for stack.
Please refer complete article on Check for Balanced Brackets in an expression (well-formedness) using Stack for more details!
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...